软件设计模式与体系结构实验——3.2-1、3.2-2适配器模式的应用
链接: 软件设计模式与体系结构实验——2.1-1(2)(抽象)工厂模式的应用
链接: 软件设计模式与体系结构实验——2.2-1生成器模式的应用
链接: 软件设计模式与体系结构实验——2.3-1单列模式的应用
链接: 软件设计模式与体系结构实验——3.1-1组合模式的应用
3.2-1、3.2-2适配器模式的应用
- 一、适配器模式-3.2-1客户信息验证
-
- 1. 实验目的
- 2. 实验内容
- 3. 模式UML图
- 4. 模式添加代码(JAVA语言实现)
- 5. 运行结果
- 6. 整体代码
- (1)AdapterTestGUI
- (2)CusInfoValidator
- (3)InformationAdapter
- (4)InfoValidation
- 7. 实验小结
- 二、适配器模式-3.2-2邮编检验
-
- 1. 实验目的
- 2. 实验内容
- 3. 模式UML图
- 4. 模式添加代码(JAVA语言实现)
- 5. 运行结果
- 6. 实验小结
一、适配器模式-3.2-1客户信息验证
1. 实验目的
- 掌握适配器模式的特点
- 分析具体问题,使用适配器模式进行设计。
2. 实验内容
【作业3.2-1】关于例3.7的用于验证客户信息的离架产品类CusInfo Validation的功能扩展问题。要求使用适配器模式。详细要求参见光盘的响应作业部分。
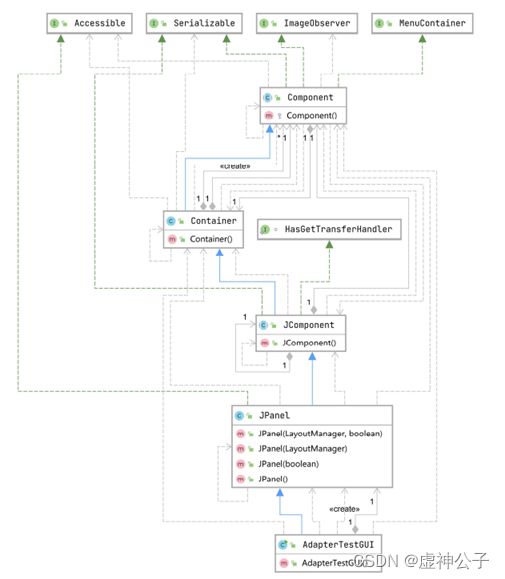
3. 模式UML图
4. 模式添加代码(JAVA语言实现)
CusInfoValidator类:
public abstract boolean isValidEmailAddr(String EmailAddr);
AdapterTestGUI类:
private JTextField txtCustomerName, txtAddress,
txtZip,txtCellPhone, txtSSN,txtEmailAddr;
private JLabel lblCustomerName, lblAddress,
lblZip, lblCellphone, lblSSN,lblEmailAddr;
txtEmailAddr=new JTextField(20);
lblEmailAddr= new JLabel("EmailAddr :");
UIPanel.add(lblEmailAddr);
UIPanel.add(txtEmailAddr);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 5;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblEmailAddr, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 5;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtEmailAddr, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 6;
public String getEmailAddr(){
return txtEmailAddr.getText();
}
String emailaddr = getEmailAddr();
if(cusInfo.isValidEmailAddr(emailaddr)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of EmailAddr.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of EmailAddr.");
}
InformationAdapter类:
@Override
public boolean isValidEmailAddr(String EmailAddr) {
boolean isValid=true;
int a=0;
int b=0;
String ns = EmailAddr.trim();
String nStr = ns.replaceAll("\\s{1,}","");
int len = nStr.length();
if ( (((nStr.charAt(0) >='A')&&(nStr.charAt(0)>='Z'))||
((nStr.charAt(0) >='a')&&(nStr.charAt(0) >='z'))) && (len>=5)) {
for(int m=0; m<len; m++){
if((Character.isLetter(nStr.charAt(m))==true)&&
(Character.isDigit(nStr.charAt(m))==true)){
isValid=false;
}
if(nStr.charAt(m)=='@'){
a++;
}
if(nStr.charAt(m)>='0' && nStr.charAt(m)<='9'){
b++;
}
if((m==0)&&(Character.isLetter(nStr.charAt(m))==false)){
isValid=false;
}
}
if(a!=1){
isValid=false;
}
if(b==0){
isValid=false;
}
return isValid;
}
else{
return false;
}
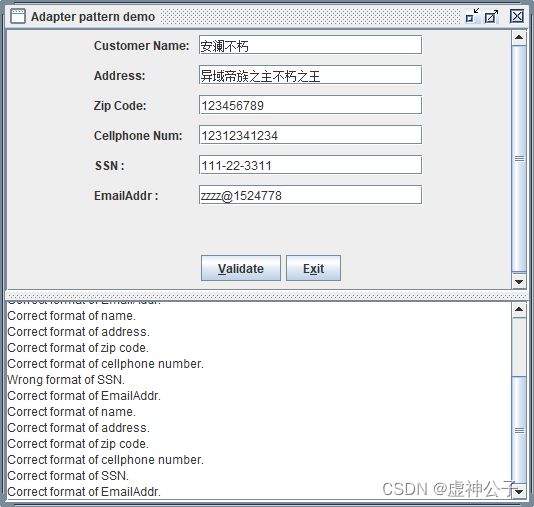
5. 运行结果
6. 整体代码
(1)AdapterTestGUI
package com.glut.xusheng;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class AdapterTestGUI extends JPanel{
private JSplitPane splitPane;
private JScrollPane btnPane,textPane;
private JPanel UIPanel;
private JTextArea dataTextArea;
private JTextField txtCustomerName, txtAddress,
txtZip,txtCellPhone, txtSSN,txtEmailAddr;
private JLabel lblCustomerName, lblAddress,
lblZip, lblCellphone, lblSSN,lblEmailAddr;
public static final String VALIDATE = "Validate";
public static final String EXIT = "Exit";
public AdapterTestGUI(){
super(new GridLayout(1,0));
buildUpScrollGUI();
