SpringBoot核心配置文件
SpringBoot核心配置文件
配置文件的名称必须是application
扩展名有两种分别为 .properties(key=value形式)和.yml(key:value)
使用application.properties
#设置端口号
server.port=8081
#设置访问应用的上下文路径
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
视图层
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class BootController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String doSome() {
return "SpringBoot应用";
}
}
此时如果我们访问之前的localhost:8081/hello就会404
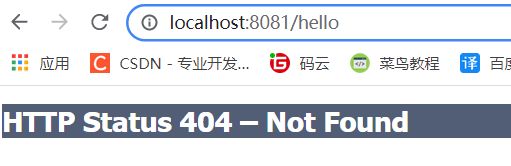
由于在配置文件中配置过了,访问时必须访问localhost:8081/myboot/hello
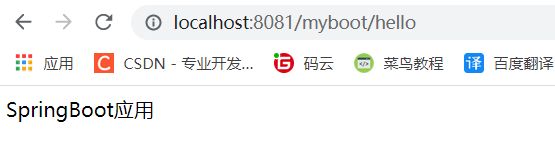
使用application.yml
我们将核心配置文件使用yml的方式创建
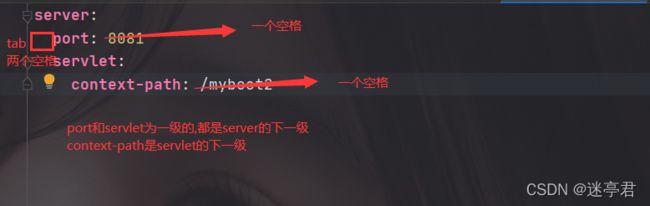
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /myboot2
这个yml和上面properties文件表示的配置一模一样,yml的优势在于结构化表示,层级更分明.
注意 :
- 每次分级都要使用tab或者两个空格
- :后必须使用一个空格在写value
如果一个项目中既有application.properties和application.yml文件,那么properties的优先级高,先生效,但是不建议一个项目中有两种类型的配置文件.
多环境配置
在实际的开发过程中,我们的项目会经历很多的阶段(开发->测试->上线),每个阶段的配置也会有所不同,例如端口号,上下文根,数据库信息等,那么这个时候为了方便在不同的环境之间切换,SpringBoot提供了多环境配置.
具体步骤如下 :
- 先创建多个配置文件,命名的规则为application-环境名称.properties(.yml)
例如开发环境 : application-dev.properties
测试环境 : application-test.properties - 在核心配置文件application.properties(.yml)指定当前需要使用哪个环境的配置文件
具体例子如下 :
文件结构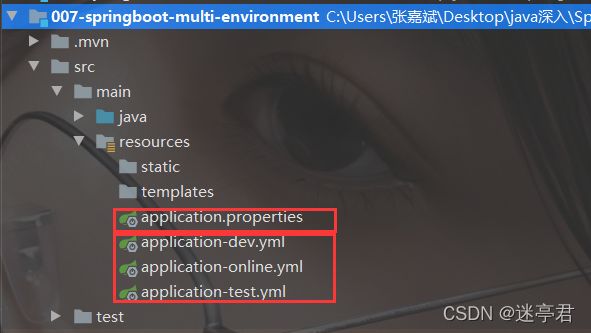
以测试的配置文件为例application-test.yml
#开发环境配置文件
server:
port: 9001
servlet:
context-path: /mytest
然后再核心配置文件中指定使用的文件application.properties
#因为会先读取这个文件,所以我们在这个文件中告诉springboot读取那个文件
#即激活使用哪一个配置文件
#激活application-test的配置文件
spring.profiles.active=test
此时我们指定的就是测试的环境,访问的url为 http://localhost:9001/mytest/hello
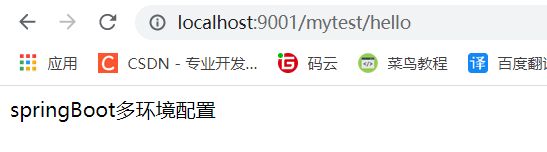
SpringBoot自定义配置
将一些内容写进application.properties文件中,我们就可以从文件中获取
@Value
直接给出例子 : 我们在application.properties中配置了如下键值对
#自定义key=value
school.name=SUST
school.website=www.baidu.com
school.address=西安市
site=www.baidu.com
我们在某处就可以使用@Value获取到
这里是在controller层中获取
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${server.servlet.context-path}")
private String contextPath;
@Value("${school.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${school.website}")
private String web;
@Value("${school.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${site}")
private String baidu;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloController{" +
"port=" + port +
", contextPath='" + contextPath + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", web='" + web + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", baidu='" + baidu + '\'' +
'}';
}
@RequestMapping("/data")
@ResponseBody
public String queryData() {
return this.toString();
}
}
当我们使用多配置文件的时候,我们只能获取到正在使用的文件的信息
看下面的例子 : 文件结构如下
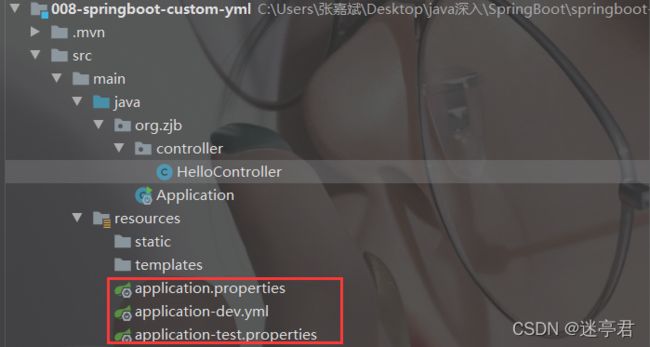
我们的application.properties文件中指定了test环境的配置文件
application.properties
#使用test环境的配置文件
spring.profiles.active=test
#自定义key=value
school.name=SUST
