对彩色花图像进行分类-基于R语言的Keras实现
该案例摘自《Keras深度学习入门、实战及进阶》第四章综合案例内容。
该案例的数据来源于Kaggle上的Flower Color Images(https://www.kaggle.com/olgabelitskaya/flower-color-images)。
数据内容非常简单:包含10种开花植物的210张图像(128×128×3)和带有标签的文件flower-labels.csv,照片文件采用.png格式,标签为整数(0~9)。
使用read.csv()将带有标签的文件flower-labels.csv导入到R中,并查看前六行。
> flowers <- read.csv('../flower_images/flower_labels.csv')
> dim(flowers)
[1] 210 2
> head(flowers)
file label
1 0001.png 0
2 0002.png 0
3 0003.png 2
4 0004.png 0
5 0005.png 0
6 0006.png 1
一共有210行2列,第1列是图像文件名称,第2列是其对应的标签值。编号为0001、0002、0004、0005的彩色图像对应的标签为0,即为福禄考;0003彩色图像对应的标签为2,即为金盏花;0006彩色图像对应的标签为1,即为玫瑰。
label是目标变量,使用as.matrix()函数将其转换为矩阵后再利用to_categorical()函数将其转换为独热(one-hot)编码,转换后的数据如下所示。
> flower_targets <- as.matrix(flowers["label"])
> flower_targets <- keras::to_categorical(flower_targets, 10)
> head(flower_targets)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7] [,8] [,9] [,10]
[1,] 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
[2,] 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
[3,] 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
[4,] 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
[5,] 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
[6,] 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
可利用list.files()函数获取flower_images目录中所有彩色图像的文件名称。
> # 获取flower_images目录中的彩色照片
> image_paths <- list.files('../flower_images',pattern = '.png')
> length(image_paths)
[1] 210
> image_paths[1:3]
[1] "0001.png" "0002.png" "0003.png"
flower_images目录中一共有210张彩色图像,前3个图像文件的名称依次为"0001.png" 、“0002.png”、 “0003.png”。利用EBImage包的readImage()函数将前面8张彩色化图像读入到R中,并进行可视化。
> names <- c('phlox','rose','calendula','iris',
+ 'max chrysanthemum','bellflower','viola',
+ 'rudbeckia laciniata','peony','aquilegia')
> options(repr.plot.width=4,repr.plot.height=4)
> op <- par(mfrow=c(2,4),mar=c(2,2,2,2))
> for(i in 1:8){
+ img <- readImage(paste('../flower_images',image_paths[i],sep = '/')) # 读入图像
+ plot(img) # 绘制图像
+ text(x = 64,y = 0,
+ label = names[flowers[flowers$file==image_paths[i],'label']+1],
+ adj = c(0,1),col = 'white',cex = 3) # 添加标签
+ }
> par(op)

自定义image_loading()函数,实现逐步将flower_iamges的彩色图像读入到R中,并进行数据转换,使其达到符合深度学习建模时所需的自变量矩阵。
> # 自定义图像数据读入及转换函数
> image_loading <- function(image_path) {
+ image <- image_load(image_path, target_size=c(128,128))
+ image <- image_to_array(image) / 255
+ image <- array_reshape(image, c(1, dim(image)))
+ return(image)
+ }
结合lapply()函数读取flower_images目录中的210张花彩色图像,由于返回结果为列表,所以再次利用array_reshape()函数对其进行转换。
> image_paths <- list.files('../flower_images',
+ pattern = '.png',
+ full.names = TRUE)
> flower_tensors <- lapply(image_paths, image_loading)
> flower_tensors <- array_reshape(flower_tensors,
+ c(length(flower_tensors),128,128,3))
> dim(flower_tensors)
[1] 210 128 128 3
> dim(flower_targets)
[1] 210 10
我们利用caret包的createDataParitition()函数对数据进行等比例抽样,使得抽样后的训练集和测试集中的各类别占比与原数据一样。
> # 等比例抽样
> index <- caret::createDataPartition(flowers$label,p = 0.9,list = FALSE) # 训练集的下标集
> train_flower_tensors <- flower_tensors[index,,,] # 训练集的自变量
> train_flower_targets <- flower_targets[index,] # 训练集的因变量
> test_flower_tensors <- flower_tensors[-index,,,] # 测试集的自变量
> test_flower_targets <- flower_targets[-index,] # 测试集的因变量
- MLP模型建立及预测
首先构建一个简单的多层感知机神经网络,利用训练集数据对网络进行训练。以下程序代码实现模型创建、编译及训练。
