有向无环图最长路径java_有向无环图的最长简单路径
给定一个有向无环图$G=(V,E)$,边权重为实数,给定图中的两个顶点$k,t$,设计动态规划算法,求从k到t的最长简单路径,子问题图是怎样的?算法的效率如何?
算法分析:
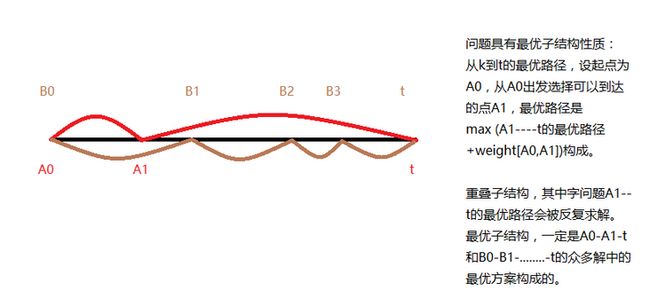
该问题不能够用贪心求解,假设从k出发,每一步取得weight最大的边,按这样的路径,并不能够保证能走到终点t。所以考虑动态规划算法。
该问题满足动态规划算法的两个特征:
一、最优子结构:
从k出发到t的最优路径,一定是$max(best , path , A_1 , to ,, t+weightA_0)$,其中$A0-->A1-->cdots t$和$B0-->B1-->cdots t$等等的诸多方案中的最优方案,构成了最优解。符合“剪贴”性质。
二、重叠子结构
有上面的公式可知,子问题:$A0-->A1-->cdots t$会被反复求解。
状态转移函数:
int q=weight[k][t];
for(int i=k+1;i<=t && weight[k][i];i++)
{
q=max(q,weight[k][i]+Find_longest_path(weight,numVertexes,i,t,r));
}
r[k]=q;
return q;
算法实现
Graphic_longest_path.h
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define INITWEIGHT 0
//用矩阵实现图
class graph
{
private:
bool isWeighted; //是否带权?
bool isDirected; //是否有向?
int numV; //顶点数
int numE; //边数
int **matrix; //邻接矩阵
public:
graph(int numV,bool isWeighted=false,bool isDirected=false);
void createGraph();
~graph();
int getVerNums()
{
return numV;
}
int getEdgeNums()
{
return numE;
}
int **getWeight()
{
return matrix;
}
void setEdgeWeight(int beg,int end,int weight);
void printAdjacentMatrix();
//检查输入
bool check(int i,int j,int w=1);
};
//类的实现
graph::graph(int numV,bool isWeighted,bool isDirected)
{
while(numV<=0)
{
cout<
cin>>numV;
}
this->numV=numV;
this->isWeighted=isWeighted;
this->isDirected=isDirected;
//private之后的成员可以被类的成员函数访问,但是不能够被使用该类的代码访问
matrix=new int *[numV];
for(int i=0;i
matrix[i]=new int [numV];
//对图进行初始化
if(!isWeighted) //无权图
{
//对所有的权值初始化为0
for(int i=0;i
for(int j=0;j
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
else //有权图
{
for(int i=0;i
for(int j=0;j
matrix[i][j]=INITWEIGHT;
}
}
//建图
void graph::createGraph()
{
cout<
while(cin>>numE && numE<0)
cout<
int i,j,w;
if(!isWeighted) //无权图
{
if(!isDirected) //无向图
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j;
while(!check(i,j))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j;
}
matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i]=1;
}
}
else
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j;
while(!check(i,j))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j;
}
matrix[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
else //有权图
{
if(!isDirected) //无向图
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j>>w;
while(!check(i,j,w))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j>>w;
}
matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i]=w;
}
}
else
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j>>w;
while(!check(i,j,w))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j>>w;
}
matrix[i][j]=w;
}
}
}
}
graph::~graph() //析构函数
{
for(int i=0;i
delete[] matrix[i];
delete[] matrix;
}
//设置指定边权值:
void graph::setEdgeWeight(int beg,int end,int weight)
{
if(isWeighted)
{
while(!check(beg,end,weight))
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end>>weight;
}
if(isDirected)
matrix[beg][end]=weight;
else
matrix[beg][end]=matrix[end][beg]=weight;
}
else
{
while(!check(beg,end,1))
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end;
}
if(isDirected) //对邻接矩阵的值进行反转,重置,1变成0,0变成1
matrix[beg][end]=1-matrix[beg][end];
else
matrix[beg][end]=matrix[end][beg]=1-matrix[beg][end];
}
}
//输入检查
bool graph::check(int i,int j,int w)
{
if(i>=0 && i=0 && j0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void graph::printAdjacentMatrix()
{
cout.setf(ios::left);
cout<
for(int i=0;i
cout<
cout<
for(int i=0;i
{
cout<
for(int j=0;j
cout<
cout<
}
}
dynamic_longest_path.h
#include "Graphic_longest_path.h"
#include
#include
#define INFINITY 0x7fffffff
int max(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int Find_longest_path(int **weight,int numVertexes,int k,int t,vector &r) //寻找k到t的最短路径
{
if(r[k]>=0)
return r[k];
if(k==t)
{
int q=0;
r[k]=q;
return q;
}
else
{
int q=weight[k][t];
for(int i=k+1;i<=t && weight[k][i];i++)
{
q=max(q,weight[k][i]+Find_longest_path(weight,numVertexes,i,t,r));
}
r[k]=q;
return q;
}
}
int dynamic_longest_path(int **weight,int numVertexes,int k,int t)
{
vector r;
r.resize(numVertexes);
for(int i=0;i
r[i]=-INFINITY;
return Find_longest_path(weight,numVertexes,k,t,r);
}
Graphic_longest_path.cpp
#include "dynamic_longest_path.h"
#include
int main()
{
cout<
bool isDirected, isWeighted;
int numV;
cout<
cout<
cin>>numV;
cout<
cin>>isWeighted;
cout<
cin>>isDirected;
graph graph(numV,isWeighted,isDirected);
cout<
isDirected ? cout<
isWeighted ? cout<
graph.createGraph();
cout<
graph.printAdjacentMatrix();
cout<
int k,t;
cout<
cin>>k>>t;
int numVertex=graph.getVerNums();
int **weight_dynamic=graph.getWeight();
cout<
cout<
int result=dynamic_longest_path(weight_dynamic,numVertex,k,t);
cout<
cout<
int beg, end, weight;
bool flag;
cout<
cin>>flag;
if(flag)
{
if(isWeighted)
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end>>weight;
graph.setEdgeWeight(beg,end,weight);
}
else
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end;
graph.setEdgeWeight(beg,end,1);
}
cout<
cout<
graph.printAdjacentMatrix();
}
return 0;
}
重构解
为了能够输出最短路径的方案,可以对解进行重构:
Graphic_longest_path.h
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define INITWEIGHT 0
//用矩阵实现图
class graph
{
private:
bool isWeighted; //是否带权?
bool isDirected; //是否有向?
int numV; //顶点数
int numE; //边数
int **matrix; //邻接矩阵
public:
graph(int numV,bool isWeighted=false,bool isDirected=false);
void createGraph();
~graph();
int getVerNums()
{
return numV;
}
int getEdgeNums()
{
return numE;
}
int **getWeight()
{
return matrix;
}
void setEdgeWeight(int beg,int end,int weight);
void printAdjacentMatrix();
//检查输入
bool check(int i,int j,int w=1);
};
//类的实现
graph::graph(int numV,bool isWeighted,bool isDirected)
{
while(numV<=0)
{
cout<
cin>>numV;
}
this->numV=numV;
this->isWeighted=isWeighted;
this->isDirected=isDirected;
//private之后的成员可以被类的成员函数访问,但是不能够被使用该类的代码访问
matrix=new int *[numV];
for(int i=0;i
matrix[i]=new int [numV];
//对图进行初始化
if(!isWeighted) //无权图
{
//对所有的权值初始化为0
for(int i=0;i
for(int j=0;j
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
else //有权图
{
for(int i=0;i
for(int j=0;j
matrix[i][j]=INITWEIGHT;
}
}
//建图
void graph::createGraph()
{
cout<
while(cin>>numE && numE<0)
cout<
int i,j,w;
if(!isWeighted) //无权图
{
if(!isDirected) //无向图
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j;
while(!check(i,j))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j;
}
matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i]=1;
}
}
else
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j;
while(!check(i,j))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j;
}
matrix[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
else //有权图
{
if(!isDirected) //无向图
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j>>w;
while(!check(i,j,w))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j>>w;
}
matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i]=w;
}
}
else
{
cout<
for(int k=0;k
{
cin>>i>>j>>w;
while(!check(i,j,w))
{
cout<
cin>>i>>j>>w;
}
matrix[i][j]=w;
}
}
}
}
graph::~graph() //析构函数
{
for(int i=0;i
delete[] matrix[i];
delete[] matrix;
}
//设置指定边权值:
void graph::setEdgeWeight(int beg,int end,int weight)
{
if(isWeighted)
{
while(!check(beg,end,weight))
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end>>weight;
}
if(isDirected)
matrix[beg][end]=weight;
else
matrix[beg][end]=matrix[end][beg]=weight;
}
else
{
while(!check(beg,end,1))
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end;
}
if(isDirected) //对邻接矩阵的值进行反转,重置,1变成0,0变成1
matrix[beg][end]=1-matrix[beg][end];
else
matrix[beg][end]=matrix[end][beg]=1-matrix[beg][end];
}
}
//输入检查
bool graph::check(int i,int j,int w)
{
if(i>=0 && i=0 && j0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void graph::printAdjacentMatrix()
{
cout.setf(ios::left);
cout<
for(int i=0;i
cout<
cout<
for(int i=0;i
{
cout<
for(int j=0;j
cout<
cout<
}
}
longest_path_constitute.h
#include "Graphic_longest_path.h"
#include
#include
#define INFINITY 0x7fffffff
int max(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int Find_longest_path(int **weight,int numVertexes,int k,int t,vector &r,int *solution) //寻找k到t的最短路径
{
if(r[k]>=0)
return r[k];
if(k==t)
{
int q=0;
r[k]=q;
solution[k]=t;
return q;
}
else
{
int q=weight[k][t];
if(weight[k][t])
solution[k]=t;
for(int i=k+1;i<=t && weight[k][i];i++)
{
int tmp=max(q,weight[k][i]+Find_longest_path(weight,numVertexes,i,t,r,solution));
if(tmp>q)
{
q=tmp;
solution[k]=i;
}
}
r[k]=q;
return q;
}
}
int dynamic_longest_path(int **weight,int numVertexes,int k,int t,int *solution)
{
vector r;
r.resize(numVertexes);
for(int i=0;i
{
r[i]=-INFINITY;
}
//完成初始化
return Find_longest_path(weight,numVertexes,k,t,r,solution);
}
void print_solution(int *solution,int k,int t)
{
if(solution[k]==-1)
cout<
else
{
cout<
cout< ";
while(k!=t)
{
cout<
if(solution[k]!=t)
{
cout< ";
}
k=solution[k];
}
cout<
}
}
Graphic_longest_path.cpp
#include "longest_path_constitute.h"
#include
int main()
{
cout<
bool isDirected, isWeighted;
int numV;
cout<
cout<
cin>>numV;
cout<
cin>>isWeighted;
cout<
cin>>isDirected;
graph graph(numV,isWeighted,isDirected);
cout<
isDirected ? cout<
isWeighted ? cout<
graph.createGraph();
cout<
graph.printAdjacentMatrix();
cout<
int k,t;
cout<
cin>>k>>t;
int numVertex=graph.getVerNums();
int **weight_dynamic=graph.getWeight();
cout<
cout<
//初始化solution:
int *solution=new int[numVertex+1];
for(int i=0;i
solution[i]=-1;
//返回最优解:
int result=dynamic_longest_path(weight_dynamic,numVertex,k,t,solution);
cout<
cout<
//返回solution的解,注意delete[]
cout<
print_solution(solution,k,t);
int beg, end, weight;
bool flag;
cout<
cin>>flag;
if(flag)
{
if(isWeighted)
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end>>weight;
graph.setEdgeWeight(beg,end,weight);
}
else
{
cout<
cin>>beg>>end;
graph.setEdgeWeight(beg,end,1);
}
cout<
cout<
graph.printAdjacentMatrix();
}
return 0;
}
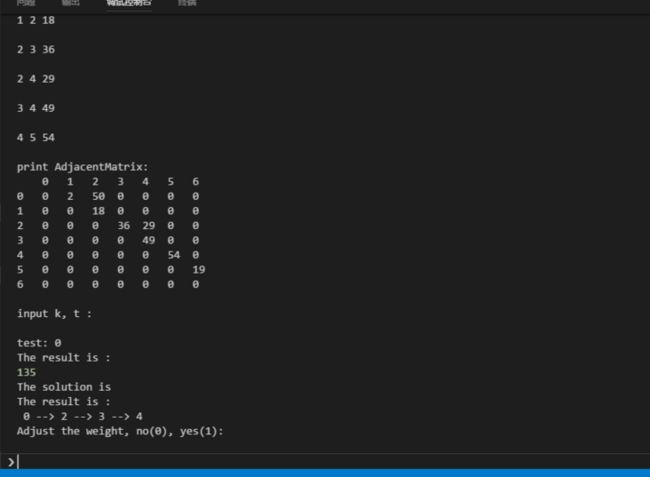
输出结果