school.website=www.baidu.com
school.address=西安市
site=www.baidu.com
application-dev.yml
#开发环境配置文件
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /mydev
#自定义键值对
dev:
name: 开发
application-test.properties
#配置测试环境
server.port=8081
#配置上下文
server.servlet.context-path=/mytest
#自定义键值对
test.name=test
controller层中获取键值对信息
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${server.servlet.context-path}")
private String contextPath;
@Value("${school.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${school.website}")
private String web;
@Value("${school.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${site}")
private String baidu;
@Value("${test.name}")
private String testName;
// @Value("${dev.name}")
// private String devName;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloController{" +
"port=" + port +
", contextPath='" + contextPath + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", web='" + web + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", baidu='" + baidu + '\'' +
", testName='" + testName + '\'' +
// ", devName='" + devName + '\'' +
'}';
}
@RequestMapping("/data")
@ResponseBody
public String queryData() {
return this.toString();
}
}
访问url得到结果
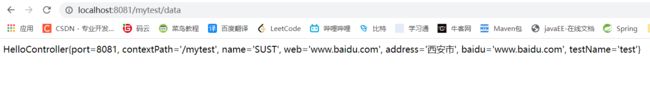
可以看到,我们可以访问到test.name,这是因为我们的核心配置文件加载到了test的配置文件,所以才可以读取只属于这个文件中的信息,而dev没有被加载,dev.name注入时会失败.
@ConfigurationProperties
前面我们获取信息是一条一条获取的,我们能否使用一个对象接受对应的信息?这就可以使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
直接给出例子 :
文件结构如下 :
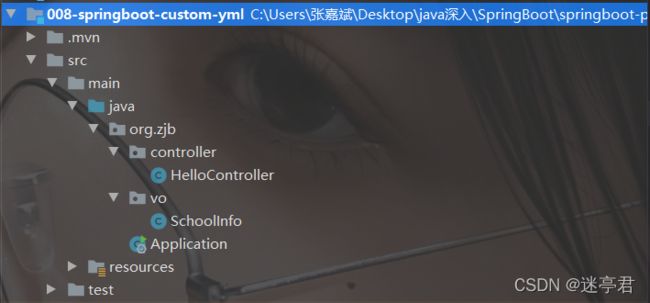
application.properties文件内容如下 :
#配置URl
server.port=8081
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
#自定义key=value
school.name=SUST
school.website=www.baidu.com
school.address=西安市
我们将这些school开头的信息注入到一个对象中
SchoolInfo类信息如下 :
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
public class SchoolInfo {
private String name;
private String website;
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SchoolInfo{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", website='" + website + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getWebsite() {
return website;
}
public void setWebsite(String website) {
this.website = website;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
在这个实体类中使用了@ConfigurationProperties注解
这个注解的prefix属性就是指前缀,框架会为我们自动识别前缀为"school"的键值对,注入到实体类SchoolInfo的成员中,匹配的规则为前缀相同,配置文件中的key和成员的名称相同则注入,在这个类上方我们还需使用注解创建对象,这里使用的是@Component创建对象,并且将对象放入容器中,我们就可以在别的地方取出这对象了.
controller类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.zjb.vo.SchoolInfo;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Resource
private SchoolInfo schoolInfo;
@RequestMapping("/info")
@ResponseBody
public String queryInfo() {
return schoolInfo.toString();
}
}
这个controller中的schoolInfo属性上使用了@Resource注解完成赋值,先在容器中寻找和该属性名相同的bean的id,找不到在找相同类型的进行赋值.