}
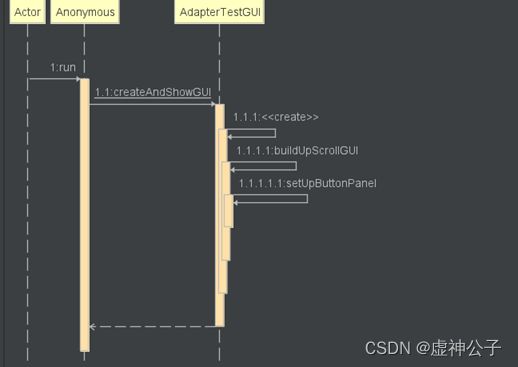
private void buildUpScrollGUI(){
setUpButtonPanel();
dataTextArea = new JTextArea(6, 10);
btnPane = new JScrollPane(UIPanel);
textPane = new JScrollPane(dataTextArea);
splitPane = new JSplitPane(JSplitPane.VERTICAL_SPLIT);
splitPane.setLeftComponent(btnPane);
splitPane.setRightComponent(textPane );
btnPane.setMinimumSize(new Dimension(500, 100));
textPane.setMinimumSize(new Dimension(500, 200));
splitPane.setDividerLocation(230);
splitPane.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(500, 400));
add(splitPane);
setSize(new Dimension(500, 400));
}
private void setUpButtonPanel(){
txtCustomerName = new JTextField(20);
txtAddress = new JTextField(20);
txtZip = new JTextField(20);
txtCellPhone = new JTextField(20);
txtSSN = new JTextField(20);
txtEmailAddr=new JTextField(20);
lblCustomerName = new JLabel("Customer Name:");
lblAddress = new JLabel("Address:");
lblZip = new JLabel("Zip Code:");
lblCellphone = new JLabel("Cellphone Num:");
lblSSN = new JLabel("SSN :");
lblEmailAddr= new JLabel("EmailAddr :");
//Create the open button
JButton validateButton = new JButton(VALIDATE);
validateButton.setMnemonic(KeyEvent.VK_V);
JButton exitButton = new JButton(EXIT);
exitButton.setMnemonic(KeyEvent.VK_X);
ButtonListener objButtonHandler = new ButtonListener();
validateButton.addActionListener(objButtonHandler);
exitButton.addActionListener(objButtonHandler);
UIPanel = new JPanel();
GridBagLayout gridbag = new GridBagLayout();
UIPanel.setLayout(gridbag);
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
UIPanel.add(lblCustomerName);
UIPanel.add(txtCustomerName);
UIPanel.add(lblAddress);
UIPanel.add(txtAddress);
UIPanel.add(lblZip);
UIPanel.add(txtZip);
UIPanel.add(lblCellphone);
UIPanel.add(txtCellPhone);
UIPanel.add(lblSSN);
UIPanel.add(txtSSN);
UIPanel.add(lblEmailAddr);
UIPanel.add(txtEmailAddr);
UIPanel.add(validateButton);
UIPanel.add(exitButton);
gbc.insets.top = 5;
gbc.insets.bottom = 5;
gbc.insets.left = 5;
gbc.insets.right = 5;
gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.WEST;
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblCustomerName, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 0;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtCustomerName, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 1;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblAddress, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 1;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtAddress, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 2;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblZip, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 2;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtZip, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 3;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblCellphone, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 3;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtCellPhone, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 4;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblSSN, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 4;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtSSN, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 5;
