【Python】python matplotlib 图像配色方案【转载】
原文链接:https://matplotlib.org/examples/color/colormaps_reference.html
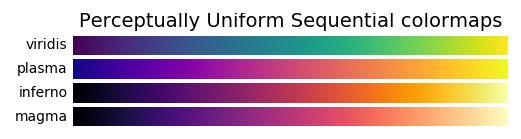
Perceptually Uniform Sequential
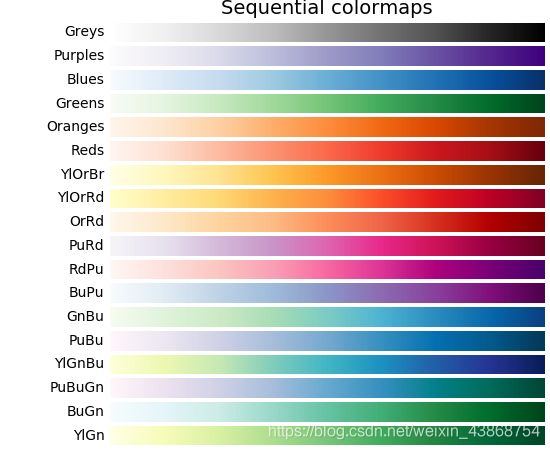
Sequential
["Greys", "Purples", "Blues", "Greens", "Oranges", "Reds", "YlOrBr", "YlOrRd", "OrRd", "PuRd", "RdPu", "BuPu", "GnBu", "PuBu", "YlGnBu", "PuBuGn", "BuGn", "YlGn"]
Sequential (2)
["binary", "gist_yarg", "gist_gray", "gray", "bone", "pink", "spring", "summer", "autumn", "winter", "cool", "Wistia", "hot", "afmhot", "gist_heat", "copper"]

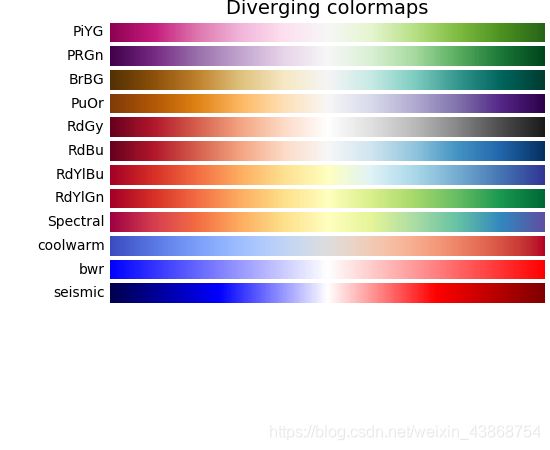
Diverging
["PiYG", "PRGn", "BrBG", "PuOr", "RdGy", "RdBu", "RdYlBu", "RdYlGn", "Spectral", "coolwarm", "bwr", "seismic"]
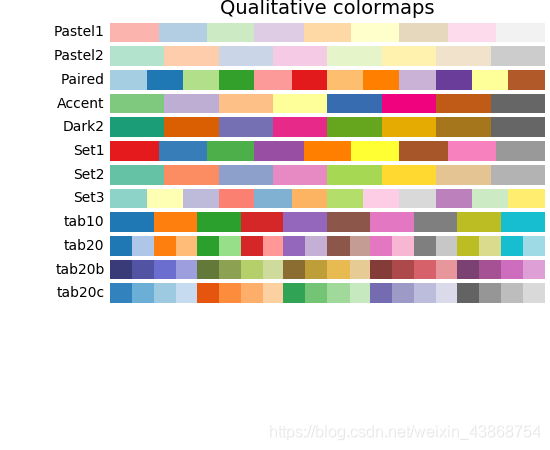
Qualitative
["Pastel1", "Pastel2", "Paired", "Accent", "Dark2", "Set1", "Set2", "Set3", "tab10", "tab20", "tab20b", "tab20c"]
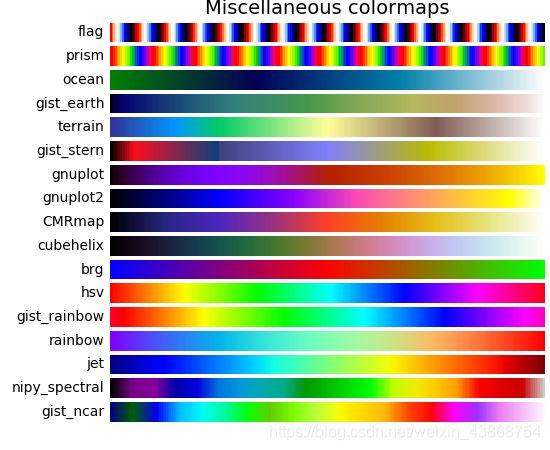
Miscellaneous
["flag", "prism", "ocean", "gist_earth", "terrain", "gist_stern", "gnuplot", "gnuplot2", "CMRmap", "cubehelix", "brg", "hsv", "gist_rainbow", "rainbow", "jet", "nipy_spectral", "gist_ncar"]
Soruce code
"""
==================
Colormap reference
==================
Reference for colormaps included with Matplotlib.