> mlp_model <- keras_model_sequential()
>
> mlp_model %>%
+ layer_dense(128, input_shape=c(128*128*3)) %>%
+ layer_activation("relu") %>%
+ layer_batch_normalization() %>%
+ layer_dense(256) %>%
+ layer_activation("relu") %>%
+ layer_batch_normalization() %>%
+ layer_dense(512) %>%
+ layer_activation("relu") %>%
+ layer_batch_normalization() %>%
+ layer_dense(1024) %>%
+ layer_activation("relu") %>%
+ layer_dropout(0.2) %>%
+ layer_dense(10) %>%
+ layer_activation("softmax")
>
> mlp_model %>%
+ compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy",optimizer="adam",metrics="accuracy")
>
> mlp_fit <- mlp_model %>%
+ fit(
+ x=array_reshape(train_flower_tensors, c(length(index),128*128*3)),
+ y=train_flower_targets,
+ shuffle=T,
+ batch_size=64,
+ validation_split=0.1,
+ epochs=30
+ )
> options(repr.plot.width=9,repr.plot.height=9)
> plot(mlp_fit)

模型出现严重过拟合现象。训练集在第8个训练周期时准确率已经达到1,此时验证集的准确率仅有0.3,且之后训练周期的验证集准确率呈现下降趋势。
最后,利用predict_classes()对测试集进行类别预测,并查看每个测试样本的实际标签及预测标签。
> pred_label <- mlp_model %>%
+ predict_classes(x=array_reshape(test_flower_tensors,
+ c(dim(test_flower_tensors)[1],128*128*3)),
+ verbose = 0) # 对测试集进行预测
>
> result <- data.frame(flowers[-index,], # 测试集实际标签
+ 'pred_label' = pred_label) # 测试集预测标签
> result$isright <- ifelse(result$label==result$pred_label,1,0) # 判断预测是否正确
> result # 查看结果
file label pred_label isright
10 0010.png 0 0 1
17 0017.png 0 9 0
30 0030.png 6 1 0
35 0035.png 3 5 0
43 0043.png 7 7 1
45 0045.png 1 0 0
52 0052.png 4 8 0
60 0060.png 8 0 0
64 0064.png 8 8 1
70 0070.png 4 8 0
71 0071.png 9 5 0
76 0076.png 3 5 0
95 0095.png 1 1 1
123 0123.png 4 5 0
160 0160.png 3 5 0
162 0162.png 9 7 0
197 0197.png 6 3 0
201 0201.png 1 5 0
207 0207.png 0 0 1
在19个训练样本中,仅有5个样本的标签被预测正确,分别为0010.png、0043.png、0064.png、0095.png和0207.png。
测试集的整体准确率为26.3%,仅仅比基准线10%(一共10个类别,随便乱猜都有10%猜对的可能)好一些。显然,此模型的结果是不太令人满意的。下一步将构建一个简单的卷积神经网络(CNN),查看模型的预测能力。
2. CNN模型建立与预测
此案例我们的卷积神经网络只包含一个卷积层,以下程序代码实现模型创建、编译及训练。
> cnn_model %>%
+ layer_conv_2d(filter = 32, kernel_size = c(3,3), input_shape = c(128, 128, 3)) %>%
+ layer_activation("relu") %>%
+ layer_max_pooling_2d(pool_size = c(2,2)) %>%
+ layer_flatten() %>%
+ layer_dense(64) %>%
+ layer_activation("relu") %>%
+ layer_dropout(0.5) %>%
+ layer_dense(10) %>%
+ layer_activation("softmax")
>
> cnn_model %>% compile(
+ loss = "categorical_crossentropy",
+ optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(lr = 0.001, decay = 1e-6),
+ metrics = "accuracy"
+ )
> cnn_fit <- cnn_model %>%
+ fit(
+ x=train_flower_tensors,
+ y=train_flower_targets,
+ shuffle=T,
+ batch_size=64,
+ validation_split=0.1,
+ epochs=30
+ )
> plot(cnn_fit)
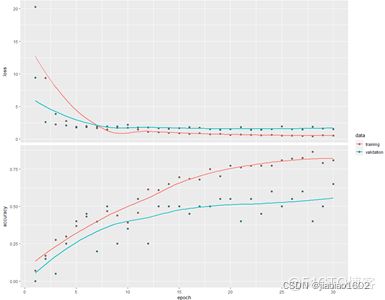
CNN效果明显优于MLP。利用训练好的CNN模型对测试集进行预测,并计算测试集的整体准确率。
> pred_label1 <- cnn_model %>%
+ predict_classes(x=test_flower_tensors,
+ verbose = 0) # 对测试集进行预测
>
> cnn_result <- data.frame(flowers[-index,], # 测试集实际标签
+ 'pred_label' = pred_label1) # 测试集预测标签
> cnn_result$isright <- ifelse(cnn_result$label==cnn_result$pred_label,1,0) #判断预测正确性
> # cnn_result # 查看结果
> # 查看测试集的整体准确率
> cat(paste('测试集的准确率为:',
+ round(sum(cnn_result$isright)*100/dim(cnn_result)[1],1),"%"))
测试集的准确率为: 57.9 %
CNN模型对测试集的预测准确率达到58%,远优于MLP模型。
本书最后面还利用数据增强技术进一步提升模型准确率。通过数据增强技术模型对测试集的预测准确率达到68%,是个不小的进步。

