基础IO(上)
基础IO(上)
- 回顾文件知识
- 回顾C文件接口
- 系统文件I/O
-
- 接口介绍
-
- open
- close
- write
- read
- 理解文件描述符fd
- 理解0 1 2 3 4....
- 文件描述符的分配规则
- 重定向的本质及相关操作
-
- 认识重定向
- 重定向的具体原理
- 重定向的操作
- 追加重定向和输入重定向
-
- 追加重定向
- 输入重定向
- 缓冲区的理解
-
- 什么是缓冲区
- 为什么要有缓冲区
- 缓冲区在哪里
- 刷新策略
- 奇怪的代码(和子进程相关)
回顾文件知识
1、文件 = 文件内容 + 文件属性(空文件也占据空间,因为文件属性也是占据文件空间的)
2、文件操作 = 文件内容的操作 + 文件属性的操作(有可能,在操作文件的过程中,既改变文件的内容,也改变文件的属性,比如在修改文件内容的时候就改变了文件最新的修改时间和文件的大小)
3、所谓的“打开”文件,究竟在干什么?将文件的属性或者内容加载到内存中(冯诺依曼体系决定,CPU只能内存中对文件进行读写)。
4、是不是所有文件都处于被打开的状态?绝对不是,没有被打开的文件,在那里?存储在磁盘中。
5、所以文件分为两类:打开的文件(内存文件)和磁盘文件
6、通常我们打开文件,访问文件,关闭文件,是谁在进行相关操作?fopen、fclose、fread、fwrite… -> 代码 -> 程序 -> 只有当我们的文件程序,运行起来的时候,才会执行相应的代码,然后才是对文件进行真正的相关操作。
总结:所以对文件真正进行操作的是进程。
7、所以学习文件就是学习进程和打开文件的关系。
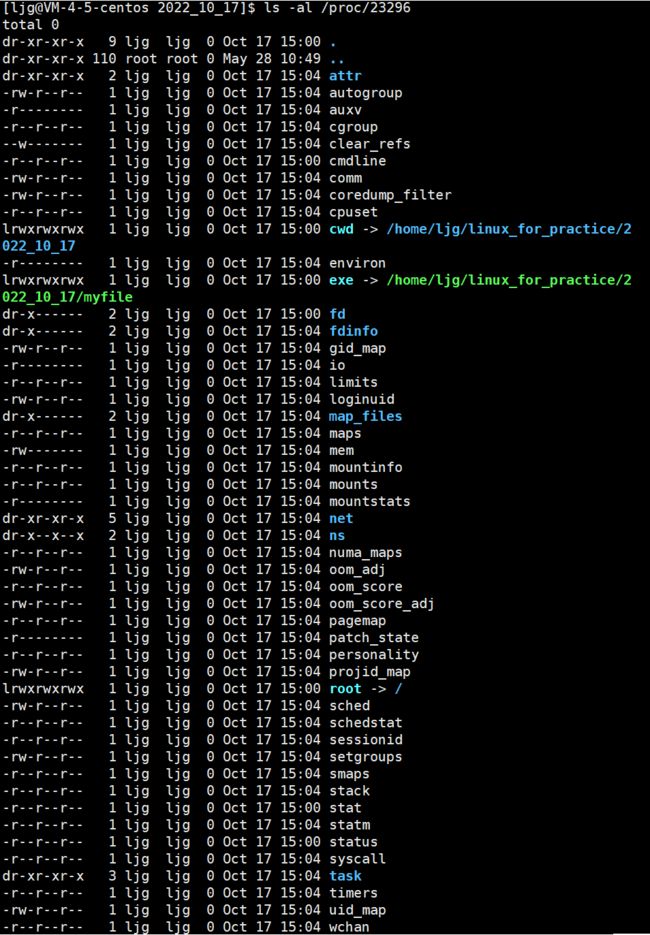
8、什么是当前路径?
