PyTorch(一):PyTorch基础 (PyTorch安装、Tensor、autograd、torch.nn、模型处理、数据处理)
本文参考
- PyTorch官方教程中文版链接:http://pytorch123.com/FirstSection/PyTorchIntro/
- Pytorch中文文档:https://pytorch-cn.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/package_references/Tensor/
- PyTorch英文文档:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html
- 《深度学习之PyTorch物体检测实战》
目录
- PyTorch 简介
- 安装 PyTorch 和 torchvision
- Tensor
-
- Tensor 类型
-
- 类型介绍
- 类型转换
-
- `int()`, `float()`, `double()`
- `type()`
- ``type_as()``
- 生成 Tensor
-
- 规定形状来创建 tensor
- 接受任意的 python 序列型对象
- `torch.zeros`, `torch.ones`, `torch.eye`
- 生成随机张量
- `torch.arange`,`torch.linspace`
- `torch.randn_like`,`torch.ones_like`,`torch.zeros_like`
- 查看 Tensor 维度以及元素个数
- Tensor 的拼接与分块
-
- 拼接: `torch.cat()`, `torch.stack()`
- 组合: `torch.chunk()`, `torch.split()`
- 索引
- 变形操作
-
- `view()`, `reshape()`
- `contiguous()`
- 原地操作函数 `resize_()`
- `squeeze()`, `unsqueeze()`
- `expand()`, `expand_as()`
- 转置与转轴 `transpose()` 和 `permute()`
- 排序 `sort()`
- 取极值 `max()`, `min()`
- Tensor 的内存共享
- Tensor 与 Numpy 转换: `torch.as_tensor()` / `torch.from_numpy()`
- 广播
- 通用函数
-
- `torch.where()`
- 张量方法
-
- `Tensor.item()`
- `Tensor.clamp()`
- `Tensor.abs`
- `Tensor.sqrt`
- `Tensor.log`
- `Tensor.pow`
- `Tensor.sin`, `Tensor.cos`
- `Tensor.matmul`
- 自动求导机制 autograd
-
- `.requires_grad`, `.grad`, `.grad_fn`
- `.detach_()`, `.requires_grad_()`, `with torch.no_grad()`
-
- `Tensor.backward()`
- 神经网络工具箱 `torch.nn`
-
- `nn.Module` 类
- `nn.Parameter()`
- `nn.functional` 库
- 实现简单版的全连接层以及二层感知机
- 查看 `nn.Module` 实例的网络结构以及参数
-
- `__str__()`
- `net.named_parameters()`, `net.parameters()`
- `nn.Sequential()`
-
- 利用 `nn.Sequential()` 实现多层感知机
- `nn.Sequential()` 动态添加网络层
- 损失函数
- 优化器 `nn.optim`
- 模型处理
-
- `torchvision.models` 库
- Transfer learning
-
- 获取 `torchvision.models` 中的预训练模型
- 保存模型 `torch.save()`
- 加载本地的预训练模型 `model.load_state_dict()`
- 设置预训练模型中的某些层不进行参数的学习
- 数据加载
- GPU 加速
-
- 指定使用某一块GPU
- 多 GPU 并行计算
PyTorch 简介
PyTorch 优点:
- 具有强大的 GPU 加速的张量计算
- 包含自动求导系统的深度神经网络
- 支持动态神经网络
PyTorch VS TensorFlow
- PyTorch 通过反向求导技术,可以零延迟地任意改变神经网络的行为,而且其实现速度快。这一灵活性是 PyTorch 对比 TensorFlow 的最大优势
- PyTorch 的代码对比 TensorFlow 而言,更加简洁直观,底层代码也更容易看懂
- 对比 TensorFlow,PyTorch 的全面性处于劣势,目前 PyTorch 还不支持快速傅里叶、沿维翻转张量和检查无穷与非数值张量;针对移动端、嵌入式部署以及高性能服务器端的部署其性能表现有待提升;其次因为这个框架较新,使得他的社区没有那么强大,在文档方面其C库大多数没有文档
安装 PyTorch 和 torchvision
# 创建一个 pytorch 虚拟环境
conda create -n pytorch anaconda
conda activate pytorch
conda env list
# 使用国内的镜像站安装
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch/
# 安装cpu版本
conda install pytorch torchvision cpuonly
# 验证安装成功
>>> import torch, torchvision
>>> x = torch.rand(5, 3)
>>> x
tensor([[0.9567, 0.8210, 0.7273],
[0.7107, 0.1292, 0.4716],