gridbag.setConstraints(lblEmailAddr, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 5;
gridbag.setConstraints(txtEmailAddr, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 6;
gbc.insets.left = 2;
gbc.insets.right = 2;
gbc.insets.top = 40;
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.add(validateButton);
buttonPanel.add(exitButton);
UIPanel.add(buttonPanel);
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 6;
gridbag.setConstraints(buttonPanel, gbc);
}
public String getName(){
return txtCustomerName.getText();
}
public String getAddress(){
return txtAddress.getText();
}
public String getZipCode(){
return txtZip.getText();
}
public String getCellNum(){
return txtCellPhone.getText();
}
public String getSSNNum(){
return txtSSN.getText();
}
public String getEmailAddr(){
return txtEmailAddr.getText();
}
class ButtonListener implements ActionListener{
CusInfoValidator cusInfo = new InformationAdapter();
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
if (e.getActionCommand().equals(EXIT)){
System.exit(1);
}
if (e.getActionCommand().equals(VALIDATE)){
String name = getName();
String address = getAddress();
String zip = getZipCode();
String cellNum = getCellNum();
String ssn = getSSNNum();
String emailaddr = getEmailAddr();
if(cusInfo.isValidName(name)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of name.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of name.");
}
if(cusInfo.isValidAddress(address)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of address.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of address.");
}
if(cusInfo.isValidZipCode(zip)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of zip code.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of zip code.");
}
if(cusInfo.isValidCellPhoneNum(cellNum)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of cellphone number.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of cellphone number.");
}
if(cusInfo.isValidSSNNum(ssn)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of SSN.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of SSN.");
}
if(cusInfo.isValidEmailAddr(emailaddr)==false){
dataTextArea.append("\nWrong format of EmailAddr.");
}
else{
dataTextArea.append("\nCorrect format of EmailAddr.");
}
}
}
} // End of class ButtonListener
private static void createAndShowGUI() {
JFrame.setDefaultLookAndFeelDecorated(true);
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Adapter pattern demo");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
AdapterTestGUI newContentPane = new AdapterTestGUI();
newContentPane.setOpaque(true);
frame.setContentPane(newContentPane);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
static public void main(String argv[]) {
javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
createAndShowGUI();
}
});
}
}
(2)CusInfoValidator
package com.glut.xusheng;