进程的当前路径:
下面的cwd(curren work directory)后面的就是进程的当前路径:
9、当我们向文件写入的时候,最终是不是向磁盘写入?是的。磁盘作为硬件,只能被操作系统访问,所有的上层访问硬件,都必须通过操作系统,所以我们C语言中对文件的相关操作函数,其底层都是封装了操作系统提供的文件相关的系统调用。
回顾C文件接口
#include基于文件操作实现简易的cat功能:
#include系统文件I/O
接口介绍
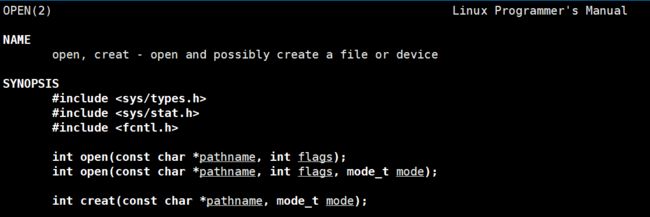
open
pathname: 要打开或创建的目标文件
flags: 打开文件时,可以传入多个参数选项,用下面的一个或者多个常量进行“或”运算,构成flags。以|进行分割。
mode: 给文件初始赋予的权限,受umask限制 //通过umask(权限掩码)可以设置新建文件的权限掩码
参数:
O_RDONLY: 只读打开
O_WRONLY: 只写打开
O_RDWR : 读,写打开
这三个常量,必须指定一个且只能指定一个
O_CREAT : 若文件不存在,则创建它。需要使用mode选项,来指明新文件的访问权限
O_APPEND: 追加写
O_TRUNC: 如果文件存在并且该文件允许进行写入就将文件清空
返回值:
成功:新打开的文件描述符
失败:-1
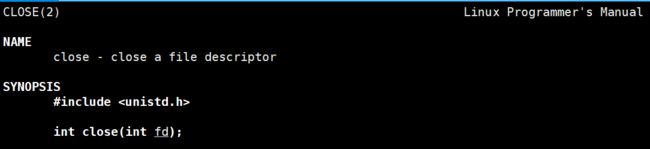
close
注意:系统传递标记位,是用位图来进行传递的!比如第一个二进制位代表O_RDOLLY(0000 0001),O_WRONLY(0000 0010)。
代码:
#include运行结果:
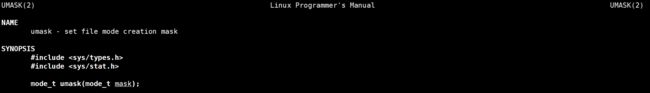
在上面的运行结果中,并没有出现666的权限,出现的是444,实际上这个地方受到了权限掩码umask的 影响,我们可以使用下面的系统调用来修改umask将其改为0即可:
umask
代码:
#include运行截图:
write
参数详解:
fd:文件描述符
buf:要写入字符串缓冲区的地址
count:要写入字符串的数目
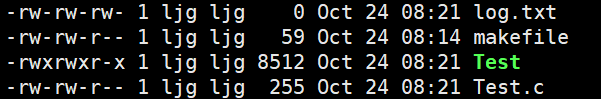
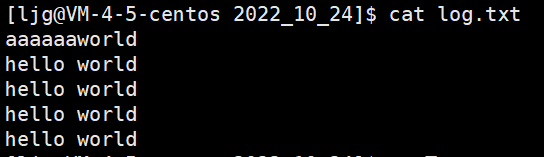