[0.2321, 0.1172, 0.6120],
[0.0253, 0.9240, 0.5838],
[0.4741, 0.6674, 0.0979]])
CUDA
- 安装 cuda10.2 (如果要使用 GPU 的话需要先到 NVIDIA 官网下载安装对应的显卡驱动,在终端中输入
nvidia-smi验证驱动是否装好。之后再安装 CUDA 与 cuDNN 库)
conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.2
# 验证 GPU 驱动和 CUDA 可用
>>> import torch
>>> torch.cuda.is_available()
Tensor
- Tensor 类似于 NumPy 的
ndarrays,同时 Tensor 可以使用 GPU 进行计算
import torch
Tensor 类型
类型介绍
torch.Tensor是默认的 tensor 类型(torch.FlaotTensor)的简称。设置默认的 Tensor 类型 (可以在局部使用完后再重新设置回torch.FloatTensor):
>>> torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.DoubleTensor')
类型转换
>>> a = torch.randn(2,2)
>>> a
tensor([[ 1.7017, -0.1865],
[-1.1735, 0.4421]])
int(), float(), double()
- 使用
int(),float(),double()等直接进行数据类型转换
>>> b = a.double()
>>> b
tensor([[ 1.7017, -0.1865],
[-1.1735, 0.4421]], dtype=torch.float64)
type()
>>> c = a.type(torch.DoubleTensor)
>>> c
tensor([[ 1.7017, -0.1865],
[-1.1735, 0.4421]], dtype=torch.float64)
type_as()
- 使用
type_as()函数可以保持 Tensor 之间的类型一致
>>> d = a.type_as(b)
>>> d
tensor([[ 1.7017, -0.1865],
[-1.1735, 0.4421]], dtype=torch.float64)
生成 Tensor
规定形状来创建 tensor
>>> torch.Tensor(2, 2)
tensor([[0.0000e+00, 0.0000e+00],
[1.6685e-10, 4.5909e-41]])
>>> torch.DoubleTensor(2, 2)
tensor([[1.6022e-306, 2.9644e-323],
[4.9407e-324, 1.1126e-306]], dtype=torch.float64)
接受任意的 python 序列型对象
- 接受任意的 python 序列型对象,生成一个新的 tensor:
>>> torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])
>>> torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])
>>> torch.Tensor(np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]))
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]])
>>> torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., -1.]])
tensor([[ 1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, -1.0000]])
>>> torch.tensor(np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]))
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]])
torch.Tensor()always copies data. If you have a Tensor data and just want to change itsrequires_gradflag, userequires_grad_()ordetach()to avoid a copy. If you have a numpy array and want to avoid a copy, usetorch.as_tensor().
torch.zeros, torch.ones, torch.eye
>>> torch.zeros(5, 3, dtype=torch.long)
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
>>> torch.ones(2, 2)
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
# 生成 对角矩阵
>>> torch.eye(2, 2)
tensor([[1., 0.],
[0., 1.]])
生成随机张量
>>> torch.randn(2, 2)
tensor([[-1.3644, 0.9027],
[ 0.3454, -0.6466]])
# randperm(num)生成长度为num的随机排列向量
>>> torch.randperm(10)
tensor([1, 6, 0, 5, 2, 8, 7, 3, 9, 4])
torch.arange,torch.linspace
>>> torch.arange(1, 6, 2)
tensor([1, 3, 5])
>>> torch.linspace(1, 6, 2)
tensor([1., 6.])
