Javascript
1.什么是Javascript?
Javascript是一种基于对象并具有安全性能的脚本语言,是由浏览器内解释器翻译成可执行格式后执行,在概念和设计方面,Java和Javascript是两种完全不同的语言。
Javascript的四个特点:基于对象的语言、简单性、动态性、跨平台性。
2.网页使用js脚本的三种方式
2.1 直接添加脚本
<input type = "button" onclick = “alert('欢迎');" value = "点击">
<html>
<head>
<title>直接添加脚本</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type = "button" onclick = "alert('hello everyone')" value = "点击">
</body>
</html>
2.2 使用script标记插入脚本
<script type = "text/javascript">
//在这里编写Javascript代码
</script>
<html>
<head>
<title>使用script标记插入脚本</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type = "text/javascript">
alert("hello everyone")
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.3 链接脚本文件(常用)
<script type = "text/javascript"
src = "文件名.js">
</script>
<html>
<head>
<title>链接脚本文件</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "1.js">
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.js
alert("hello everyone")
3.js编程
3.1 js编程概述
1、js支持的两种类型的注释
(1)行注释——在行末(//注释)
(2)块注释——可以跨越多行(/注释/)
2、分号是语句的结束符号
3、大小写
(1)Javascript 是大小写敏感的,这意味着大写字母相应的小写字母是不同的
(2)Javascript的保留关键字是小写的
3.2 js保留关键字
| break | case | catch | continue | debugger |
| default | delete | do | else | false |
| finally | for | function | if | in |
| instanceof | new | null | return | switch |
| this | throw | true | try | typeof |
| var | void | while | with |
3.2 js变量
(1)变量的声明
使用var关键字进行变量的声明: var x;
在声明的时候可以同时对变量进行初始化:var y = 4;
使用逗号将多个变量隔开:var x,y = 5, z = ‘hello’;
(2)变量的命名
变量必须由字母、数字和下划线组成
字母或者是下划线开头,不可以是数字
变量不可以是保留字
(3)变量区分大小写
3.4 js数据类型
1、字符串、数字、布尔、数组、对象、Nul、Undefined
2、拥有动态类型
相同的变量可用作不同的类型,typeof(x)可以得到变量的类型
var x; //x 为 undefined
var x = 6; //x为数字
var x = "Bill"; //x为字符串
3、运算符
(1)算数运算法
+、-、*、/、%、++、--
(2)逻辑运算符
&&、||、!
(3)比较运算符
==、>、<、>=、<=、!=、 ===
(4)位运算符
~、&、!、^、<<、>>、>>>(无符号右移)
(5)字符串运算符
+(合并运算符)
(6)赋值运算符
=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=
(7)条件运算符
?:(条件?结果1:结果2)
3.5 js控制语句
1、if语句
if(条件表达式)
{
执行语句或语句群;
}
else
{
执行语句或语句群
}
2、switch语句
switch(表达式){
case 值1: 执行表达语句1;break;
case 值2: 执行表达语句2;break;
case 值n: 执行表达语句n;break;
}
3、for语句
for(初始量;判断语句;调整值){
执行语句或语句群
}
4、while语句
while(条件表达式){
执行语句;
}
5、do while语句
do{
执行语句
}while(条件表达式);
3.6 js函数
函数的语法结构:
function 函数名(参数1,参数2,…){函数体}
函数参数不是函数的必选内容(在调用一个需要参数的函数时没有传递参数,Javascript就会将参数表示为未定义(undefined))
案例:
//1.js
function myfun(arg){
//定义一个变量
var a = 100;
alert(typeof(a));
var str = arg;
alert(str);
return a;
}
function fun1{
var b = "b = ";
b += myfun(10);
alert(b);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>js</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "2.js"> </script>
<body>
<input type = "button" name = "mybutton" value = "点击" onclick = "fun1()">
</body>
</html>
3.7 js对象