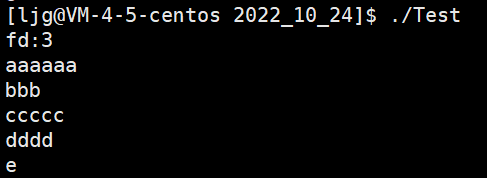
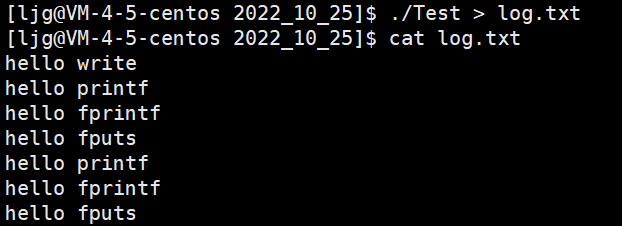
注意:当我们再次运行下面的代码就会出现下面的情况:
#include查看log.txt:
文件并没有清空,是因为我们open函数中没有加O_TRUNC这个选项对原来的文件进行清空,加上之后就会出现下面的清空:
int fd = open("log.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);//这三个选项,相当于C语言中fopen的'w'
此外:
O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND //相当于fopen的'a',在文件末尾进行追加
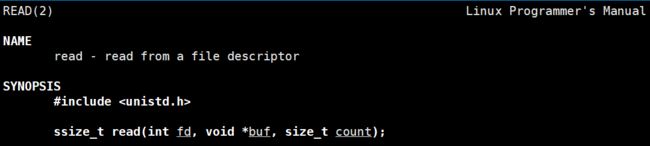
read
参数详解:
参数:
fd:文件描述符
buf:要写入的区域
count:想要读入的字符数
返回值:
实际读入的字符数//注意:ssize_t是有符号整数
代码练习:
Test.c文件代码:
#includelog.txt文件:
运行截图:
理解文件描述符fd
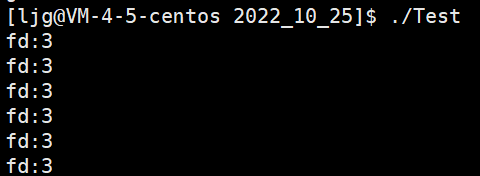
首先先进行一个实验:
代码:
#include运行截图:
此时查看open的返回值描述:
![]()
如果返回-1就说明错误发生了,只有当fd>=0才说明文件打开成功。
为什么从3开始?0 1 2是什么?
0 1 2被默认打开了:
0:标准输入:键盘
1:标准输出:显示器
2:标准输出:显示器
上面的可以类比C语言中的stdin,stdout,stderr
两者有什么区别呢?0 1 2是针对系统接口的概念,而stdin,stdout,stderr是C语言中的概念。
C语言中有FILE*类型的文件指针,那么FILE是什么呢?FILE是一个结构体,封装了很多成员,其中就封装了fd。
下面进行验证:
#include#include #include #include #include #include int main() { //先验证0 1 2就是标准IO char buffer[1024]; ssize_t s = read(0, buffer, sizeof(buffer)- 1);//从标准输入中读数据到buffer中 if(s > 0) { buffer[s] = '\0'; printf("echo:%s", buffer); } return 0; } 运行截图:
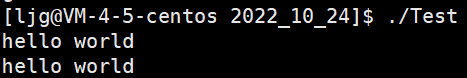
#include#include #include #include #include #include int main() { const char* str = "hello world\n"; write(1, str, strlen(str));//将str字符串中的内容写到标准输出(stdout)中去 write(2, str, strlen(str));//将str字符串中的内容写到标准错误(stderr)中去 return 0; }
下面再次进行验证stdin stdout stderror和0 1 2之间的对应关系:
代码:
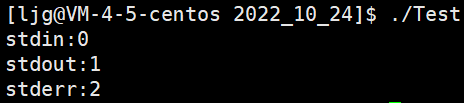
#include#include #include #include #include #include int main() { printf("stdin:%d\n", stdin->_fileno); printf("stdout:%d\n", stdout->_fileno); printf("stderr:%d\n", stderr->_fileno); return 0; }
总结:
函数接口的对应:
fopen/fwrite/fread… -> open/write/read/…
数据类型的对应:
FILE -> fd
理解0 1 2 3 4…
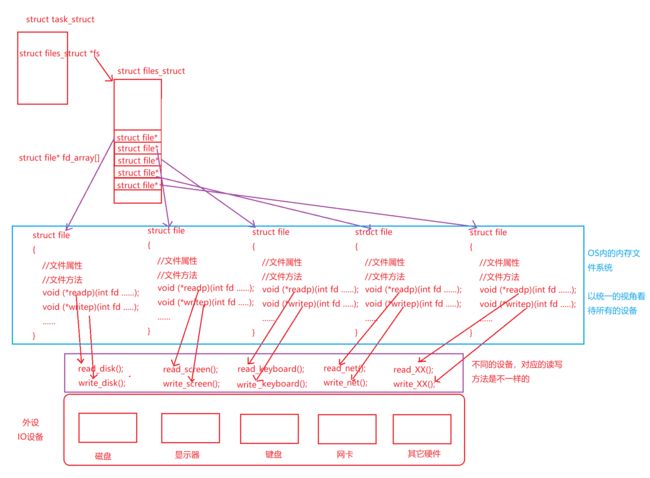
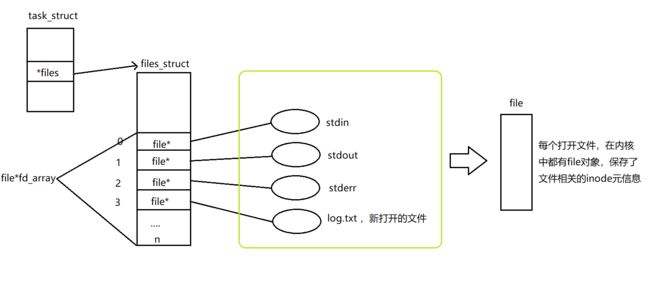
一个进程可以打开文件,包括标准输入、标准输出、标准错误还有其它文件(打开的文件在内存中),进程 : 打开的文件 = 1 : n ,所以系统在运行中有大量被打开的文件,OS要对这些文件进行管理,所以就要先描述后组织。所以一个文件被打开,在内核中就要创建该被打开的文件的内核数据结构,这是描述的过程。
struct file
{
//包含了文件的大部分内容和属性
struct file* next;