torch.randn_like,torch.ones_like,torch.zeros_like
>>> x
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> x = torch.randn_like(x, dtype=torch.float)
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.8157, 0.6115, 0.5099],
[-1.7238, 0.7658, 0.1270],
[ 0.2794, -0.2724, 0.4168],
[ 1.5144, -1.6933, -0.6357],
[-0.1833, 1.0657, -1.0282]])
>>> torch.ones_like(x)
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
>>> torch.zeros_like(x)
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
查看 Tensor 维度以及元素个数
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([5, 3])
>>> x.shape
torch.Size([5, 3])
>>> x.numel()
15
>>> x.nelement()
15
Tensor 的拼接与分块
拼接: torch.cat(), torch.stack()
- 除了拼接的维度之外,其他维度必须相同
>>> a = torch.arange(1, 5).reshape(2, 2)
>>> b = torch.arange(5, 9).reshape(2, 2)
>>> a
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
>>> b
tensor([[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
>>> torch.cat([a, b], 0)
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
>>> torch.cat([a, b], 1)
tensor([[1, 2, 5, 6],
[3, 4, 7, 8]])
# 以第0维进行stack,叠加的基本单位为序列本身,即a和b,因此输出[a, b]
>>> torch.stack([a, b], 0)
tensor([[[1, 2],
[3, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])
>>> torch.stack([a, b], 0).shape
torch.Size([2, 2, 2])
# 以第1维进行stack,叠加的基本单位为一行
>>> torch.stack([a, b], 1)
tensor([[[1, 2],
[5, 6]],
[[3, 4],
[7, 8]]])
>>> torch.stack([a, b], 1).shape
torch.Size([2, 2, 2])
# 以第2维进行stack,叠加的基本单位为每一行的每一个元素
>>> torch.stack([a, b], 2)
tensor([[[1, 5],
[2, 6]],
[[3, 7],
[4, 8]]])
>>> torch.stack([a, b], 2).shape
torch.Size([2, 2, 2])
组合: torch.chunk(), torch.split()
torch.chunk()需要指定分块的数量
>>> a = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)
>>> a
tensor([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])
# 沿着第0维进行分块,一共分成两块
>>> torch.chunk(a, 2, 0)
(tensor([[0, 1, 2]]), tensor([[3, 4, 5]]))
# 沿着第1维进行分块,一共分成两块.当不能整除时,最后一个的维数会小于前面的
>>> torch.chunk(a, 2, 1)
(tensor([[0, 1],
[3, 4]]), tensor([[2],
[5]]))
torch.split()需要指定每一块的大小,以整型或者list表示
# 沿着第0维分块,每一块维度为2,由于第0维维度总共为2,因此相当于没有分割
>>> torch.split(a, 2, 0)
(tensor([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]]),)
# 沿着第1维分块,每一块维度为2
>>> torch.split(a, 2, 1)
(tensor([[0, 1],
[3, 4]]), tensor([[2],
[5]]))
# 沿着第1维分块,list中的元素代表每一块占的维度
>>> torch.split(a, [1, 2], 1)
(tensor([[0],
[3]]), tensor([[1, 2],
[4, 5]]))
索引
- Tensor 的索引类似于 numpy 的
ndarray,也支持布尔索引和神奇索引
>>> a=torch.randn(2,2)
>>> a
tensor([[ 0.3150, -1.8297],
[ 0.0648, -1.1429]])
>>> a>0
tensor([[ True, False],
[ True, False]])
>>> a[~(a>0)]
tensor([-1.8297, -1.1429])
>>> x
tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 4],
[5, 5, 5, 5],
[6, 6, 6, 6],
[7, 7, 7, 7]])
>>> x[[4, 3, 0, 6]]
tensor([[4, 4, 4, 4],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[6, 6, 6, 6]])
>>> x[[0, 3, 1, 2], :]
tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2]])
>>> x[[0, 1, 2, 3], [0, 1, 2, 3]]
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3])
变形操作
view(), reshape()
