(七)转置卷积
欢迎访问个人网络日志知行空间
1.基础情况介绍
在语义分割任务使用的网络结构中,除了使用卷积神经网络进行降采样,为了恢复图像的大小,还需要使用转置卷积。转置卷积被称为transposed convolution,fractionally-strided convolution也有些地方称为deconvolution。转置卷积只是恢复的feature map的空间尺寸并不等同于卷积的逆运算,所以称之为deconvolution是不合适的。
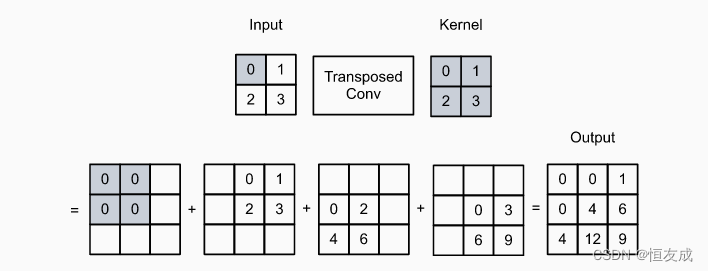
为了简化介绍,假设通道channle=1,对于 n h × n ω n_h\times n_\omega nh×nω的输入和 k h × k ω k_h \times k_\omega kh×kω的卷积核,对于stride=1, padding=0的转置卷积,其计算过程为,将 k h × k ω k_h \times k_\omega kh×kω的卷积核在的输入的每一行每一列上滑动,得到 n h n ω n_h n_\omega nhnω个中间结果,每个中间结果的空间尺寸为 ( n h + k h − 1 ) × ( n ω + k ω − 1 ) (n_h + k_h - 1) \times (n_\omega + k_\omega - 1) (nh+kh−1)×(nω+kω−1),其值初时化为0,然后对于输入中的每个元素,与卷积核相乘得到 k h × k ω k_h \times k_\omega kh×kω的结果替换掉 ( n h + k h − 1 ) × ( n ω + k ω − 1 ) (n_h + k_h - 1) \times (n_\omega + k_\omega - 1) (nh+kh−1)×(nω+kω−1)矩阵中的对应部分,最后将所有的中间结果相加得到最后的输出。
使用numpy数组实现上述过程为:
import numpy as np
X = np.array([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
K = np.array([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
def trans_conv(X, K):
K = K.reshape((2,2))
X = X.reshape((2, 2))
h, w = X.shape
kh, kw = K.shape
o = np.zeros((h + kh - 1, w + kw - 1))
for i in range(h):
for j in range(w):
o[i : i + h, j : j + w] += X[i][j] * K
return o
trans_conv(X, K)
"""output
array([[ 0., 0., 1.],
[ 0., 4., 6.],
[ 4., 12., 9.]])
"""
可见程序的输出与上图计算过程的结果一致。
借用pytorch中的ConvTranspose2d实现的计算的过程为:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
X = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
K = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
X, K = X.reshape(1, 1, 2, 2), K.reshape(1, 1, 2, 2)
tconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1, 1, kernel_size=2, bias=False)
tconv.weight.data = K
tconv(X)
"""output
tensor([[[[ 0., 0., 1.],
[ 0., 4., 6.],
[ 4., 12., 9.]]]], grad_fn=)
"""
可见这三个地方计算的结果是一致的。
2.使用paddding/stride/dilation/多通道时
2.1 stride
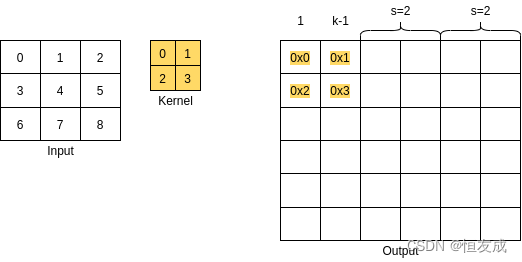
stride表示的是卷积核在输出张量上滑动的步长,前面的例子中使用的是stride=1的场景,在使用stride时,输出张量的空间尺寸 o h o_h oh和 o ω o_\omega oω的计算方式为 o h = ( n h − 1 ) × s t r i d e + ( k h − 1 ) + 1 o_h = (n_h - 1)\times stride + (k_h - 1) + 1 oh=(nh−1)×stride+(kh−1)+1, 如下图:
如上图中 n h = n ω = 3 , k h = k ω = 2 n_h=n_\omega =3, k_h=k_\omega = 2 nh=nω=3,kh=kω=2,则 o h = o ω = 6 o_h=o_\omega = 6 oh=oω=6
使用pytorch验证上述计算过程,则
X = torch.range(0, 8).reshape((1, 1, 3,3))
K = torch.range(0, 3).reshape((1, 1, 2,2))
tconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1, 1, kernel_size=2, stride=2, bias=False)
tconv.weight.data = K
Y = tconv(X)
print(Y.shape)
print(Y)
"""output
torch.Size([1, 1, 6, 6])
tensor([[[[ 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 2.],
[ 0., 0., 2., 3., 4., 6.],
[ 0., 3., 0., 4., 0., 5.],
[ 6., 9., 8., 12., 10., 15.],
[ 0., 6., 0., 7., 0., 8.],
[12., 18., 14., 21., 16., 24.]]]],
grad_fn=)
"""
2.2 padding
padding是在transpose convolution计算过程中作用在输出张量上面的,因此计算结束后需要裁剪掉padding的大小。
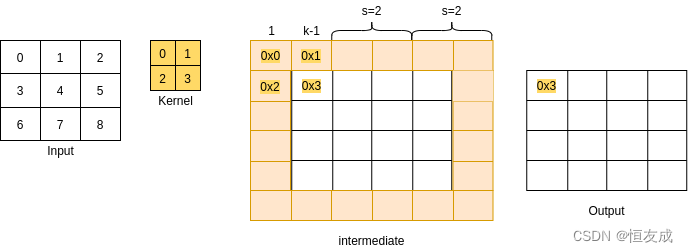
如 (2.1)[###2.1 stride]中的例子,假设padding=1,则输出张量的最外围一圈将被裁剪掉,如下图:
此时
o h = ( n h − 1 ) × s t r i d e + ( k h − 1 ) + 1 − 2 × p a d d i n g o_h = (n_h - 1)\times stride + (k_h - 1) + 1 - 2\times padding oh=(nh−1)×stride+(kh−1)+1−2×padding
使用pytorch ConvTranspose2d API时,只需要加入padding=1参数即可,
X = torch.range(0, 8).reshape((1, 1, 3,3))