struct file* prev;
//只是为了方便描述,实际上内核数据结构有自己的链接方式和结构,但是相互链接是确定的
}
理解Linux下一切皆文件
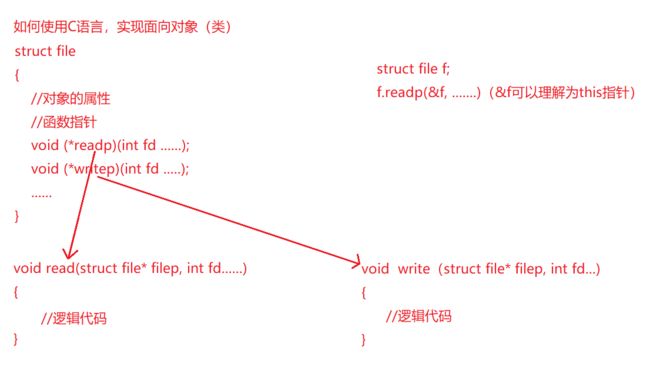
首先先理解一下C语言是如何实现面向对象中的多态的?
一切皆文件的理解:
注意:磁盘、显示器、键盘、网卡等的read和write的具体方法是驱动负责的。
注意:OS内的文件系统也叫做VFS,即虚拟文件系统。
我们可以通过ulimit -a指令来查看打开文件的个数:
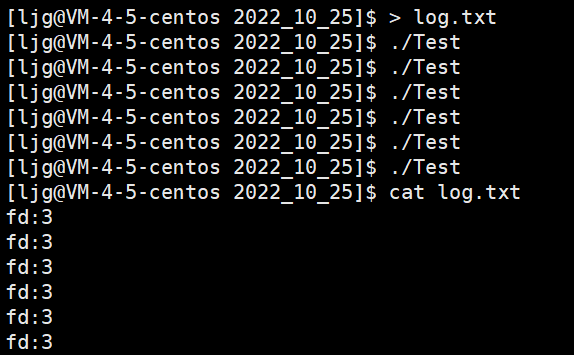
文件描述符的分配规则
从头遍历fd_array数组,找到一个最小的且没有被使用的下标分配给新的文件。
代码:
#include运行截图:
重定向的本质及相关操作
认识重定向
下面以一个小例子来了解重定向:
#include运行截图:
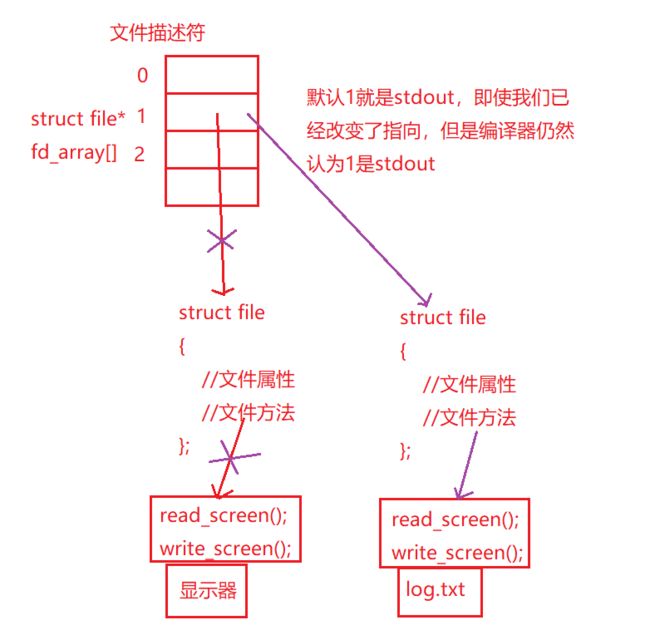
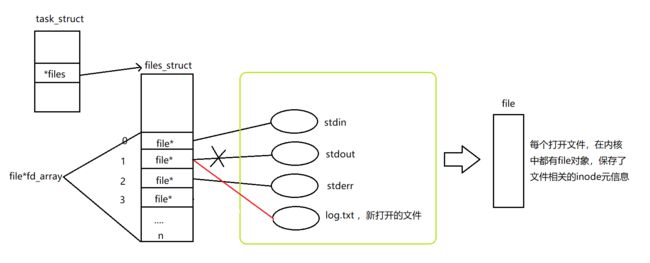
如果我们要进行重定向,上层只任0,1,2,3,4,5这样的fd,我们可以在OS内部,,通过这一方式调整数组的特定下标的内容(指向),我们就可以完成重定向操作。
总结:本来应该向显示器打印,最终变成了向指定文件打印,这就是重定向。
重定向的具体原理
如果我们要进行重定向,操作系统只认识0 1 2 3…这样的fd,我们可以在OS内部,通过一定的方式调整数组特定下标的内容(指向),我们就可以完成重定向操作。
在上面的例子中,就像下面这样进行改变:
printf是向1(log.txt文件)中进行写入,操作系统仍然认为1是stdout,所以程序运行的结果是向log.txt文件中进行写入。
重定向的操作
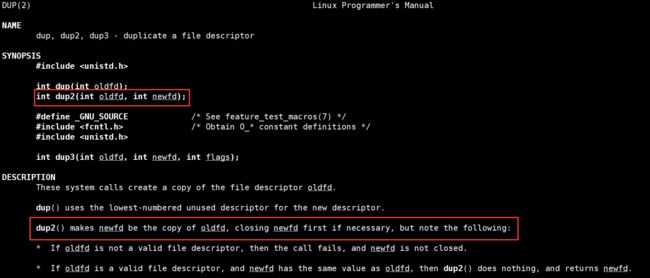
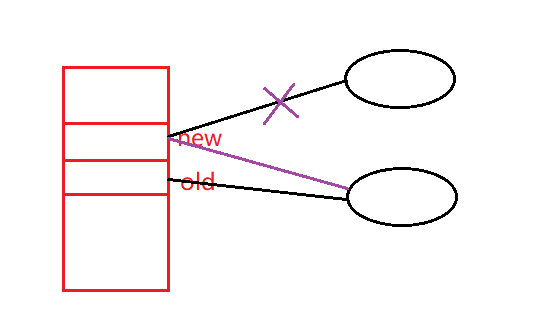
dup2作用:让新的fd称为旧的fd的拷贝,最终只剩下了旧的fd,如果必要的话,新的fd会被关闭。
注意:拷贝的不是数组下标,而是相应的数组下标所存储的内容,即struct file*。
返回值:
返回的是新的,即new文件描述符。
问:一个文件是怎么做到被打开多次的呢?