- 二者作用基本相同,调整前后的 Tensor 共享内存
>>> a
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3])
>>> a.view(2,2)
tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3]])
>>> a.reshape(2,2)
tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3]])
contiguous()
- 在进行 Tensor 操作时,有些操作如
transpose(),permute()等可能会把 Tensor 在内存中变得不连续,而有些操作如view()是需要 Tensor 内存连续的,这种情况下需要使用contiguous()将内存变为连续的 reshape()就相当于Tensor.contiguous().view()
原地操作函数 resize_()
>>> a
tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3]])
>>> a.resize_(8)
tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3,
1910660200560, 1910660200560, 1910660200560, 1910660200560])
>>> a
tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3,
1910660200560, 1910660200560, 1910660200560, 1910660200560])
# 如果resize后小于原Tensor大小,则剩余的部分仍然会隐藏保留
>>> a.resize_(2)
tensor([0, 1])
>>> a
tensor([0, 1])
>>> a.resize_(4)
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3])
squeeze(), unsqueeze()
squeeze()去除 size 为 1 的维度unsqueeze()将指定维度的 size 变为 1
>>> a=torch.arange(3)
>>> a.shape
torch.Size([3])
>>> a.unsqueeze(0).shape
torch.Size([1, 3])
>>> a.unsqueeze(0).squeeze(0).shape
torch.Size([3])
expand(), expand_as()
- 采用复制元素的方式来扩展 Tensor 的维度
expand()将 size 为 1 的维度复制扩展为指定大小,也可以用expand_as()指定 Tensor 维度
>>> a=torch.randn(2,2,1)
>>> a
tensor([[[ 0.1891],
[ 2.6933]],
[[-1.6266],
[ 1.3337]]])
>>> a.expand(2,2,3)
tensor([[[ 0.1891, 0.1891, 0.1891],
[ 2.6933, 2.6933, 2.6933]],
[[-1.6266, -1.6266, -1.6266],
[ 1.3337, 1.3337, 1.3337]]])
>>> b=torch.randn(2,2,3)
>>> a.expand_as(b)
tensor([[[ 0.1891, 0.1891, 0.1891],
[ 2.6933, 2.6933, 2.6933]],
[[-1.6266, -1.6266, -1.6266],
[ 1.3337, 1.3337, 1.3337]]])
转置与转轴 transpose() 和 permute()
transpose()将指定的两个维度的元素进行转置permute()按照给定的维度进行维度变换, 相当于 numpy 中的transpose()
>>> a=torch.randn(2,2,2)
>>> a
tensor([[[-0.0487, 0.1411],
[-0.9727, -1.0517]],
[[-0.6619, 0.1907],
[ 0.1305, -1.2069]]])
>>> a.transpose(0,1)
tensor([[[-0.0487, 0.1411],
[-0.6619, 0.1907]],
[[-0.9727, -1.0517],
[ 0.1305, -1.2069]]])
>>> a.permute(2,1,0)
tensor([[[-0.0487, -0.6619],
[-0.9727, 0.1305]],
[[ 0.1411, 0.1907],
[-1.0517, -1.2069]]])
排序 sort()
sort()沿指定维度排序,返回排序后的 Tensor 及对应的索引位置
>>> a=torch.randn(3,3)
>>> a
tensor([[ 1.9710, -1.0310, -0.6732],
[-0.4766, 0.3254, 1.5063],
[-0.5229, -0.0387, 0.8007]])
# True表示降序
>>> a.sort(0, True)[0]
tensor([[ 1.9710, 0.3254, 1.5063],
[-0.4766, -0.0387, 0.8007],
[-0.5229, -1.0310, -0.6732]])
>>> a.sort(0, True)[1]
tensor([[0, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 2],
[2, 0, 0]])
取极值 max(), min()
>>> a
tensor([[ 1.9710, -1.0310, -0.6732],
[-0.4766, 0.3254, 1.5063],
[-0.5229, -0.0387, 0.8007]])
>>> a.max(0)[0]
tensor([1.9710, 0.3254, 1.5063])
>>> a.max(0)[1]
tensor([0, 1, 1])
>>> a.max()
tensor(1.9710)
torch.max(input, other, out=None) → Tensor
- Each element of the tensor
inputis compared with the corresponding element of the tensorotherand an element-wise maximum is taken. The shapes ofinputandotherdon’t need to match, but they must be broadcastable.