This reference example shows all colormaps included with Matplotlib. Note that
any colormap listed here can be reversed by appending "_r" (e.g., "pink_r").
These colormaps are divided into the following categories:
Sequential:
These colormaps are approximately monochromatic colormaps varying smoothly
between two color tones---usually from low saturation (e.g. white) to high
saturation (e.g. a bright blue). Sequential colormaps are ideal for
representing most scientific data since they show a clear progression from
low-to-high values.
Diverging:
These colormaps have a median value (usually light in color) and vary
smoothly to two different color tones at high and low values. Diverging
colormaps are ideal when your data has a median value that is significant
(e.g. 0, such that positive and negative values are represented by
different colors of the colormap).
Qualitative:
These colormaps vary rapidly in color. Qualitative colormaps are useful for
choosing a set of discrete colors. For example::
color_list = plt.cm.Set3(np.linspace(0, 1, 12))
gives a list of RGB colors that are good for plotting a series of lines on
a dark background.
Miscellaneous:
Colormaps that don"t fit into the categories above.
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Have colormaps separated into categories:
# http://matplotlib.org/examples/color/colormaps_reference.html
cmaps = [("Perceptually Uniform Sequential", [
"viridis", "plasma", "inferno", "magma"]),
("Sequential", [
"Greys", "Purples", "Blues", "Greens", "Oranges", "Reds",
"YlOrBr", "YlOrRd", "OrRd", "PuRd", "RdPu", "BuPu",
"GnBu", "PuBu", "YlGnBu", "PuBuGn", "BuGn", "YlGn"]),
("Sequential (2)", [
"binary", "gist_yarg", "gist_gray", "gray", "bone", "pink",
"spring", "summer", "autumn", "winter", "cool", "Wistia",
"hot", "afmhot", "gist_heat", "copper"]),
("Diverging", [
"PiYG", "PRGn", "BrBG", "PuOr", "RdGy", "RdBu",
"RdYlBu", "RdYlGn", "Spectral", "coolwarm", "bwr", "seismic"]),
("Qualitative", [
"Pastel1", "Pastel2", "Paired", "Accent",
"Dark2", "Set1", "Set2", "Set3",
"tab10", "tab20", "tab20b", "tab20c"]),
("Miscellaneous", [
"flag", "prism", "ocean", "gist_earth", "terrain", "gist_stern",
"gnuplot", "gnuplot2", "CMRmap", "cubehelix", "brg", "hsv",
"gist_rainbow", "rainbow", "jet", "nipy_spectral", "gist_ncar"])]
nrows = max(len(cmap_list) for cmap_category, cmap_list in cmaps)
gradient = np.linspace(0, 1, 256)
gradient = np.vstack((gradient, gradient))
def plot_color_gradients(cmap_category, cmap_list, nrows):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=nrows)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0.01, left=0.2, right=0.99)
axes[0].set_title(cmap_category + " colormaps", fontsize=14)
for ax, name in zip(axes, cmap_list):
ax.imshow(gradient, aspect="auto", cmap=plt.get_cmap(name))
pos = list(ax.get_position().bounds)
x_text = pos[0] - 0.01
y_text = pos[1] + pos[3]/2.
fig.text(x_text, y_text, name, va="center", ha="right", fontsize=10)
# Turn off *all* ticks & spines, not just the ones with colormaps.
for ax in axes:
ax.set_axis_off()
for cmap_category, cmap_list in cmaps:
plot_color_gradients(cmap_category, cmap_list, nrows)
plt.show()