js是面向对象的编程语言(OOP)
对象是一种特殊的数据类型,拥有属性和方法,其中属性是指与对象有关的值;方法是指对象可以执行的行为。其中Javascript中的常用对象:浏览器对象Window、文本对象Document(HTML DOM)、内部对象Date、Math、String。
3.7.1 浏览器对象(window对象)
window对象表示浏览器中打开的窗口,打开一个HTML网页会创建window对象
Window对象是全局对象
window.open()打开一个新的窗口
window.close()关闭当前窗口
window.location.href:返回完整的URL;对其进行赋值,则能够跳转到相应的网页
//window.js
function do_get_url(){
var myurl = "当前网页的url: ";
myurl += window.location.href;
alert(myurl);
}
function do_set_url(){
//在原网页进行网页的跳转
//window.location.href = "http://www.baidu.com";
//在新页面打开
window.open("http://www.baidu.com");
}
function do_close_html(){
//浏览器不同,结果可能不同
window.close();
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>使用window对象</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "window.js"></script>
<body>
<input type = "button" name = "" value = "获取当前网页的url" onclick = "do_get_url()">
<br>
<br>
<input type = "button" name = "" value = "跳转网页" onclick = "do_set_url()">
<br>
<br>
<input type = "button" name = "" value = "关闭当前网页" onclick = "do_close_html()">
</body>
</html>
3.7.2 文本对象(Document对象)
每个载入浏览器的HTML文档都会成为Document对象。
Document对象使我们可以从对HTML页面中的所有元素进行访问
1、提供了从js脚本中对HTML页面中的所有元素进行访问;
2、可以通过getElementById()方法,来根据对应的ID号去访问、控制HTML页面中的标签元素;
3、可以通过title,URL属性获取当前文档的标题,URL信息等;
4、可以通过write方法在HTML页面中写入HTML表达式。
function myfun(){
alert("网页标题:" + document.title());
//获取网页的url
alert("网页网址: +"document.URL);
//通过getElementById获取或者指定标签的值
var value = document.getElementById("mylabel").innerHTML;
alert(value);
document.getElementById("mylabel").innnerHTML = "hello world";
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>使用document对象</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "04_document.js"> </script>
<body>
<input type = "button" name = "" value = "点击一下" onclick = "myfun()">
<br>
<br>
<label id = "mylabel">这是将来存放js文件发过来的数据</label>
</body>
</html>
3.7.3 内部对象(Date对象)
提供了操作时间和日期的方法
拥有一些类属性和方法,可以用来获取系统当前时间或者设置Date对象中的时间
通过getTime()方法可返回1970年1月1日00:00:00:000(GMT时间)到现在的毫秒数。GMT是格林威治标准时间
(1)Date对象方法
getFullYear():返回当前年份;
getMonth():返回当前月份,0~11
getDay():返回星期中的某一天,0~6,6表示周日
getDate():返回一月中的某一天
getHours():返回当前时间的小时,0~23
getMinutes():返回当前时间的分钟,0~59
getSeconds():返回当前时间的秒,0~59
(2)setTimeout()与setInterval()函数区别:
setTimeout函数设置超时调用函数,超时后自动调用所设置的函数。超时候自动调用了回调函数,如果还想调用回调函数,必须重新调用setTimeout进行超时设置。而setInterval函数只需要设置一次,就可以多次调用回调函数,直到调用clearInterval
例1:
//05_data.js
var d = new Date();
document.write("
");
document.write("现在的时间是:");
document.write(d.getFullYear());
document.write("年");
document.write(d.getMonth()+1);
document.write("月");
document.write(d.getDate()+1);
document.write("日");
document.write("星期");
document.write(d.getDay()+ " ");
document.write(d.getHours());