也就是说,可以利用广播来对两个Tensor进行取最大值的操作
Tensor 的内存共享
- 直接通过 Tensor 来初始化另一个 Tensor,或者通过 Tensor 的组合、分块、索引、变形操作来初始化另一个 Tensor ,则这两个 Tensor 共享内存
- 原地操作符 (in-place operation)。任何原地操作符都加了一个后缀 “
_”,如add_(),resize_()
>>> a
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
>>> b
tensor([[ 0.5857, -0.7018],
[-0.2838, -0.4451]])
>>> c=a.add_(b)
# add_()使a也发生了改变
>>> a
tensor([[1.5857, 0.2982],
[0.7162, 0.5549]])
Tensor 与 Numpy 转换: torch.as_tensor() / torch.from_numpy()
- Tensor 与 Numpy 可以进行高效转换,转换前后的变量共享内存。有时可以通过将 Tensor 转换为
ndarray来曲线救国; 使用torch.as_tensor()进行转换是会共享内存的
>>> b=np.random.randn(2,2)
>>> a=torch.as_tensor(b) # a=torch.from_numpy(b)
>>> a
tensor([[ 0.1027, 0.0642],
[-0.1120, 0.2536]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> b
array([[ 0.10268475, 0.0642312 ],
[-0.11195517, 0.25361295]])
>>> b[0,0]=1
>>> a
tensor([[ 1.0000, 0.0642],
[-0.1120, 0.2536]], dtype=torch.float64)
- Tensor 转换为
ndarray可以使用Tensor.numpy()方法,该方法返回一个 numpy 数组
广播
- 类似于 Numpy,Tensor 也支持广播
通用函数
| 函数名 | 功能 |
|---|---|
torch.where(condition, x, y) |
满足 condition 的位置输出 x,否则输出 y |
torch.where()
>>> x
tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 4],
[5, 5, 5, 5],
[6, 6, 6, 6],
[7, 7, 7, 7]])
>>> torch.where(x > 4, torch.ones_like(x), x)
tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 4],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]])
张量方法
Tensor.item()
- Use
torch.Tensor.item()to get a Python number from a tensor containing a single value:
>>> x = torch.tensor(2.5)
>>> x
tensor(2.5000)
>>> x.item()
2.5
Tensor.clamp()
Tensor.clamp(min, max): 限制 Tensor 元素的最大值与最小值
>>> a
tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3]])
>>> a.clamp(1, 2)
tensor([[1, 1],
[2, 2]])
Tensor.abs
Tensor.sqrt
Tensor.log
Tensor.pow
Tensor.sin, Tensor.cos
Tensor.matmul
- 张量点积
自动求导机制 autograd
- 自动求导机制 autograd 将前向传播的计算记录成计算图,自动完成求导。PyTorch 建立的计算图是动态的。动态图是指程序运行时,每次前向传播时从头开始构建计算图,这样不同的前向传播就有不同的计算图,不需要事先把所有的图都构建出来,并且可以很方便的查看中间过程变量
.requires_grad, .grad, .grad_fn
torch.Tensor是包的核心类。如果将其属性.requires_grad(默认为False) 设置为True,则会开始跟踪针对 tensor 的所有操作,且依赖于该 Tensor 之后的所有节点都需要求导。完成计算后,可以调用Tensor.backward()来自动计算所有梯度。该张量的梯度将累积到.grad属性中- 还有一个类对于 autograd 实现非常重要那就是
Function。Tensor 和 Function 互相连接并构建一个非循环图,它保存整个完整的计算过程的历史信息。每个张量都有一个.grad_fn属性保存着创建了张量的 Function 的引用,即该 Tensor 经过了怎么样的操作,用作反向传播的梯度计算(如果用户自己创建张量,则grad_fn是None)
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
>>> x
tensor([[-1.1423, -0.0149],
[-0.4527, -0.4478]], requires_grad=True)
>>> y = x + 2
>>> y
tensor([[0.8577, 1.9851],
[1.5473, 1.5522]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
>>> y.requires_grad # 由于依赖的Tensor需要求导,因此y也需要求导
True
>>> z = 3 * y**2
>>> out = z.mean()
>>> z
tensor([[ 2.2071, 11.8215],
[ 7.1822, 7.2281]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
>>> out
tensor(7.1097, grad_fn=<MeanBackward0>)
.detach_(), .requires_grad_(), with torch.no_grad()
- 要停止 tensor 历史记录的跟踪,可以调用
.detach(),它将其与计算历史记录分离,并防止将来的计算被跟踪。还可以将代码块使用with torch.no_grad(): 包装起来。在评估模型时特别有用。 - 启用自动求导可以调用
.requires_grad()
>>> a = torch.randn(2, 2)
>>> a.requires_grad
False
>>> a.requires_grad_()
tensor([[-0.2342, -1.2398],
[-0.8127, -0.9557]], requires_grad=True)
>>> a.detach_()
tensor([[-0.2342, -1.2398],
[-0.8127, -0.9557]])
>>> a.requires_grad
False
>>> b
tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... print((b**2).requires_grad)
...