答:是通过类似引用计数的方式,当被打开一次的时候,引用计数就+1,close之后,引用计数就-1,当引用计数变成0的时候,文件才会彻底关闭。
追加重定向和输入重定向
追加重定向
代码:
#include运行截图:
输入重定向
代码:
#include运行截图:
缓冲区的理解
什么是缓冲区
缓冲区的本质:就是一段内存。
为什么要有缓冲区
- 解放当前使用缓冲区的进程的时间(即解放当前进程的时间,因为如果当前进程要直接将数据传输到外设中的话,,这个过程要花费很多的时间,且无法处理后面的代码)
- 缓冲区的存在可以集中处理数据刷新,减少IO的次数,从而达到提高整机的效率
缓冲区在哪里
代码测试:
#includesleep前:
sleep后:
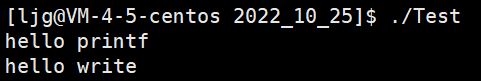
将上面的代码进行如下修改:
#include运行截图:
sleep前:
sleep后:
分析:首先printf封装了write,write是立即刷新的,即一旦有数据传给write就会立即在显示器上打印出来,hello printf没有先显示的原因是被存放到了缓冲区中,缓冲区没有被刷新,即缓冲区中的数据没有被传给write函数,所以没有被打印出来,当进程结束的时候,会将数据直接传给write函数,数据被立即刷新,所以最后hello printf被打印了出来。
总结:缓冲区在哪里呢,只能是由特定的语言提供的,stdout的类型是FILE类型的,缓冲区就封装在这个结构体中,缓冲区不是内核级别的。缓冲区在FILE内部,在C语言中,每一次打开一个文件,都要有一个FILE*会返回,意味着每一个文件都有一个fd和属于它自己的语言级别的缓冲区。所以open函数在打开文件的时候创建了一个FILE类型的结构体对象。
//在 / usr / include / libio.h
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
#define _IO_file_flags _flags
//缓冲区相关
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
/* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */
char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char* _IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char* _IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char* _IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker* _markers;
struct _IO_FILE* _chain;
int _fileno; //封装的文件描述符
#if 0
int _blksize;
#else
int _flags2;
#endif
_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
#define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary */
/* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */
_IO_lock_t* _lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
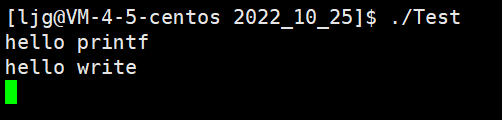
问:在上面的例子中,如果关闭了1会发生什么情况?
答:
代码:
#include#include #include #include #include #include int main() { printf("hello printf"); const char* str = "hello write"; write(1, str, strlen(str)); close(1); sleep(5); return 0; } 运行截图:
问:为什么会出现这样的情况呢?
答:因为下标1的file*指针已经不再指向stdout的file结构体了,自然无法找到之前的缓冲区然后调用write去刷新数据了。
刷新策略
什么时候刷新?
常规:
- 无缓冲(立即刷新)
- 行缓冲(逐行刷新):显示器文件
- 全缓冲(缓冲区写满才刷新):块设备(磁盘文件)
特殊情况:
- 进程退出
- 用户强制刷新(fflush)
注意:exit()和_exit()的区别,exit()会刷新缓冲区,_exit会清空缓冲区。
奇怪的代码(和子进程相关)
代码:
#include运行截图:
如果我们通过重定向改为向文件中进行写入:
两次的结果是不一样的。
首先先明确:向显示器写入的刷新策略是行缓冲,向文件进行写入的刷新策略是全缓冲。
刷新的本质:把刷新区的数据write到OS内部,然后清空缓冲区,注意:清空缓冲区时就对缓冲区中的数据进行了修改。
缓冲区是自己的FILE内部进行维护的,属于父进程的数据区域。所以清空缓冲区时,必然发生了写时拷贝。那么无论子进程还是父进程先
退出,都相当于有了两份缓冲区中的数据,都会向文件中进行写入,所以最终输出结果有两份。