Matplotlib三维绘图,这一篇就够了
Matplotlib三维绘图,这一篇就够了
-
- 1. 效果图
-
- 1.1 3D线效果图
- 1.2 3D散点效果图
- 1.3 3D随机颜色散点效果图
- 1.4 3D散点不同mark点效果图
- 1.5 3D线框效果图
- 1.6 3D曲面不透明效果图
- 1.7 3D曲面透明效果图
- 2. 源码
- 参考
这篇博客将介绍使用 mplot3d 工具包进行三维绘图,支持简单的 3D 图形,包括曲面、线框、散点图和条形图。
1. 效果图
1.1 3D线效果图
1.2 3D散点效果图
3D散点图(标记了着色以呈现深度外观)效果如下:
1.3 3D随机颜色散点效果图
1.4 3D散点不同mark点效果图
1.5 3D线框效果图
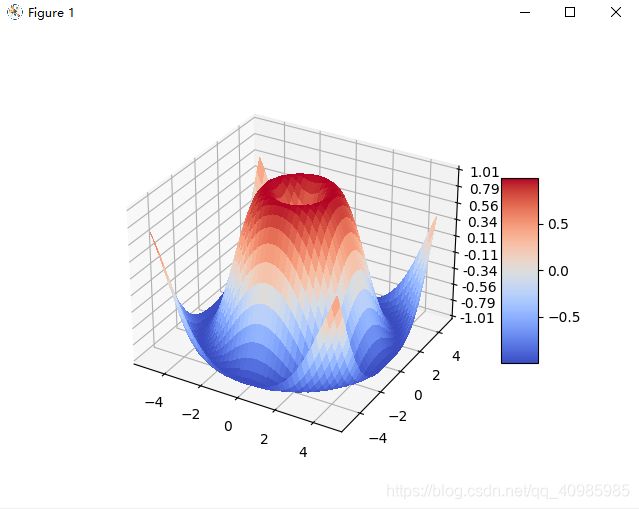
1.6 3D曲面不透明效果图
1.7 3D曲面透明效果图
2. 源码
# matplotlib 3D绘图
# 3D 轴(属于 Axes3D 类)是通过将 projection="3d" 关键字参数传递给 Figure.add_subplot 来创建的:
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(100)
y = np.random.randint(0, 300, 100)
z = np.random.randint(0, 200, 100)
# 3D线图
def line_3d():
# 线
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
# c颜色,marker:样式*雪花
ax.plot(xs=x, ys=y, zs=z, c="y", marker="*")
plt.show()
# 3D散点图
def scatter_3d():
# 散点图
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
# s:marker标记的大小
# c: 颜色 可为单个,可为序列
# depthshade: 是否为散点标记着色以呈现深度外观。对 scatter() 的每次调用都将独立执行其深度着色。
# marker:样式
ax.scatter(xs=x, ys=y, zs=0, zdir='z', s=30, c="g", depthshade=True, cmap="jet", marker="^")
plt.show()
def randrange(n, vmin, vmax):
"""
Helper function to make an array of random numbers having shape (n, )
with each number distributed Uniform(vmin, vmax).
"""
return (vmax - vmin) * np.random.rand(n) + vmin
# 3D随机颜色散点图
def scatter_random_color_3d():
# 随机颜色散点图
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
# c: 颜色 可为单个,可为序列
# ‘b’ blue 蓝色、g’ green 绿色、‘r’ red 红色、‘c’ cyan 兰青色
# ‘m’ magenta 紫色、‘y’ yellow 黄色、‘k’ black 黑色、‘w’white 白色
colors = ['b', 'g', 'r', 'c', 'm', 'y', 'k', 'w']
c = np.repeat(colors, 15)[:100]
ax.scatter(xs=x, ys=y, zs=0, zdir='z', s=30, c=c, depthshade=True, cmap="jet", marker="^")
plt.show()
# demo示例
# 设置种子以便重现随机值
np.random.seed(19680801)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
n = 100
# 每一个样式,绘制n个随机点
# 定义 x in [23, 32], y in [0, 100], z in [zlow, zhigh].
for m, zlow, zhigh in [('o', -50, -25), ('^', -30, -5)]:
xs = randrange(n, 23, 32)
ys = randrange(n, 0, 100)
zs = randrange(n, zlow, zhigh)
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, marker=m)
ax.set_xlabel('X Label')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Label')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Label')
plt.show()
# 线框图
def wireframe_3d():
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
x = np.random.randint(-30, high=30, size=(50,)).reshape((25, 2))
y = np.random.randint(-30, high=30, size=(50,)).reshape((25, 2))
z = np.zeros(50).reshape((25, 2))
# c: 颜色
# ‘b’ blue 蓝色、g’ green 绿色、‘r’ red 红色、‘c’ cyan 兰青色
# ‘m’ magenta 紫色、‘y’ yellow 黄色、‘k’ black 黑色、‘w’white 白色
ax.plot_wireframe(x, y, z, color='m')
plt.show()
# demo示例
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
# 获取测试数据
X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05)
# 绘制基本的线框图
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, color='c', rstride=10, cstride=10)
plt.show()
# 曲面图,默认情况下,它将以纯色的阴影着色,但它也通过提供 cmap 参数支持颜色映射。
# rcount 和 ccount kwargs 都默认为 50,决定了每个方向使用的最大样本数。如果输入数据较大,则会将其下采样(通过切片)到这些点数。
# 为了最大限度地提高渲染速度,将 rstride 和 cstride 分别设置为行数减 1 和列数减 1 的除数。例如,给定 51 行,rstride 可以是 50 的任何除数。
# 同样,设置 rstride 和 cstride 等于 1(或 rcount 和 ccount 等于行数和列数)可以使用优化路径。
def surface_3d():
# 3D 表面(颜色图)演示绘制使用冷暖色图着色的 3D 表面。通过使用 antialiased=False 使表面变得不透明。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
# 构建数据
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X ** 2 + Y ** 2)
Z = np.sin(R)
# 绘制曲面图
# 绘制使用冷暖色图着色的 3D 表面。通过使用 antialiased=False 使表面变得不透明。
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
# 定制z轴
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
# A StrMethodFormatter is used automatically
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter('{x:.02f}')
# 添加一个颜色条形图展示颜色区间
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()
# 绘制曲面图
# 绘制使用冷暖色图着色的 3D 表面。通过使用 antialiased=True 使表面变得透明。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=True)
# 定制z轴
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
# A StrMethodFormatter is used automatically
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter('{x:.02f}')
# 添加一个颜色条形图展示颜色区间
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()
# 三角曲面图
def tri_surface_3d():
n_radii = 8
n_angles = 36
# 将半径和角度设为等差数组(省略半径r=0以消除重复)
# start,stop,n,endpoint 默认endpoint为True,包含stop,为False不包含stop
radii = np.linspace(0.125, 1.0, n_radii)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False)[..., np.newaxis]
# 将polar极坐标(半径、角度)转换为cartesian笛卡尔坐标(x、y)
# (0,0)在此阶段手动添加,因此(x,y)平面中的点不会重复
x = np.append(0, (radii * np.cos(angles)).flatten())
y = np.append(0, (radii * np.sin(angles)).flatten())
# 计算z以生成pringle surface普林格尔曲面
z = np.sin(-x * y)
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, linewidth=0.2, antialiased=True)
plt.show()
# 3D线图
line_3d()
# 3D散点图
scatter_3d()
# 3D随机颜色散点图
scatter_random_color_3d()
# 线框图
wireframe_3d()
# 曲面图,默认情况下,它将以纯色的阴影着色,但它也通过提供 cmap 参数支持颜色映射。
surface_3d()
# 三角曲面图
tri_surface_3d()
参考
- https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/toolkits/mplot3d.html#toolkit-mplot3d-tutorial