False
Tensor.backward()
- 如果你想计算导数,你可以调用
Tensor.backward()。.backward()还有一个参数grad_variabels,代表根结点的导数,如果 Tensor 是标量,则不需要指定任何参数,backward()等同于backward(torch.tensor(1.))。但是如果它有更多元素,则需要指定一个gradient参数来指定张量的形状 - 当有多个输出需要同时进行梯度反向传播时,需要将
retain_graph设置为True(如果设置为False计算图中的中间变量在计算完后就会被释放),使计算多个输出的梯度时互不影响
>>> x = torch.randn(1)
>>> x
tensor([0.2249])
>>> w = torch.ones(1, requires_grad=True)
>>> b = torch.ones(1, requires_grad=True)
# is_leaf表示x, w, b为计算图中的叶结点
>>> x.is_leaf, w.is_leaf, b.is_leaf
(True, True, True)
>>> y = w * x
>>> z = y + b
>>> z.backward(retain_graph=True)
>>> w.grad
tensor([0.2249])
>>> b.grad
tensor([1.])
神经网络工具箱 torch.nn
import os
import json
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import optim
import torchvision
from torchvision import models
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
torch.nn接口构建于 autograd 之上,提供了网络模组、优化器和初始化策略等一系列功能
nn.Module 类
nn.Module类实现了网络各层的定义及前向传播与反向传播机制- 如果想实现某个神经网络,只需继承
nn.Module类,在初始化中定义模型结构和参数,在forward()中编写网络前向传播过程即可。nn.Module类的__call__中调用了forward方法
- 如果想实现某个神经网络,只需继承
nn.Parameter()
- 一种特殊的
Tensor构造方式,可在nn.Module子类的__init__()中定义网络参数。默认requires_grad=True
nn.functional 库
nn.functional库也提供了很多网络层和函数,但nn.functional定义的网络层不可自动学习参数,还需要使用nn.Parameter封装。nn.functional的设计初衷是定义一些不需要学习参数的层,如激活层、池化层、BN 层- 总的来说,对于需要学习参数的层,最好用
nn.Module,无参数学习的层,可以使用nn.functional
实现简单版的全连接层以及二层感知机
- 尽管 Pytorch 中提供了全连接层、卷积层、池化层等,但是为了熟悉一下网络的定义方法,还是手动实现一个简单版的全连接层并用它构造一个二层感知机
class Linear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim):
super(Linear, self).__init__()
self.w = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(in_dim, out_dim))
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(out_dim))
def forward(self, x):
x = x.matmul(self.w)
y = x + self.b
return y
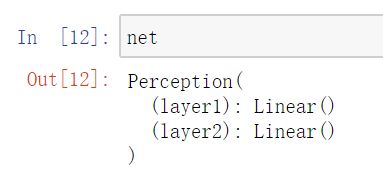
class Perception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, hid_dim, out_dim):
super(Perception, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = Linear(in_dim, hid_dim)
self.layer2 = Linear(hid_dim, out_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x) # nn.Module类的__call__中调用了forward方法
y = torch.sigmoid(x)
y = self.layer2(y)
y = torch.sigmoid(y)
return y
查看 nn.Module 实例的网络结构以及参数
__str__()
net.named_parameters(), net.parameters()
- 通过
net.named_parameters()/net.parameters()查看网络参数
nn.Sequential()
- 当模型只是简单的前馈网络 (上一层的输出直接作为下一层的输入) 时,可用
nn.Sequential()快速搭建模型,而不必在forward()中一层层地前向传播
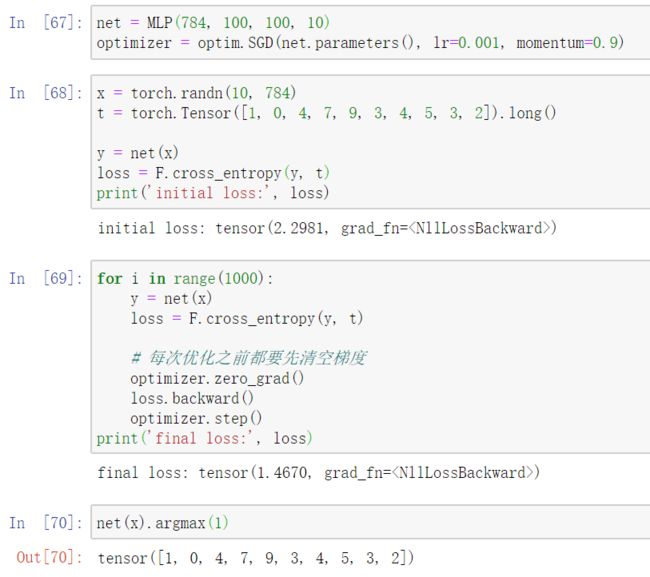
利用 nn.Sequential() 实现多层感知机
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, hid_dim1, hid_dim2, out_dim):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_dim, hid_dim1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hid_dim1, hid_dim2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hid_dim2, out_dim),
nn.Softmax(dim=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
# 直接调用__call__
x = self.layer(x)
# 也可以利用迭代协议
for layer in self.layer:
x = layer(x)
return x
nn.Sequential() 动态添加网络层
torch.nn.Module.add_module(name, module)
- Adds a child module to the current module. The module can be accessed as an attribute using the given name.