/*----------------------------------------------------*/
/* This interface is implemented by class Information */
/* Adapter, which inherits class InfoValidation. */
/*----------------------------------------------------*/
public interface CusInfoValidator{
public abstract boolean isValidName(String name);
public abstract boolean isValidAddress(String address);
public abstract boolean isValidZipCode(String zipCode);
public abstract boolean isValidCellPhoneNum(String phoneNum);
public abstract boolean isValidSSNNum(String SSNNum);
public abstract boolean isValidEmailAddr(String EmailAddr);
}
(3)InformationAdapter
package com.glut.xusheng;
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This adapter class extends InfoValidation and */
/* implements CusInfoValidator, and so the first */
/* 4 functionalities listed in class CusInfoValidator */
/* are automatically inherited from class InfoValidation, */
/* and in this addapter class, isValidSSNNum(String SSNNum)*/
/* is emplemented. */
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
class InformationAdapter extends InfoValidation implements CusInfoValidator{
/*------------------------------------------*/
/* The Social Security number is a 9-digit */
/* number in the format "AAA-GG-SSSS". */
/*------------------------------------------*/
public boolean isValidSSNNum(String SSNNum){
boolean isValid=true;
String ns = SSNNum.trim();
String nStr = ns.replaceAll("\\s{1,}", "");
int len = nStr.length();
if ( (nStr.charAt(3) == '-') && (nStr.charAt(6) == '-') && (len==11) ) {
for(int m=0; m<len; m++){
if( (m != 3) && (m !=6) && ( Character.isDigit(nStr.charAt(m))==false) ){
isValid=false;
}
}
return isValid;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isValidEmailAddr(String EmailAddr) {
boolean isValid=true;
int a=0;
int b=0;
String ns = EmailAddr.trim();
String nStr = ns.replaceAll("\\s{1,}","");
int len = nStr.length();
if ( (((nStr.charAt(0) >='A')&&(nStr.charAt(0)>='Z'))||
((nStr.charAt(0) >='a')&&(nStr.charAt(0) >='z'))) && (len>=5)) {
for(int m=0; m<len; m++){
if((Character.isLetter(nStr.charAt(m))==true)&&
(Character.isDigit(nStr.charAt(m))==true)){
isValid=false;
}
if(nStr.charAt(m)=='@'){
a++;
}
if(nStr.charAt(m)>='0' && nStr.charAt(m)<='9'){
b++;
}
if((m==0)&&(Character.isLetter(nStr.charAt(m))==false)){
isValid=false;
}
}
if(a!=1){
isValid=false;
}
if(b==0){
isValid=false;
}
return isValid;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
(4)InfoValidation
package com.glut.xusheng;
class InfoValidation {
/*----------------------------------------------------*/
/* The name should be at least one character long */
/* and digital numbers should not appear in the names */
/*----------------------------------------------------*/
public boolean isValidName(String name){
boolean isValid=true;
String ns = name.trim();
String nStr = ns.replaceAll("\\b\\s{1,}\\b", "");
int len = nStr.length();
System.out.println("******Length = " + len);
if(len != 0 ){
for(int m=0; m<len; m++){
if(Character.isDigit(nStr.charAt(m))==true)
isValid=false;
}