访问页面得到如下结果 :
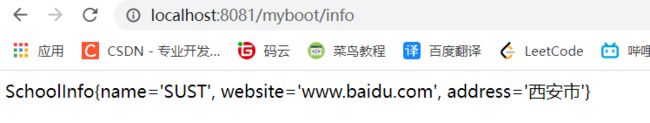
SpringBoot中使用jsp
首先强调一点是springboot并不推荐使用jsp,默认框架也不支持使用jsp,需要经过一些配置才能使用jsp,现在已经使用模板技术替代jsp.
使用jsp需要做哪些处理?
- 加入一个处理jsp的依赖,负责编译jsp文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasperartifactId>
dependency>
- 如果需要使用servlet,jsp或者jstl等功能需要加对应的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-apiartifactId>
<version>2.3.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>jstlartifactId>
dependency>
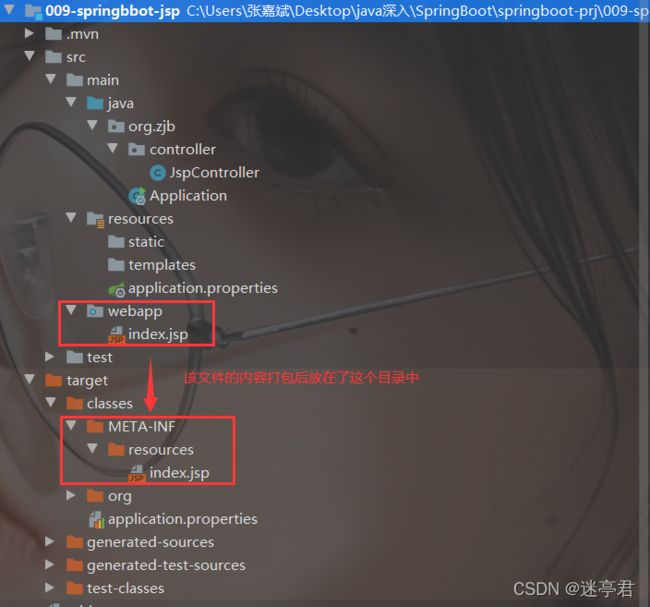
- 创建一个存放jsp的目录,一般叫做webapp
将这个webapp目录放在存放目录main文件下,之后这个将这个文件的性质改变才能创建jsp
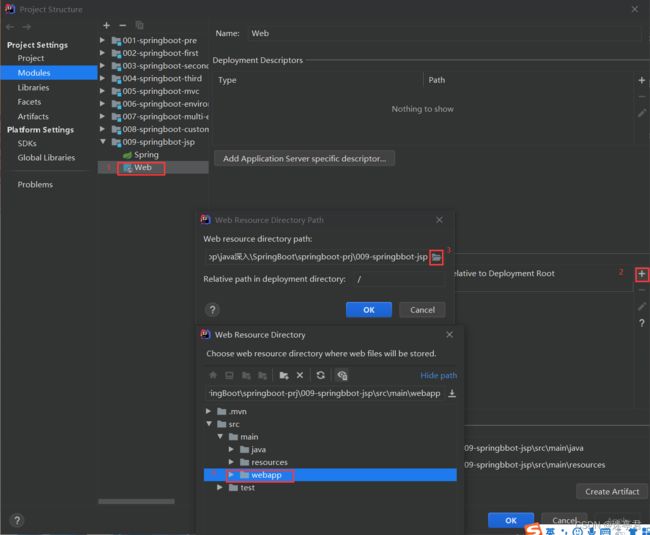
之后这个webapp就变成了一个小蓝点的文件,如下
- 需要在pom.xml文件中指定jsp文件编译后的目录
META-INF/resources - 创建Controller,范文jsp
- 在application.properties文件中配置视图解析器
下面给出一个具体的小例子
- 加入对应依赖和指定jsp编译后存放的目录
pom.xml文件如下
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.4.2version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>org.zjbgroupId>
<artifactId>009-springbbot-jspartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasperartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/webappdirectory>
<targetPath>META-INF/resourcestargetPath>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*include>
includes>
resource>
resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
- 加入webapp目录并编写jsp文件
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
jsp
使用jsp显示Controller中的数据 ${data}
- 编写controller视图层
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller
public class JspController {
// public String doJsp(HttpServletRequest request) {
//
// request.setAttribute("data", "Springboot使用JSP");
// // 视图的逻辑名称
// return "index";
// }
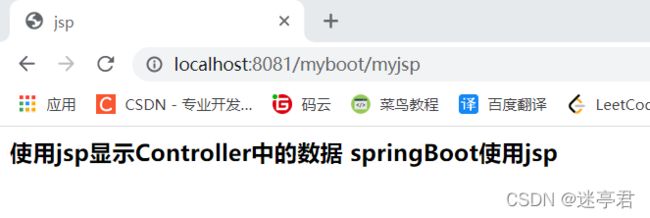
@RequestMapping("/myjsp")
public String doJsp(Model model) {
// 将数据放入到request作用域
model.addAttribute("data", "springBoot使用jsp");
return "index";
}
}
- 在核心配置文件中配置视图解析器
application.properties内容如下:
server.port=8081
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
#配置视图解析器
#配置前缀 /代表src/main/webapp
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
#配置后缀
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
SpringBoot中使用ApplicationContext
想通过代码从容器中获取对象可以使用如下方法:
SpringApplication.run()的返回值获取到容器对象.
点进该方法,
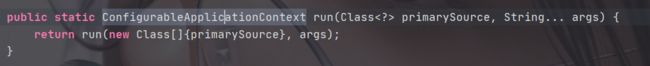
可以看见这个方法的返回值为ConfigurableApplicationContext
这个接口的信息如下:
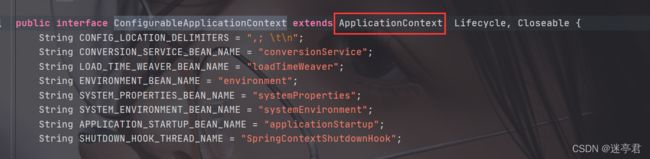
它继承了ApplicationContext容器对象,说明run方法的返回值就是容器对象
我们给出例子:
service接口实现类,使用注解创建对象并注入容器中
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.zjb.service.UserService;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("hello" + name);
}
}
application.java中获取容器对象,并且将其中的bean取出.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.zjb.service.UserService;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
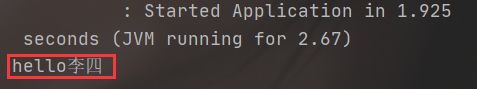
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取容器对象
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
// 从容器中获取对象
UserService userService = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService");
userService.sayHello("李四");
}
}
CommandLineRunner接口和ApplicationRunner接口
这两个接口都有一个run()方法,执行的时间是容器对象创建好后,我们可以依靠这个run方法在容器创建好之后完成一些操作,如数据库对象的赋值等.
例子如下 :
service实现类
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.zjb.service.HelloService;
@Service("helloService")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "你好" + name;
}
}
application.java如下 :
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.zjb.service.HelloService;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Resource
private HelloService helloService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建容器对象
System.out.println("准备创建容器");
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
System.out.println("容器创建后");
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(helloService.sayHello("张三"));
// 可以这里做自定义的操作,比如读取文件,数据库等
System.out.println("在容器对象创建后执行的方法");
}
}
执行代码观察执行顺序,如下 :
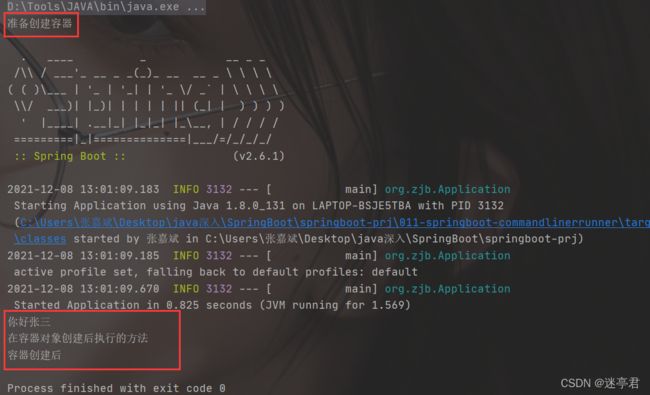
可见容器创建的时候才会执行commandlineRunner的run()方法,同时单例的bean在容器创建之初就已经注入到容器中.
执行的顺序如下
- 先SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args)创建容器
- 注入单例bean
- 执行CommandLineRunner的run()方法
- 执行之后的代码