name(string) – name of the child module. The child module can be accessed from this module using the given namemodule(Module) – child module to be added to the module.
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(100, 10))
net.add_module('extra-layer',nn.Linear(10, 20))
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=10, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=20, bias=True)
)
损失函数
- PyTorch 在
torch.nn和torch.nn.functional中都提供了各种损失函数,它们的功能是一样的,区别在于torch.nn将损失函数看作网络的某一层放到模型定义中,而torch.nn.functional则是直接将损失函数当作功能函数放到前向传播的过程中
# 以一个样本的三分类问题为例
>>> y = torch.Tensor([0.1, 0.3, 0.6]).unsqueeze(0)
>>> t = torch.Tensor([2]).long()
>>> loss_f = F.cross_entropy(y, t)
>>> loss_f
tensor(0.8533)
>>> criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
>>> loss_nn = criterion(y, t)
>>> loss_nn
tensor(0.8533)
优化器 nn.optim
- 定义优化器
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
- 梯度下降
# 每次优化之前都要先清空梯度
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
学习率调整:
- 不同参数层分配不同的学习率
- 学习率动态调整
# 手动调整学习率
def set_learning_rate(optimizer, lr):
"""Sets the learning rate to the given value"""
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr
模型处理
torchvision.models 库
torchvision.models库提供了众多经典网络结构与预训练模型,如 VGG, ResNet, Inception
- 以 VGG 为例,VGG 的特征层和分类层分别用
vgg.features与vgg.classifier表示,每个部分都是nn.Sequential实例
>>> from torchvision import models
>>> net = models.vgg16()
# VGG16的特征层包含13个卷积层、13个Relu层、5个池化层
>>> len(net.features)
31
# VGG16的分类层包含3个全连接层、2个Relu层、2个Dropout层
>>> len(net.classifier)
7
# 可以通过索引选取网络中的某些层
>>> net.classifier[-1]
Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)
Transfer learning
获取 torchvision.models 中的预训练模型
net = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
- 如果想要提前将模型下载到本地,可以在这里找各个模型的下载地址,存到本地后再加载
model = models.vgg16(pretrained=False)
state_dict = torch.load('./vgg16.pth')
model.load_state_dict(state_dict )
保存模型 torch.save()
- 网络的
state_dict()方法可以获取网络的当前状态数据
# 以VGG16为例,net.state_dict()中保存了该网络16个带权重的层的参数
>>> type(net.state_dict())
<class 'collections.OrderedDict'>
>>> for key in net.state_dict():
... print(key)
...
