力扣2022/3/16每日一题解析
*今日题目偏难,建议学习链表后前来看文章进行学习
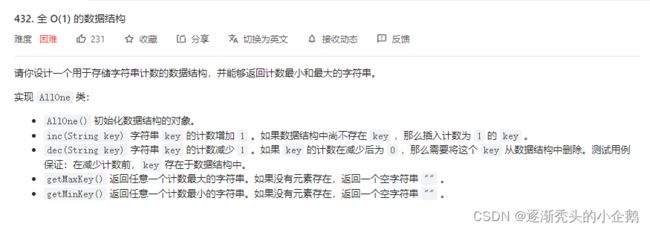
废话不多说,直接上题目!
本题被列为困难题,主要考察的是手写双链表,实现LFU缓存。
首先,题目对空间复杂速度不做限制,但是要求所有操作的时间复杂度O(1)。这个条件就否定了最朴素的哈希表计数方案,因为单纯用哈希表计数,增删操作是O(1)的,但查询最大最小值需要遍历哈希表,是O(N)时间的。
所以我就想到了第一个方法:暴力解题,硬刚就完事了!
但是!由于哈希表中存储的数据结构是无序的,因此无法维护最大频率和最小频率,只能暴力遍历所有的key-value pair来求最大频率和最小频率
代码如下:
class AllOne {
private:
unordered_map mp;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
AllOne() = default;
/** Inserts a new key with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */
void inc(string key) {
++mp[key];
}
/** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */
void dec(string key) {
auto it = mp.find(key);
if (it == mp.end()){
return;
}
else{
if (--it->second == 0){
mp.erase(it);
}
}
}
/** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */
string getMaxKey() {
if (mp.empty()){
return "";
}
else{
auto ans = mp.begin();
for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); ++it){
if (it->second > ans->second){
ans = it;
}
}
return ans->first;
}
}
/** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */
string getMinKey() {
if (mp.empty()){
return "";
}
else{
auto ans = mp.begin();
for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); ++it){
if (it->second < ans->second){
ans = it;
}
}
return ans->first;
}
}
};
很容易想到,可以缓存一个中间结果来做一些简单的优化——事实上这个优化过的暴力算法因为题目数据的原因击败了 100% 的 C++ 提交……
class AllOne {
private:
unordered_map mp;
unordered_map::iterator maxIt;
unordered_map::iterator minIt;
bool isMaxCached;
bool isMinCached;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
AllOne(): isMaxCached(false), isMinCached(false) {}
/** Inserts a new key with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */
void inc(string key) {
++mp[key];
isMaxCached = false;
isMinCached = false;
}
/** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */
void dec(string key) {
auto it = mp.find(key);
if (it == mp.end()){
return;
}
isMaxCached = false;
isMinCached = false;
if (--it->second == 0){
mp.erase(it);
}
}
/** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */
string getMaxKey() {
if (mp.empty()){
return "";
}
else{
if (isMaxCached){
return maxIt->first;
}
else{
auto ans = mp.begin();
for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); ++it){
if (it->second > ans->second){
ans = it;
}
}
isMaxCached = true;
maxIt = ans;
return ans->first;
}
}
}
/** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */
string getMinKey() {
if (mp.empty()){
return "";
}
else{
if (isMinCached){
return minIt->first;
}
else{
auto ans = mp.begin();
for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); ++it){
if (it->second < ans->second){
ans = it;
}
}
isMinCached = true;
minIt = ans;
return ans->first;
}
}
}
};
上述做法的时间复杂度:
int()是O(1)的,dec()是O(1)的,getMaxKey()和getMinKey()都是O(n)的,其中n是数据结构中不同字符串的个数。
上述做法虽然在本题的提交中显得很快,但是:这只是因为本题的数据太小,所以才能有优势,数据量大就要等着妥妥的 TLE 吧!
由于本题的性能瓶颈最大还是体现在找最大频率和最小频率的节点,如果能自动维护有序,那么时间复杂度就可以有很大的改善。因此,我们需要维护一个自动有序的数据结构,也就是平衡二叉搜索树
class AllOne {
private:
unordered_map freqHashMap;
map> freqTreeMap;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
AllOne() = default;
/** Inserts a new key with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */
void inc(string key) {
int curFreq = freqHashMap[key]++;
if (curFreq == 0){
freqTreeMap[1].insert(key);
}
else{
auto it = freqTreeMap.lower_bound(curFreq);
it->second.erase(key);
if (it->second.empty()){
it = freqTreeMap.erase(it);
}
else{
++it;
}
if (it != freqTreeMap.end() && it->first == curFreq + 1){
it->second.insert(key);
}
else{
freqTreeMap[curFreq + 1].insert(key);
}
}
}
/** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */
void dec(string key) {
auto freqHashMapItr = freqHashMap.find(key);
if (freqHashMapItr == freqHashMap.end()){
return;
}
int curFreq = freqHashMapItr->second--;
if (curFreq == 1){
freqHashMap.erase(freqHashMapItr);
auto it = freqTreeMap.begin();
it->second.erase(key);
if (it->second.empty()){
freqTreeMap.erase(it);
}
}
else{
auto it = freqTreeMap.lower_bound(curFreq);
it->second.erase(key);
if (it->second.empty()){
it = freqTreeMap.erase(it);
}
if (it != freqTreeMap.begin() && (--it)->first == curFreq - 1){
it->second.insert(key);
}
else{
freqTreeMap[curFreq - 1].insert(key);
}
}
}
/** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */
string getMaxKey() {
return freqTreeMap.empty() ? "" : *(freqTreeMap.rbegin()->second.begin());
}
/** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */
string getMinKey() {
return freqTreeMap.empty() ? "" : *(freqTreeMap.begin()->second.begin());
}
};
这个新的算法中,我们同时维护了两个 map,一个有序的 map,key 是频率,value 是这个频率对应的所有字符串。每次增减的时候,直接在红黑树里查找对应的节点并进行增减操作,因此 inc 和 dec 的时间复杂度都是O(log n) 的。而查询操作就比较简单了,直接去红黑树的开头结尾查询即可,对于 C++ 来说,时间复杂度是 O\left(1\right)O(1) 的。根据我对 Java 的 TreeMap 的源码阅读,我发现这个 firstEntry 和 lastEntry 每次都要傻乎乎地在红黑树中重新找,因此同样我也加入了缓存技术,如果缓存是有效的,直接从缓存中取!
Java TreeMap 相关源码如下:
final Entry getFirstEntry() {
Entry p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
public Map.Entry firstEntry() {
return exportEntry(getFirstEntry());
}
final Entry getLastEntry() {
Entry p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
return p;
}
public Map.Entry lastEntry() {
return exportEntry(getLastEntry());
}
当然,这里我们考虑问题需要注意边界情况。以 C++ 代码为例:增加元素频率的时候,如果是原来频率为 0,那么很简单;但是如果原来频率不是 0,那么我们在原来位置中删除元素的时候还要注意判断移除这个元素之后,这个频率是否不存在元素。如果不存在的话,应当进行删除;减少元素频率的时候,如果找不到(原来的频率是 0),应当直接返回;如果原来频率是 1,意味着是直接删除,同样和增加的情况一样,我们要注意频率为 1 的元素是否仅仅剩下这个字符串,这个情况同样也适用于其他的频率,只不过这个时候和频率为 1 的情况不同的是,我们还需要重新插入频率减 1 的节点。
但题目的 follow-up 希望我们所有的操作全部是O(1)的,而这样的操作,满足要求的数据结构,有且仅有哈希表。显然,我们仍然需要维护一个从字符串到频率的哈希表。但为了让对频率键值对的修改的时间复杂度变为 O(1),我们只能使用一个有序链表来进行存储,只有在链表中进行修改的时间复杂度才是 O(1) 的,不过大体的思路和上面仍然是一样的。但是,自己来维护一个有序链表,自然会给代码的边界条件的处理上要求更细心,例如增加最大频率,减小最低频率,增加频率为 0,减少频率为 1,增加频率移动节点的时候,相邻节点是否是可以直接合并,当前频率元素只有一个的时候,应该如何处理删除和插入等,具体实现请参考下面的代码,有详细的注释,这道题可以说是一个对 C++ STL 迭代器很好的训练题。
由于 Java 的链表并不能做到实际上的 O(1)(因为要一个一个找元素而不能像 C++ 那样直接删除节点),因此只给出 C++ 的实现:
class AllOne {
#ifndef AllOneDebug
// #define AllOneDebug
#endif
private:
unordered_map>>::iterator> freqMap;
list>> freqList;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
AllOne() = default;
/** Inserts a new key with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */
void inc(string key) {
#ifdef AllOneDebug
cout << "increasing: " << key << '\n';
#endif
auto it = freqMap.find(key);
int curFreq = it == freqMap.end() ? 0 : it->second->first;
if (curFreq > 0) {
// existing key
auto listItr = it->second;
freqMap.erase(it);
auto &tmp = listItr->second;
if (tmp.size() == 1) {
// the current node has only one string
if (listItr == --freqList.end()) {
// increasing the maximum frequency
freqList.pop_back();
freqList.push_back({curFreq + 1, {key}});
freqMap.insert({key, --freqList.end()});
} else {
listItr = freqList.erase(listItr);
// remove the current node and get the next node
if (listItr->first == curFreq + 1) {
// merge it to next node
listItr->second.insert(key);
} else {
// create a new node before current node
listItr = freqList.insert(listItr, {curFreq + 1, {key}});
}
freqMap.insert({key, listItr});
}
} else {
// the current node has multiple strings
tmp.erase(key);
if (listItr == --freqList.end()) {
// increasing the maximum frequency
freqList.push_back({curFreq + 1, {key}});
freqMap.insert({key, --freqList.end()});
} else {
++listItr;
// get the next node
if (listItr->first == curFreq + 1) {
// merge it to next node
listItr->second.insert(key);
} else {
// create a new node before current node with higher frequency
listItr = freqList.insert(listItr, {curFreq + 1, {key}});
}
freqMap.insert({key, listItr});
}
}
} else {
// new key
if (!freqList.empty() && freqList.front().first == 1) {
// we have existing keys whose frequencies are 1.
freqList.front().second.insert(key);
} else {
// create a new node
freqList.push_front({1, {key}});
}
freqMap.insert({key, freqList.begin()});
}
#ifdef AllOneDebug
debug();
#endif
}
/** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */
void dec(string key) {
#ifdef AllOneDebug
cout << "decreasing: " << key << '\n';
#endif
auto it = freqMap.find(key);
if (it == freqMap.end()) {
#ifdef AllOneDebug
debug();
#endif
// the key doesn't exist
return;
}
auto listItr = it->second;
freqMap.erase(it);
int curFreq = listItr->first;
if (curFreq == 1) {
// remove the string from our data structure.
// It is obvious that the node must be the beginning of the linked list.
auto &tmp = listItr->second;
if (tmp.size() == 1) {
// there are no more existing keys with frequency 1
freqList.pop_front();
} else {
// there are still existing keys with frequency 1
tmp.erase(key);
}
} else {
auto &tmp = listItr->second;
if (tmp.size() == 1) {
// there are no more existing keys with current frequency
if (listItr == freqList.begin()) {
// decreasing the frequency of key with minimum frequency
freqList.pop_front();
freqList.push_front({curFreq - 1, {key}});
freqMap.insert({key, freqList.begin()});
} else {
listItr = freqList.erase(listItr);
--listItr;
// get the prev node in the linked list
if (listItr->first == curFreq - 1) {
// so we just merge key in this node
listItr->second.insert(key);
} else {
// we need to create a new node
++listItr;
// get the node before which we will create the new node.
listItr = freqList.insert(listItr, {curFreq - 1, {key}});
}
freqMap.insert({key, listItr});
}
} else {
// keys with current frequency still exists
tmp.erase(key);
if (listItr == freqList.begin()) {
// decreasing the frequency of key with minimum frequency
freqList.push_front({curFreq - 1, {key}});
freqMap.insert({key, freqList.begin()});
} else {
--listItr;
// get the prev node in the linked list
if (listItr->first == curFreq - 1) {
// so we just merge key in this node
listItr->second.insert(key);
freqMap.insert({key, listItr});
} else {
// we need to create a new node
++listItr;
listItr = freqList.insert(listItr, {curFreq - 1, {key}});
freqMap.insert({key, listItr});
}
}
}
}
#ifdef AllOneDebug
debug();
#endif
}
/** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */
string getMaxKey() {
return freqList.empty() ? "" : *(freqList.back().second.begin());
}
/** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */
string getMinKey() {
return freqList.empty() ? "" : *(freqList.front().second.begin());
}
private:
void debug() {
for (const auto &[x, y] : freqList) {
cout << "{" << x << " = ";
for (const auto &z : y) {
cout << z << " ";
}
cout << "}\n";
}
cout << '\n';
}
};
这里面全部是对链表和哈希表的操作,而且链表操作位置都是缓存的结果,因此时间复杂度是真O(1) 的。
END!下次再见!