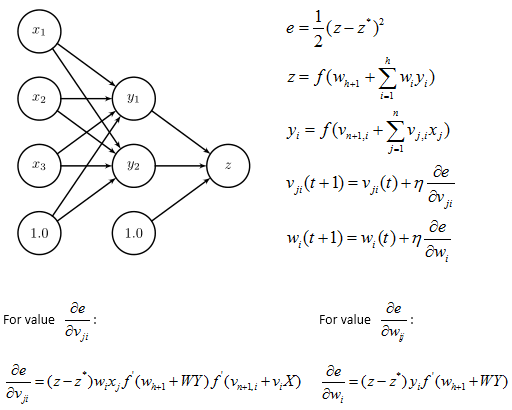
Multi–Layer Perceptron & Back-propagation algorithm
As for Multi-Layer Perceptron, it can be taken as a combination of many Linear Classifications, using many hyper plane to split the space and separate the dataset, to get a better classification, also MLP can be used in regression and Dimension reduce. In this blog, we’ll take about the MLP in classification, how to calculate the neutron network and show the main code.
As for a MLP with 2-layer, the following picture show the combination of 2 neutron (or two hyper plane), simplify the neutron as the picture bellow and define the functions:
The Back-propagation algorithm
It is an iterative algorithm, repeating the following steps
1. Pick a pair (X, z∗) randomly from the training set
2. Forward pass
3. Backward pass
In step2: Forward Pass we calculate Y, Y’, z and z’
In step2: Backward Pass we calculate update W, wn, V, vn, Error
1 /** 2 * computes the forward pass of the backpropagation algorithm 3 * calculate Y, Yp, z and zp; X have N coefficients 4 */ 5 private void forward(final Vector X){ 6 //calculate Y,Yp 7 for(int i=0;i<K;i++){ 8 double temp= vn.get(i)+X.dot(V[i]); 9 temp=Math.tanh(temp); 10 Y.set(i, temp); 11 temp=1-temp*temp; 12 Yp.set(i, temp); 13 } 14 //calculate z & zp 15 z=wn+Y.dot(W); 16 z=Math.tanh(z); 17 zp=1-z*z; 18 } 19 /** 20 * computes the backward pass of the backpropagation algorithm, 21 * with X as input and as desired output c 22 * update W, wn, V , vn, E 23 */ 24 private void backward(final Vector X, double c){ 25 double pout=-(z-c)*zp; 26 //System.out.println(zp); 27 //update W & wn 28 for(int i=0;i<K;i++){ 29 double delt_v=eta*Y.get(i)*pout; 30 W.set(i, W.get(i)+delt_v); 31 double pin=pout*W.get(i)*Yp.get(i); 32 //update V & vn 33 for(int j=0;j<N;j++) 34 V[i].set(j, V[i].get(j)+etaout*X.get(j)*pin); 35 vn.set(i, vn.get(i)+etaout*pin); 36 } 37 wn+=eta*pout; 38 } 39 /** 40 * returns true if the output of the MLP for X is positive, 41 * false if the output of the MLP for X is negative 42 */ 43 public boolean classify(final Vector X){ 44 Vector Yclassify=new Vector(K); 45 46 for(int i=0;i<K;i++){ 47 double temp= vn.get(i)+X.dot(V[i]); 48 temp=Math.tanh(temp); 49 Yclassify.set(i, temp); 50 } 51 //calculate z & zp 52 z=wn+Yclassify.dot(W); 53 return z>0; 54 } 55 /** 56 * updates W, wn, V ,vn update_weights implements 57 * one iteration of the backpropagation algorithm 58 */ 59 public void update(final Vector X, boolean inClass){ 60 double c= inClass? 1:-1; 61 forward(X); 62 backward(X, c); 63 }
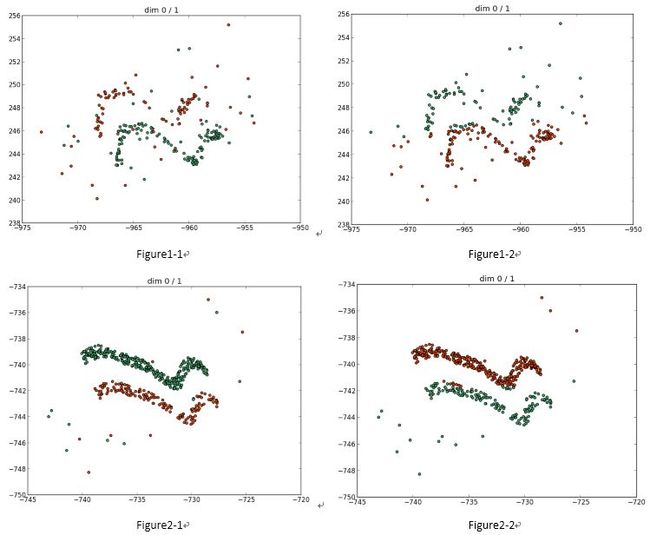
The following picture shows the result of 2 dataset running MLP (the Figure1/2-1 is the dataset, and the Figure1/2-2 is result).
参考资料:
http://page.mi.fu-berlin.de/rojas/neural/chapter/K7.pdf
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multilayer_perceptron
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backpropagation
http://www.marmakoide.org/download/teaching/dm/dm-perceptron-2.pdf