features.0.weight
features.0.bias
features.2.weight
features.2.bias
features.5.weight
features.5.bias
features.7.weight
features.7.bias
features.10.weight
features.10.bias
features.12.weight
features.12.bias
features.14.weight
features.14.bias
features.17.weight
features.17.bias
features.19.weight
features.19.bias
features.21.weight
features.21.bias
features.24.weight
features.24.bias
features.26.weight
features.26.bias
features.28.weight
features.28.bias
classifier.0.weight
classifier.0.bias
classifier.3.weight
classifier.3.bias
classifier.6.weight
classifier.6.bias
torch.save({
'model': net.state_dict(),
'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict()},
'D:/vgg16.pth')
加载本地的预训练模型 model.load_state_dict()
net = models.vgg16()
state_dict = torch.load('D:/vgg16.pth')
net.load_state_dict({k:v for k, v in state_dict['model'].items() if k in net.state_dict()})
设置预训练模型中的某些层不进行参数的学习
- 以 VGG16 为例,设置前三个卷积模组不进行参数学习
for layer in range(7):
for p in net.features[layer].parameters():
p.requires_grad = False
数据加载
- (1) 可以利用
torchvision.datasets直接加载 Imagenet,CIFAR10,MNIST 等公共数据集; 也可以继承torch.utils.data.Dataset抽象类,实现__len__()和__getitem__()方法,即可进行数据集迭代- 其中
__len__()用来提供数据集大小(可选),而__getitem__()用来支持整数索引 (必须)
- 其中
- (2) 数据变换与增强
torchvision.transforms- 利用
torchvision.transforms可以方便的进行图像缩放、裁剪、随机翻转、填充以及张量的归一化等操作。操作对象可以是 PIL 的 Image 或者 Tensor - 如果需要进行多个变换功能,可以利用
transforms.Compose将多个变换整合起来。在实际使用时,常会将变换操作集成到Dataset类中
- 利用
- (3) 继承
torch.utils.data.DataLoader类- 经过前两步后已经可以获取每一个变换后的样本,而经过
torch.utils.data.DataLoader类包装之后就可以实现批量处理、随机选取等操作 DataLoader类是一个可迭代对象,对它的实例进行迭代即可用于训练过程
- 经过前两步后已经可以获取每一个变换后的样本,而经过
- 这里以一个红绿灯数据集为例; 该数据集在
img和json文件夹中分别存有图片与标注,文件名为0.jpg,1.jpg…0.json,1.json… 读取代码如下:
class MyData(Dataset):
def __init__(self, img_path, annotation_path, transforms=None):
# 初始化,读取数据集
self.annotation_path = annotation_path
self.img_path = img_path
self.transforms = transforms
def __len__(self):
return len(os.listdir(self.img_path))
def __getitem__(self, index):
annotation = json.load(open(self.annotation_path + '/' + str(index) + '.json'))
img = Image.open(self.img_path + '/' + str(index) + '.jpg')
# plt.imshow(img)
if self.transforms:
img = self.transforms(img)
return img, annotation
dataset = MyData('D:/Download/Dataset/traffic_light/train/img', 'D:/Download/Dataset/traffic_light/train/json',
transforms=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(240), # 将图像最短边缩至240,宽高比例不变
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 以0.5的概率左右翻转图像
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL图像转为Tensor,并且进行归一化
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]) # 进行mean与std为0.5的标准化
]))
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True)#, num_workers=2) # num_workers表示使用几个线程来加载数据 我的电脑加了这个参数就报错,可能不支持多线程操作
data_iter = iter(dataloader)
for step in range(1000):
data = next(data_iter)
# 下面即可将data用于训练网络
GPU 加速
指定使用某一块GPU
torch.cuda.is_available判断当前 GPU 是否可用- 对于 Tensor 和模型,
cuda()方法可以将数据转移到 GPU 上运行,并且可以输入数字来指定转移到哪一块 GPU 上运行
a = torch.randn(3, 3)
b = models.vgg16()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
a = a.cuda()
b = b.cuda(1)
- 也可以用
torch.device()指定使用哪一个GPU
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
c = torch.randn(3, 3, device=device)
model.to(device)
c = c.to(device)
- 全局指定使用哪一块 GPU:
# 在终端执行脚本时指定
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 python train.py
torch.cuda.set_device(1)
多 GPU 并行计算
- 首先将模型加载到主 GPU 上,然后复制模型到各个指定的 GPU 上,将输入数据按 batch 的维度进行划分 (将一个 batch 分为几个更小的 mini-batch),分配到每个 GPU 上独立进行前向传播,再将得到的损失求和并反向传播更新单个 GPU 上的参数,最后将更新后的参数复制到各个 GPU 上
model_gpu = nn.DataParallel(model)
output = model_gpu(input)