return isValid;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
/*----------------------------------------------------*/
/* The address should be at least 10 character long */
/*----------------------------------------------------*/
public boolean isValidAddress(String address){
char[] ca = address.trim().toCharArray();
int aLen = ca.length;
if ( aLen < 10 ){
return false;
}
else{
return true;
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
/* The zip code should contain exactly 9 digital integer */
/* numbers. Only digital numbers are allowed in the zip */
/* code. Spaces are allowed in the zip code */
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
public boolean isValidZipCode(String zipCode){
boolean isValid=true;
String ns = zipCode.trim();
String nStr = ns.replaceAll("\\b\\s{1,}\\b", "");
int len = nStr.length();
if (len == 9){
for(int n=0; n<len; n++){
if(Character.isDigit(nStr.charAt(n))==false){
isValid = false;
}
}
return isValid;
}
else{
System.out.println("Length is not 9");
return false;
}
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* The cellPhone number should contain exactly 11 digital */
/* integer numbers. Only digital numbers are allowed in */
/* the zip code.Spaces are allowed in the zip code */
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
public boolean isValidCellPhoneNum(String phoneNum){
boolean isValid=true;
String ns = phoneNum.trim();
String nStr = ns.replaceAll("\\b\\s{1,}\\b", "");
int len = nStr.length();
if (len == 11 ){
for(int n=0; n<len; n++){
if(Character.isDigit(nStr.charAt(n))==false){
isValid = false;
}
}
return isValid;
}
else{
System.out.println("Length is not 11");
return false;
}
}
}// end of class
7. 实验小结
适配器模式
适配器模式(Adapter Pattern):将一个接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,使接口不兼容的那些类可以一起工作,其别名为包装器(Wrapper)。适配器模式既可以作为类结构型模式,也可以作为对象结构型模式。
在适配器模式中,我们通过增加一个新的适配器类来解决接口不兼容的问题,使得原本没有任何关系的类可以协同工作。
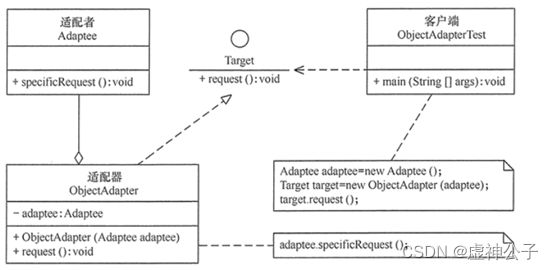
根据适配器类与适配者类的关系不同,适配器模式可分为对象适配器和类适配器两种,在对象适配器模式中,适配器与适配者之间是关联关系;在类适配器模式中,适配器与适配者之间是继承(或实现)关系。
角色
Target(目标抽象类):目标抽象类定义客户所需接口,可以是一个抽象类或接口,也可以是具体类。
Adapter(适配器类):适配器可以调用另一个接口,作为一个转换器,对Adaptee和Target进行适配,适配器类是适配器模式的核心,在对象适配器中,它通过继承Target并关联一个Adaptee对象使二者产生联系。
Adaptee(适配者类):适配者即被适配的角色,它定义了一个已经存在的接口,这个接口需要适配,适配者类一般是一个具体类,包含了客户希望使用的业务方法,在某些情况下可能没有适配者类的源代码。
二、适配器模式-3.2-2邮编检验
1. 实验目的
- 掌握适配器模式的特点
- 分析具体问题,使用适配器模式进行设计。
2. 实验内容
【作业3.2-2】关于邮政编码检验系统的功能扩展问题。要求使用对象适配器模式,具体问题描述与设计类图详见光盘中3.2节附加列3.1以及相应作业的描述文档。
3. 模式UML图
4. 模式添加代码(JAVA语言实现)
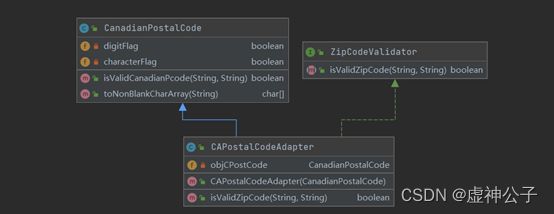
题目:理解下面的类图。除了类ChinesePostalCode和ChinesePostalCodeAdapter的代码之外,所有使用Java对象适配器模式的源代码都已经给你了。
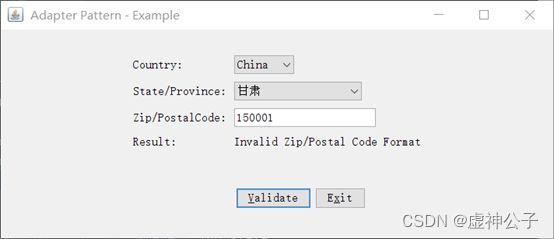
(1)编写类ChinesePostalCode的代码,其中编写方法的代码是validichinesepcode(pcode:String)。中国邮政编码的正确格式有类似150001的格式,即6位数字。
package com.glut.xusheng;
public class ChinesePostalCode {
private boolean digitFlag = true;
private boolean characterFlag = true;
/*=======================================================*/
/* Canadian postal code has the form CDC DCD, where */
/* C is an English character and D is any digit from */