document.write("点");
document.write(d.getMinute());
document.write("分");
document.write(d.getSeconds());
document.write("秒");
document.write("
");
document.write("
");
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>获取当前时间</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "05_data.js"></script>
<body>
</body>
</html>
例2:
//06_timeout.js
var stop_flag = 0;
function timeout(){
var time = new Date();
var h = time.getHours();
var m = time.getMinutes();
var s = time.getSeconds();
document.getElementById("time").value = h+":"+m+":"+s;
stop_flag = setTimeout("timeout()",1000);指定的毫秒数后调用函数timeout
}
function start_onload(){
timeout();
}
function stop(){
clearTimeout(stop_flag); //通过setTimeout返回值,停止定时
}
function start(){
timeout();
}
<html>
<head>
<title>从当前时间开始进行计时</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "06_timeout.js"> </script>
<body onload = "start_onload()"> <!-- onload属性用于设置后面js语句在页面打开时就立马执行 -->
<div align = "center">
<h1>Qfedu Timer</h1>
<input type = "text" id = "time">
<br>
<br>
<input type = "button" value = "开始" onclick = "start()">
<input type = "button" value = "暂时" onclick = "stop()">
</div>
</html>
3.7.4 内部对象(Math对象)
执行常见的算数任务
使用Math的属性和方法的语法:
var pi_value = Math.PI; var sqrt_value = Math.sqrt(15);
Math对象属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| E | 返回算数常量e,即自然对数的底数(约等于2.718) |
| LN2 | 返回2的自然对数(约等于0.693) |
| LN10 | 返回10的自然对数(约等于2.302) |
| LOG2E | 返回以2为底的e的对数(约等于1.414) |
| LOG10E | 返回以10为底的e的对数(约等于0.434) |
| PI | 返回圆周率(约等于3.14159) |
| SORT1_2 | 返回返回2的平方根的倒数(约等于0.707) |
| SORT2 | 返回2的平方根(约等于1.414) |
Math对象方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | 返回数的绝对值 |
| acos(x) | 返回数的反余弦值 |
| asin(x) | 返回数的反正弦值 |
| atan(x) | 返回从x轴到点(x,y)的角度 |
| ceil(x) | 对数进行上舍入 |
| cos(x) | 返回值的余弦 |
| exp(x) | 返回e的指数 |
| floor(x) | 对数进行下舍入 |
| log(x) | 返回数的自然对数 |
| max(x,y) | 返回x和y中的最高值 |
| min(x,y) | 返回x和y中的最低值 |
| pow(x,y)返回x的y次幂 | |
| random() | 返回0~1之间的随机数 |
| round(x) | 四舍五入 |
| sin(x) | 返回数的正弦 |
| sqrt(x) | 返回数的平方根 |
| tan(x) | 返回角的正切 |
| toSource() | 返回该对象的源代码 |
| valueOf() | 返回Math对象的原始值 |
//07_math.js
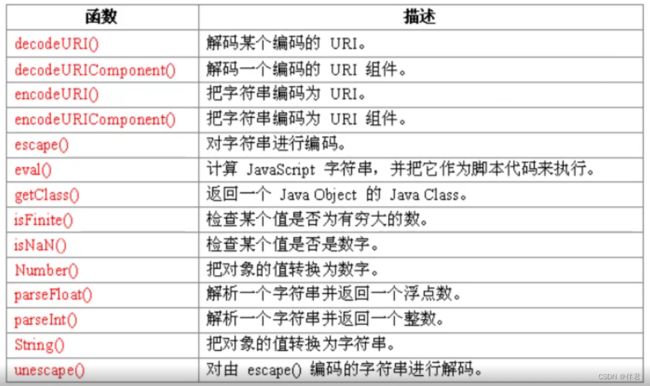
function mymath(arg){
//获取两个文本的内容
var num1 = document.getElementById("num1").value;
var num2 = document.getElementById("num2").value;
if(isNaN(num1) || isNaN(num2)){
alert("请输入数字!");
}
else{
switch(arg){
case 1:
document.getElementById("num3").value = Math.max(num1,num2);
case 2:
document.getElementById("num3").value = Math.min(num1,num2);
case 1:
document.getElementById("num3").value = Number(num1) + Number(num2);
case 1:
document.getElementById("num3").value = Number(num1) - Number(num2);
}