K = torch.range(0, 3).reshape((1, 1, 2,2))
tconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1, 1, kernel_size=2, padding=1, stride=2, bias=False)
tconv.weight.data = K
Y = tconv(X)
print(Y.shape)
print(Y)
"""output
torch.Size([1, 1, 4, 4])
tensor([[[[ 0., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 3., 0., 4., 0.],
[ 9., 8., 12., 10.],
[ 6., 0., 7., 0.]]]], grad_fn=)
"""
此外还有output_padding,这个是对转置卷积后输出的张量进行的扩充,这会增大输出张量的尺寸,不过pytorch ConvTranspose2d API的实现只对输出张量的一边(H,W较大的那一边)进行了扩充,因此其对输出张量空间尺寸的影响为:
o h = ( n h − 1 ) × s t r i d e + ( k h − 1 ) + 1 − 2 × p a d d i n g + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g o_h = (n_h - 1)\times stride + (k_h - 1) + 1 - 2\times padding + output\_padding oh=(nh−1)×stride+(kh−1)+1−2×padding+output_padding
2.3 dilation
dilation即扩张卷积,卷积核中存在空洞,因此也称空洞卷积。如下图是dilation=2的dilated convolution:
在Transposed Convolution中使用dilation时,输出的空间尺寸计算可参考下图:
由上图可得:
o h = ( n h − 1 ) × s t r i d e + d i l a t i o n × ( k h − 1 ) + 1 − 2 × p a d d i n g o_h = (n_h - 1)\times stride + dilation\times (k_h - 1) + 1 - 2\times padding oh=(nh−1)×stride+dilation×(kh−1)+1−2×padding
o h = 2 × 2 + 2 × 1 + 1 = 7 o_h = 2 \times 2 + 2 \times 1 + 1 = 7 oh=2×2+2×1+1=7
使用pytorch验证上图中的例子,可得
X = torch.range(0, 8).reshape((1, 1, 3,3))
K = torch.range(0, 3).reshape((1, 1, 2,2))
tconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(1, 1, kernel_size=2, dilation=2, stride=2, bias=False)
tconv.weight.data = K
Y = tconv(X)
print(Y.shape)
print(Y)
"""output
torch.Size([1, 1, 7, 7])
tensor([[[[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 2.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 5., 0., 11., 0., 11.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 6., 0., 23., 0., 29., 0., 23.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[12., 0., 32., 0., 37., 0., 24.]]]],
grad_fn=)
"""
综上,对于由padding/stride/dilation/output_padding时,输出张量的计算方式为:
o h = ( n h − 1 ) × s t r i d e + d i l a t i o n × ( k h − 1 ) + 1 − 2 × p a d d i n g + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g o_h = (n_h - 1)\times stride + dilation\times(k_h - 1) + 1 - 2\times padding + output\_padding oh=(nh−1)×stride+dilation×(kh−1)+1−2×padding+output_padding
2.4 multi-channles
同常规的卷积操作,转置卷积对多通道的处理,同样是将每个卷积核在输入张量的各个维度上进行卷积,然后在将各个维度上的卷积结果相加求和即可。
如下代码示例,可见最后的输出正是两个通道上卷积结果求和所得:
X = torch.tensor([[[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]],[[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]]])
K = torch.tensor([[[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]],[[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]]])
X, K = X.reshape(1, 2, 2, 2), K.reshape(2, 1, 2, 2)
tconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(2, 1, kernel_size=2, bias=False)
tconv.weight.data = K
tconv(X)
"""output
tensor([[[[ 0., 0., 2.],
[ 0., 8., 12.],
[ 8., 24., 18.]]]], grad_fn=)
"""
参考资料
- 1.https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d.html
- 2.https://github.com/onnx/onnx/pull/2343/commits/09b3b64c99c1e18947b310d2688dc0187dcdccac
- 3.https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic/blob/master/README.md
- 4.https://d2l.ai/chapter_computer-vision/transposed-conv.html
欢迎访问个人网络日志知行空间