数据结构之顺序表
本章重点:
1.线性表
2.顺序表
3.链表
4.顺序表和链表的区别和联系
目录
1.线性表
2.顺序表
2.1概念及结构
2.2接口实现
2.2.1 SeqList.h
2.2.2 SeqList.c
2.3数组相关面试题
2.3.1移除元素
2.3.2删除有序数组中的重复项 编辑
2.3.3合并两个有序数组
2.4 顺序表的问题及思考
1.线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
2.顺序表
2.1概念及结构
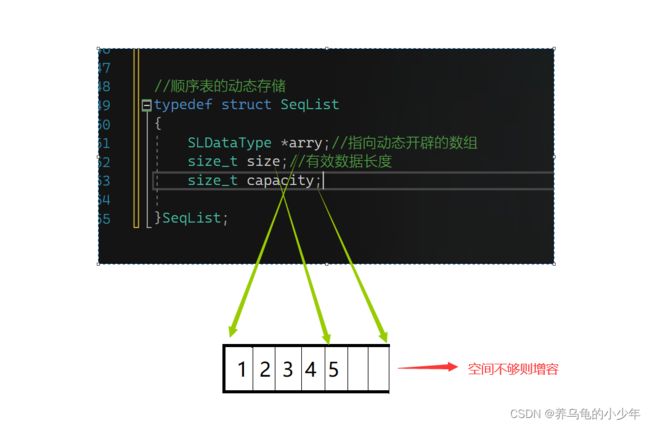
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1.静态顺序表:使用指定长数组存储元素
静态顺序表的缺点就是长度一旦确定 就不能被修改,容易造成内存浪费,或者内存不够
2.动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储
2.2接口实现
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间大小,所以下面我们实现动态顺序表
2.2.1 SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define INIT_CAPACITY 4
typedef int SLDataType; //类型重定义将int 类型 重定义一下 方便以后类型修改
// 定义一个结构体 带有SLDataType 类型指针
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType *a;
int size;//元素个数
int capacity;//元素容量
}SL;
//增删查改
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps);
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//显示
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
//插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
//擦除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//检查容量
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
2.2.2 SeqList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
//增删查改
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
//检查指针是否为空
assert(ps);
//动态开辟空间 初始容量为4个SLDataType大小
ps->a = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType)*INIT_CAPACITY);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc:fail");
return;
}
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = INIT_CAPACITY;
}
//检查容量
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->size)
{
//扩容成为原来容量的二倍容量大小 不确定空间 异地扩容
SLDataType *temp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDataType) *ps->capacity * 2);
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc:fail");
return;
}
ps->a = temp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
//assert(ps);
//SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
//assert(ps);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
//ps->size--;
SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1);
}
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
//assert(ps);
//SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//int end = ps->size- 1;
//while (end >= 0)
//{
// ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
// --end;
//}
//ps->a[0] = x;
//ps->size++;
SLInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
//assert(ps);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
//int begin = 1;
//while (begin < ps->size)
//{
// ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
//}
//ps->size--;
SLErase(ps, 0);
}
//显示
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity == 0;
}
//插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//擦除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size - 1);
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}
//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
2.3数组相关面试题
2.3.1移除元素
解题思路:空间复杂度要求为O(1),最好在原数组上操作,定义两个下标,src负责去遍历,des负责接收不等于val的值,
解题代码如下:
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
int src = 0;
int des = 0;
while(src2.3.2删除有序数组中的重复项

解题思路:类似上一题,定义两个下标,src位置在des位置的下一个,当src位置等于des位置时,src向后++,src位置不但能于dst位置就让des先递增在赋值。代码如下:
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
int des = 0;
int src = 1;
while(src2.3.3合并两个有序数组
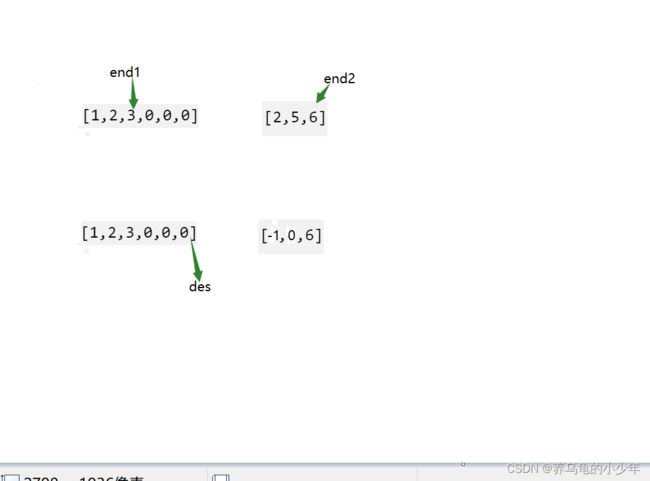
解题思路:类似于三个指针的方式,定义end1这个下标指向m - 1,定义end2下标指向 n - 1,在定义一个des下标 指向 m + n - 1,比较end1和end2 下标谁的比较大,放在des处,然后递减 再比较,如下图所示:
解析代码如下:
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){
int end1 = m - 1;
int end2 = n - 1;
int des = m + n - 1;
while(end1 >= 0 && end2>= 0 )
{
if(nums1[end1]>=nums2[end2])
nums1[des--] = nums1[end1–];
else
nums1[des--] = nums2[end2–];
}
while(end2>=0)
{
nums1[des--] = nums2[end2–];
}
}2.4 顺序表的问题及思考
问题:
1. 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2. 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
思考:如何解决以上问题呢?下面给出了链表的结构来看看。