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>简易计算器</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "07_math.js"> </script>
<body>
<div align = "center">
<h2>简易计算器</h2>
<br>
<br>
num1:<input type = "text" id = "num1">
<br>
<br>
num2:<input type = "text" id = "num2">
<br>
<br>
结果:<input type = "text" id = "num3">
<br>
<br>
<input type= "button" value = "最大值" onclick = "mymath(1)">
<input type= "button" value = "最小值" onclick = "mymath(2)">
<input type= "button" value = "加法" onclick = "mymath(3)">
<input type= "button" value = "减法" onclick = "mymath(4)">
</body>
</html>
3.7.5 内部对象(String 类对象)
String对象用于处理文本(字符串)
字符串是Javascript的一种基本的数据类型;
String对象定义了大量操作字符串的方法,例如从字符串中提取字符或子串,或者检索字符等常用方法;
常用方法:
chatAt()返回在指定位置的字符;
indexOf()检索字符串;
substr()从起始索引号提取字符串中指定数目的字符串
substring()提取字符串中两个指定的索引号之间的字符串。
//08_string.js
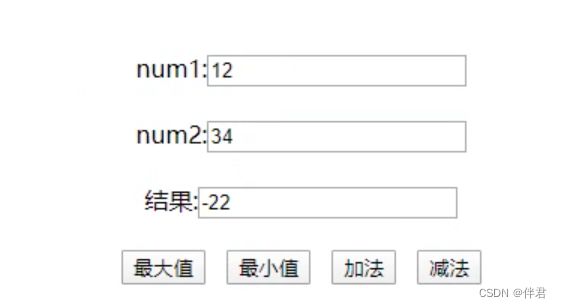
function deal_string(deal_num){
var src = document.getElementById("src").value;
var way = document.getElementById("way").value;
var dest; //存储处理结果
switch(deal_num){
case 1:
dest = src.charAt(Number(way)); //返回在指定位置的字符
break;
case 2:
dest = src.indexOf(way); //lastIndexOf()从后向前搜索
case 3:
// src.substr(start,length)
var start = way.substr(0,1);
var length = way.substr(1,2);
dest = src.substr(Number(start),Number(length));
break;
case 4:
// src.substring(start,stop)
var start = way.substring(0,1);
var stop = way.substring(2);
dest = src.substring(Number(start),Number(stop));
}
document.getElementById("dest").value = dest; //显示结果
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>String对象</title>
</head>
<script text = "text/javascript" src = "08_string.js"> </script>
<body>
原字符串:<input type = "text" id = "src" size = 50>
<br>
<br>
处理方式:<input type = "text" id = "way" size = 50>
<br>
<br>
得到结果:<input type = "text" id = "dest" size = 50>
<br>
<br>
<input type = "button" value = "1.返回指定位置字符" onclick = "deal_string(1)">
<input type = "button" value = "2.检索字符串" onclick = "deal_string(2)">
<br>
<input type = "button" value = "3.从起始索引号提取字符串中指定数目的字符" onclick = "deal_string(3)">
<br>
<input type = "button" value = "4.提取字符串中介于两个指定下标之间的字符" onclick = "deal_string(4)">
</body>
</html>
3.7.6 其他对象
//09_other.js
var str = "成功人士
专家正在讲课:什么是成功人士你们知道吗?
成功人士就是:"
var index = 0;
var time;
function printer(){
if(index == str.length){
clearInterval(timer);
}
else{
document.getElementById("content").innerHTML = str.substring(0,index);
index++;
}
}
function start_printer(){
timer = setInterval("printer",100);
}
<html>
<head>
<title>打印机</title>
</head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "09_other.js"> </script>
<body onload = "start_printer()">
<div id = "content" style = "text-align:center;font-size:20px;"></div>
</body>
</html>