linux多线程编程详解
注:如果unubtu下 man手册不全,需要安装 apt-get install manpages-posix-dev
一、线程创建
PTHREAD_CREATE(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_CREATE(3)
NAME
pthread_create - create a new thread
SYNOPSIS
#include
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
Compile and link with -pthread.
参数:第二参数attr是线程的属性,可以设置为NULL使用默认属性
二、获取线程ID
PTHREAD_SELF(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_SELF(3)
NAME
pthread_self - obtain ID of the calling thread
SYNOPSIS
#include
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
Compile and link with -pthread.
三、线程ID比较
PTHREAD_EQUAL(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_EQUAL(3)
NAME
pthread_equal - compare thread IDs
SYNOPSIS
#include
int pthread_equal(pthread_t t1, pthread_t t2);
Compile and link with -pthread.
四、线程终止
PTHREAD_EXIT(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_EXIT(3)
NAME
pthread_exit - terminate calling thread
SYNOPSIS
#include
void pthread_exit(void *retval);
Compile and link with -pthread.
五、阻塞等待指定线程退出
PTHREAD_JOIN(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_JOIN(3)
NAME
pthread_join - join with a terminated thread
SYNOPSIS
#include
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
Compile and link with -pthread. 注:如果线程已经处于分离状态,pthread_join就会处于调用失败。
六、取消同一进程中的其他线程
PTHREAD_CANCEL(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_CANCEL(3)
NAME
pthread_cancel - send a cancellation request to a thread
SYNOPSIS
#include
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
Compile and link with -pthread.
注:线程可以选择忽略取消或者控制如何被取消。
七、分离线程函数
PTHREAD_DETACH(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_DETACH(3)
NAME
pthread_detach - detach a thread
SYNOPSIS
#include
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
Compile and link with -pthread.
一个比较完整的例子,用到了上面的7个函数:gcc pthread_create.c -pthread
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void Perror(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void* fun2(void *arg)
{
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
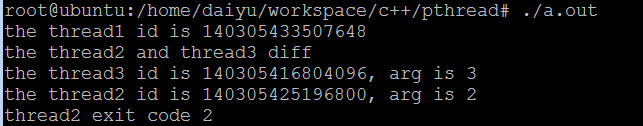
printf("the thread2 id is %ld, arg is %d\n", (long)thread_id, *(int*)arg);
sleep(1); /* wait for join */
pthread_exit((void*)2);
}
void* fun3(void *arg)
{
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
printf("the thread3 id is %ld, arg is %d\n", (long)thread_id, *(int*)arg);
sleep(60); /* wait for cancel */
}
int main()
{
int err;
pthread_t thread1;
pthread_t thread2;
pthread_t thread3;
int arg2 = 2;
int arg3 = 3;
thread1 = pthread_self();
printf("the thread1 id is %ld\n", (long)thread1);
// Create thread
err = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, fun2, (void*)&arg2);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't create thread2\n");
}
err = pthread_create(&thread3, NULL, fun3, (void*)&arg3);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't create thread3\n");
}
// detach thread3
err = pthread_detach(thread3);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't detach thread3\n");
}
// if equal
if (pthread_equal(thread2, thread3) != 0)
printf("the thread2 and thread3 same\n");
else
printf("the thread2 and thread3 diff\n");
// wait thread2 exit
void *retval;
int res = pthread_join(thread2, &retval);
if (res != 0)
printf("can't join with thread2\n");
else
printf("thread2 exit code %ld\n", (long)retval);
// cancel thread3
err = pthread_cancel(thread3);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't cancel thread3\n");
}
sleep(60);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
注:通过pstree命令也观察到线程数如程序设置一样。
参考:《unix环境高级编程》·第三版
End;