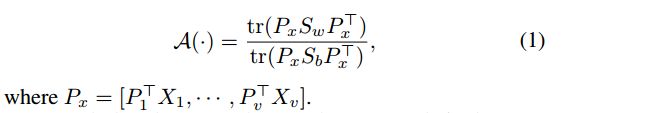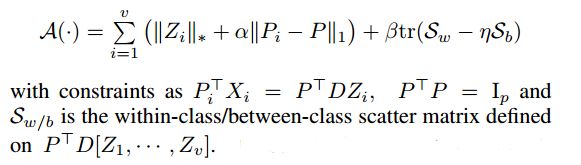低秩矩阵完备_多源域和多视角 “秩约束”
Robust Multi-view Representation: A Unified Perspective from Multi-view Learning to Domain Adaption
可以通用使用下面这个框架:
第一项多视角配准
第二项特征学习约束:使用label信息或者数据的本身结构
多视角学习:
一、多视角聚类
融合多个视角的知识,寻找一个一致的聚类结果
- canonical correlation analysis (CCA)给每个视角一个投影矩阵
,把数据转化到共同的子空间。通过maximizing the cross correlation across two views:
变种:
- Multi-view CCA, i=1, ..., V
- deep CCA 把
转化成
*2. semi-nonnegative matrix factorization+图约束保持几何结构
由于没有lable信息,通常使用数据的潜在分布来学习共同的特征表达。
二、多视角分类
使用了标签信息
两种场景:
First, one view will be used to recognize other views with the learned model. In this case, the label information across training and test data is different;【zero shot learning can also be modeled as a special case of multi-view learning, which involves two views, i.e., visual features and semantic features.】
Second, specifically for multi-features based learning, is that v-view training data is used to seek a model by fusing the cross-view knowledge, which is also used as gallery data to recognize v-view probe data.
- generalized multi-view analysis (GMA)
2. partial least squares (PLS) regression 使用了一个平滑约束:they only explored the constraints on the poses in their neighborhoods.
GMA和PLS只考虑了within-view,忽略了between-view信息
3. multi-view discriminant analysis 提出了一种多视角判别分析方法,通过同时学习v视角特定投影,实现所有视角的单一判别共享空间
变种: multi-view deep network(MvDN) includes two sub-networks, one is view-specific sub-networkview-specific variations and the other is common sub-networkto reduce
shared representation across all views.to seek
![]()
*4. Coupled Marginalized Auto-Encoders
针对源视图和目标视图设计了两个边缘去噪自动编码器。为了更好地对齐两个去噪的自动编码器,引入了一个特征映射来适应中间视图和目标视图之间的知识。此外,将最大边际准则maximum margin criterion 应用于顶层,以学习跨这些域的更多区分性的表达。
*5. view-specific and view-shared networks
三、zero shot learning(ZSL)
分类在训练中没有见过的类别。使用视觉特征和语义特征。核心是找到两个views的映射,并且generalize well到测试集上
*1. Low-rank Embedded ensemble Semantic Dictionary learning
假设:从可见类别中学习到的 latent semantic dictionary,应该包含不可见类别的大部分信息。此外,我们通过集成(ensemble)策略,利用multiple transferable dictionaries,更好地为不可见数据恢复潜在的语义空间:
四、When Probe View is Unknown
如果测试集的视角信息是不知道的,multiple view-specific projections cannot be used to learn its specific feature representations.
*1 view-invariant projection
给每个视角学习一个共同的变换矩阵P:第一项低秩重建,在共同的低秩空间中,实现视角特定的特征到视角无关的特征的转换;第二项supervised cross-view regularizer,实现 不同视角 但是是同一个类 的数据的配准。
虽然这些方法在语义鸿沟的预测任务中很有前景,但它通常表现在相似的视觉概念之间,例如不同的对象、不同的动物类别或同一主题的不同观角。未来的发展方向将是一种更通用的学习范式,用于针对 较大语义差异的智能识别。
域自适应
重建误差reconstruction error 和 Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD)是两个常用距离度量方法。
一、Transfer Subspace Learning
*1. Transfer Subspace Learning
把源域和目标域变换到一个域无关的子空间,目标样本通过邻域的几个源域(理想情况是同一个类的数据)重建,使用低秩约束, 因此保证了结构信息。
2. Joint feature selection and structure preservation for domain adaptation
加入了特征选择
3. imbalanced cross-domain data
不同域标签数量不同
它能够挖掘数据域内部和跨数据域(within and across data domains)的潜在子域,并学习一个共同的特征空间,用于联合适应和分类。
这些方法忽略了条件分布
*4 加上条件分布
二、Missing Modality Transfer Learning
*1. 目标数据的模态在源域中没有,所以从两个方向解决问题:cross-modality 和 cross-dataset
where a latent factor W is generated to seek the underlying structure of the missing modality from the observed modalities.
跟zero shot learning有点像,但是这个方法可以refer to辅助数据集。
三、 Incomplete Multi-Source Transfer Learning
*1. cross domain 使用低秩 implicitly recover the missing categories in each source【感觉这句话和zero shot learning 有点相同思想】
cross source 融合多源信息 使用graph term 来补偿缺失的类别from one source to another
四、Deep Domain Adaption
*1. a stacked deep low-rank coding framework
对神经网络每一层,获得 low-rank coding with the guidance of marginalized denoising strategy and an iterative structured term. 可以很好的减少marginal and conditional differences。
五、Domain Generalization
现在都假设训练时,目标域 is available即使没有label。实际上,可能inaccessible in advance。
*1. deep domain generalization algorithm
从多个availble的源域中寻找一致的知识,使用structured low-rank reconstruction to guide the knowledge transfer from each source to the unseen target domain。
multiple domain-specific DNNs to learn the rich knowledge within multiple source domains;a domain-shared DNNs to capture the common information across multiple sources
总结
focus on the following factors: imbalanced, incomplete, and large-scale datasets, as identified in our previous discussions