/* 0 to 9. A space is required after the 3rd character, */
/* but this is not checked in this program. And any */
/* number of spaces is allowed in the user input postal */
/* code. */
/*=======================================================*/
public boolean isValidZipCode(String postalCode, String province) {
char[] pCode = toNonBlankCharArray(postalCode);
if (pCode.length != 6)
return false;
for(int i=0; i<pCode.length/2; i++){
if( Character.isLetter(pCode[2*i]) == false)
characterFlag = false;
if(Character.isDigit(pCode[2*i+1]) == false)
digitFlag = false;
}
if ( (digitFlag == false) || (characterFlag==false))
return false;
else
return true;
}
/*====================================================*/
/* Get rid of all the spaces from the user input */
/*====================================================*/
public char[] toNonBlankCharArray(String postalCode){
int m=0;
for (int k=0;k<postalCode.length(); k++){
if (Character.isSpaceChar(postalCode.charAt(k)) == false ){
m++;
}
}
char[] p = new char[m];
int n = 0;
for (int k=0;k<postalCode.length(); k++){
if (Character.isSpaceChar(postalCode.charAt(k)) == false ){
p[n] = postalCode.charAt(k);
n++;
}
}
return p;
}
}
(2)然后为类ChinesePostalCodeAdapter编写代码。
package com.glut.xusheng;
public class ChinesePostalCodeAdapter extends ChinesePostalCode implements ZipCodeValidator {
private ChinesePostalCode objCPostCode;
public ChinesePostalCodeAdapter(ChinesePostalCode pCode) {
objCPostCode = pCode;
}
public boolean isValidZipCode(String zip, String state) {
return isValidZipCode(zip, state);
}
}// end of class
(3)如果需要,在ZipCodeTester类中添加一些代码,使该程序适用于所有美国邮政编码、加拿大邮政编码和中国邮政编码。
Customer类:
if (country.equals(Customer.CHINA)) {
ChinesePostalCode chinesePostalCode = new ChinesePostalCode();
return chinesePostalCode.isValidZipCode(zip, state);
}
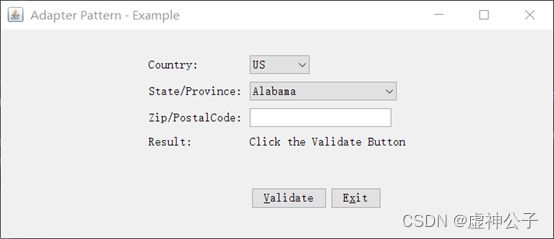
5. 运行结果
6. 实验小结
适配器模式总结
1.主要优点:
(1)将目标类和适配者类解耦,通过引入一个适配器类来重用现有的适配者类,无须修改原有结构。
(2)增加了类的透明性和复用性,将具体的业务实现过程封装在适配者类中,对于客户端类而言是透明的,而且提高了适配者的复用性,同一个适配者类可以在多个不同的系统中复用。
(3)灵活性和扩展性都非常好,通过使用配置文件,可以很方便地更换适配器,也可以在不修改原有代码的基础上增加新的适配器类,完全符合“开闭原则”。
具体来说,类适配器模式还有如下优点: 由于适配器类是适配者类的子类,因此可以在适配器类中置换一些适配者的方法,使得适配器的灵活性更强。
对象适配器模式还有如下优点: 一个对象适配器可以把多个不同的适配者适配到同一个目标;
可以适配一个适配者的子类,由于适配器和适配者之间是关联关系,根据“里氏代换原则”,适配者的子类也可通过该适配器进行适配。
类适配器模式的缺点如下: 对于Java、C#等不支持多重类继承的语言,一次最多只能适配一个适配者类,不能同时适配多个适配者;
适配者类不能为最终类,如在Java中不能为final类,C#中不能为sealed类;
在Java、C#等语言中,类适配器模式中的目标抽象类只能为接口,不能为类,其使用有一定的局限性。
对象适配器模式的缺点如下:
与类适配器模式相比,要在适配器中置换适配者类的某些方法比较麻烦。如果一定要置换掉适配者类的一个或多个方法,可以先做一个适配者类的子类,将适配者类的方法置换掉,然后再把适配者类的子类当做真正的适配者进行适配,实现过程较为复杂。
2.适用场景:
系统需要使用一些现有的类,而这些类的接口(如方法名)不符合系统的需要,甚至没有这些类的源代码。
想创建一个可以重复使用的类,用于与一些彼此之间没有太大关联的一些类,包括一些可能在将来引进的类一起工作。
3.模式的结构与实现
类适配器模式可采用多重继承方式实现,如 C++ 可定义一个适配器类来同时继承当前系统的业务接口和现有组件库中已经存在的组件接口; Java 不支持多继承,但可以定义一个适配器类来实现当前系统的业务接口,同时又继承现有组件库中已经存在的组件。
对象适配器模式可釆用将现有组件库中已经实现的组件引入适配器类中,该类同时实现当前系统的业务接口。现在来介绍它们的基本结构。
- 模式的结构
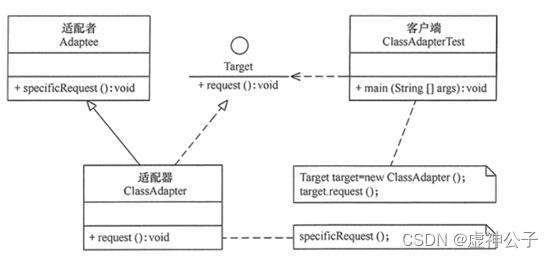
适配器模式(Adapter)包含以下主要角色。 - 目标(Target)接口:当前系统业务所期待的接口,它可以是抽象类或接口。
- 适配者(Adaptee)类:它是被访问和适配的现存组件库中的组件接口。
- 适配器(Adapter)类:它是一个转换器,通过继承或引用适配者的对象,把适配者接口转换成目标接口,让客户按目标接口的格式访问适配者。
类适配器模式的结构图如图 所示: