labelme和coco数据集
目录
1、labelme(Json to Dataset)
2、json转txt原理
2.1. 转txt(不是coco)
2.2. json转coco
1、labelme(Json to Dataset)
labelme标注完了之后生成.json文件,需要用脚本把它转换成coco或者其他txt格式的数据集来使用。本文总结了labelme产生的json文件转化成coco,txt和yolo三种方法。
下面是labelme安装教程,这里作者给出了json_to_dataset.py方法,但是不是转化成coco格式的,下面是原文章:
Labelme安装及使用教程_志愿无倦的博客-CSDN博客_labelme安装
靠谱的博客:(一站式解决普通labelme中json到coco,上次用分割方式标的数据集转化成功了)
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39435411/article/details/120776118?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522164103107516780366532500%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334..%2522%257D&request_id=164103107516780366532500&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~top_positive~default-1-120776118.first_rank_v2_pc_rank_v29&utm_term=labelme%E8%BD%ACcoco&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
2、json转txt原理
2.1. 转txt(不是coco)
目的:将labelme标注的json文件中的坐标和label信息提取到txt文件中
注意:labelme标注时使用“polygon”即画点标注方式,不是“rectangle”和“circle”标注方式,每个点坐标包括x和y,所以总共输出8个坐标值和1个label值
json格式
{
"version": "4.6.0",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "B4",
"points": [
[
157.25806451612902,
639.516129032258
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "B4",
"points": [
[
156.0483870967742,
689.1129032258065
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "B4",
"points": [
[
278.6290322580645,
683.0645161290323
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "B4",
"points": [
[
275.80645161290323,
634.6774193548387
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
}
],
"imagePath": "4496.jpg",
"imageData": "/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD",
"imageHeight": 1024,
"imageWidth": 1280
}批量转换:
dir_json为json文件夹
dir_txt为txt文件夹
同级目录下创建json2txt.py文件,文件内容复制如下
# coding:utf-8
import os
import json
import numpy as np
def json2txt(path_json,path_txt):
with open(path_json,'r', encoding='gb18030') as path_json:
jsonx=json.load(path_json)
with open(path_txt,'w+') as ftxt:
for shape in jsonx['shapes']: # shapes里面放的是标签的数据,比如四个点的类别和坐标
xy=np.array(shape['points'])# shapes里面的points是点的x,y坐标
label=str(shape['label']) # 类别信息
strxy = ''
for m,n in xy:
strxy+=str(m)+','+str(n)+','
strxy+=label
ftxt.writelines(strxy+"\n")
dir_json = 'json/'
dir_txt = 'txt/'
if not os.path.exists(dir_txt):
os.makedirs(dir_txt)
list_json = os.listdir(dir_json)
for cnt,json_name in enumerate(list_json):
print('cnt=%d,name=%s'%(cnt,json_name))
path_json = dir_json + json_name
path_txt = dir_txt + json_name.replace('.json','.txt')
# print(path_json, path_txt)
json2txt(path_json, path_txt)
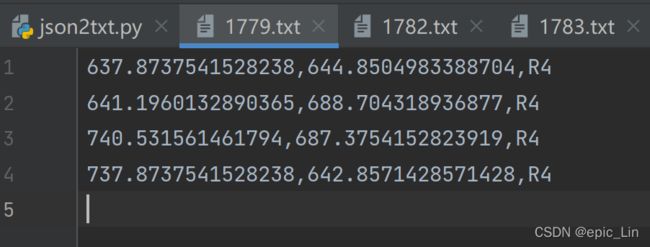
txt文件输出示例
这个格式不是coco格式,coco格式如下:
2.2. json转coco
# 命令行执行: python labelme2coco.py --input_dir images --output_dir coco --labels labels.txt
# 输出文件夹必须为空文件夹
import argparse
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import uuid
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
try:
import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:
print("Please install pycocotools:\n\n pip install pycocotools\n")
sys.exit(1)
def to_coco(args,label_files,train):
# 创建 总标签data
now = datetime.datetime.now()
data = dict(
info=dict(
description=None,
url=None,
version=None,
year=now.year,
contributor=None,
date_created=now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"),
),
licenses=[dict(url=None, id=0, name=None,)],
images=[
# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id
],
type="instances",
annotations=[
# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id
],
categories=[
# supercategory, id, name
],
)
# 创建一个 {类名 : id} 的字典,并保存到 总标签data 字典中。
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip() # strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__" # background:0, class1:1, ,,
continue
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
data["categories"].append(
dict(supercategory=None, id=class_id, name=class_name,)
)
if train:
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations","instances_train2017.json")
else:
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations","instances_val2017.json")
for image_id, filename in enumerate(label_files):
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0] # 文件名不带后缀
if train:
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "train2017", base + ".jpg")
else:
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "val2017", base + ".jpg")
print("| ",out_img_file)
# ************************** 对图片的处理开始 *******************************************
# 将标签文件对应的图片进行保存到对应的 文件夹。train保存到 train2017/ test保存到 val2017/
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData) # .json文件中包含图像,用函数提出来
imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img) # 将图像保存到输出路径
# ************************** 对图片的处理结束 *******************************************
# ************************** 对标签的处理开始 *******************************************
data["images"].append(
dict(
license=0,
url=None,
file_name=osp.relpath(out_img_file, osp.dirname(out_ann_file)),
# out_img_file = "/coco/train2017/1.jpg"
# out_ann_file = "/coco/annotations/annotations_train2017.json"
# osp.dirname(out_ann_file) = "/coco/annotations"
# file_name = ..\train2017\1.jpg out_ann_file文件所在目录下 找 out_img_file 的相对路径
height=img.shape[0],
width=img.shape[1],
date_captured=None,
id=image_id,
)
)
masks = {} # for area
segmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentation
for shape in label_file.shapes:
points = shape["points"]
label = shape["label"]
group_id = shape.get("group_id")
shape_type = shape.get("shape_type", "polygon")
mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(
img.shape[:2], points, shape_type
)
if group_id is None:
group_id = uuid.uuid1()
instance = (label, group_id)
if instance in masks:
masks[instance] = masks[instance] | mask
else:
masks[instance] = mask
if shape_type == "rectangle":
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
x1, x2 = sorted([x1, x2])
y1, y2 = sorted([y1, y2])
points = [x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]
else:
points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()
segmentations[instance].append(points)
segmentations = dict(segmentations)
for instance, mask in masks.items():
cls_name, group_id = instance
if cls_name not in class_name_to_id:
continue
cls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]
mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)
area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))
bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()
data["annotations"].append(
dict(
id=len(data["annotations"]),
image_id=image_id,
category_id=cls_id,
segmentation=segmentations[instance],
area=area,
bbox=bbox,
iscrowd=0,
)
)
# ************************** 对标签的处理结束 *******************************************
# ************************** 可视化的处理开始 *******************************************
if not args.noviz:
labels, captions, masks = zip(
*[
(class_name_to_id[cnm], cnm, msk)
for (cnm, gid), msk in masks.items()
if cnm in class_name_to_id
]
)
viz = imgviz.instances2rgb(
image=img,
labels=labels,
masks=masks,
captions=captions,
font_size=15,
line_width=2,
)
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "visualization", base + ".jpg"
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
# ************************** 可视化的处理结束 *******************************************
with open(out_ann_file, "w") as f: # 将每个标签文件汇总成data后,保存总标签data文件
json.dump(data, f)
# 主程序执行
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument("--input_dir", help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", help="labels file", required=True)
parser.add_argument("--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true")
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
print("| Creating dataset dir:", args.output_dir)
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "visualization"))
# 创建保存的文件夹
if not os.path.exists(osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations")):
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations"))
if not os.path.exists(osp.join(args.output_dir, "train2017")):
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "train2017"))
if not os.path.exists(osp.join(args.output_dir, "val2017")):
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "val2017"))
# 获取目录下所有的.jpg文件列表
feature_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.jpg"))
print('| Image number: ', len(feature_files))
# 获取目录下所有的joson文件列表
label_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json"))
print('| Json number: ', len(label_files))
# feature_files:待划分的样本特征集合 label_files:待划分的样本标签集合 test_size:测试集所占比例
# x_train:划分出的训练集特征 x_test:划分出的测试集特征 y_train:划分出的训练集标签 y_test:划分出的测试集标签
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(feature_files, label_files, test_size=0.3)
print("| Train number:", len(y_train), '\t Value number:', len(y_test))
# 把训练集标签转化为COCO的格式,并将标签对应的图片保存到目录 /train2017/
print("—"*50)
print("| Train images:")
to_coco(args,y_train,train=True)
# 把测试集标签转化为COCO的格式,并将标签对应的图片保存到目录 /val2017/
print("—"*50)
print("| Test images:")
to_coco(args,y_test,train=False)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("—"*50)
main()
print("—"*50)CRT的labels.txt:
__ignore__
_background_
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
BO
Bs
Bb
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
RO
Rs
Rb
Drone在labelme2coco.py文件的目录下,打开命令行执行:
python labelme2coco.py --input_dir data --output_dir coco --labels labels.txt3、 json转yolo(附代码)
3.1. labelme分割格式(polygon)转yolo代码
# coding:utf-8
import os
import cv2 as cv2
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""
1. One row per object
2. Each row is class x_center y_center width height format.
3. Box coordinates must be in normalized xywh format (from 0 - 1).
If your boxes are in pixels, divide x_center and width by image width, and y_center and height by image height.
4. Class numbers are zero-indexed (start from 0).
"""
# labelme 中预设的类别名和类别 id 的对应关系
label_idx_map = {"B1": 0, "B2": 1, "B3": 2, "B4": 3, "B5": 4, "BO": 5, "Bs": 6, "Bb": 7,"R1": 8, "R2": 9, "R3": 10, "R4": 11, "R5": 12, "RO": 13, "Rs": 14, "Rb": 15}
color_list = [[200, 0, 0], [0, 200, 0], [0, 0, 200], [200, 200, 0], [0, 200, 200], [200, 0, 200], [0, 0, 0],
[128, 128, 0],[200, 0, 0], [70, 20, 0], [100, 0, 200], [200, 200, 200], [0, 20, 200], [200, 0, 200], [0, 0, 0],
[128, 128, 0]]
def labelme_to_yolo(img_dir, json_dir, save_dir,save_jpg_dir):
name_list = os.listdir(json_dir) # 可以和图片是同一个文件夹
for name in name_list:
if name.endswith('.json'):
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, name.replace(".json", ".txt")) # 创建txt路径
im_path = os.path.join(img_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpg")) # 拼装图片路径
json_path = os.path.join(json_dir, name) # 拼装json路径
if(os.path.exists(im_path)):
im = cv2.imread(im_path) # 读取图片
name_jpg = os.path.join(save_jpg_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpg")) # 保存图片的路径
else:
im_path = os.path.join(img_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpeg")) # 如果找不到jpg,就去找jpeg
im = cv2.imread(im_path) # 读取图片
name_jpg = os.path.join(save_jpg_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpeg")) # 创建保存图片的路径
label_dict = json.load(open(json_path, 'r')) # 读取json文件
height = label_dict["imageHeight"]
width = label_dict["imageWidth"]
loc_info_list = label_dict["shapes"]
label_info_list = list()
for loc_info in loc_info_list:
obj_name = loc_info.get("label")
label_id = label_idx_map.get(obj_name)
# print(label_id)
loc = loc_info.get("points")
x0, y0 = loc[0] # 左上角点
x1, y1 = loc[1] # 左下角点
x2, y2 = loc[2] # 右下角点
x3, y3 = loc[3] # 右上角点
if x2<=x0 or y2<=y0:
print("error:",name)
x_max = max(x0,x1,x2,x3)
x_min = min(x0,x1,x2,x3)
y_max = max(y0,y1,y2,y3)
y_min = min(y0,y1,y2,y3)
cv2.rectangle(im, (int(x_max), int(y_max)), (int(x_min), int(y_min)), color_list[label_id], 2)
cv2.imwrite(name_jpg, im)
x_center = (x_max + x_min) / 2 / width
y_center = (y_max + y_min ) / 2 / height
box_w = (abs(x_max - x_min)) / width
box_h = (abs(y_max - y_min)) / height
x0 = x0 / width
x1 = x1 / width
x2 = x2 / width
x3 = x3 / width
y0 = y0 / height
y1 = y1 / height
y2 = y2 / height
y3 = y3 / height
label_info_list.append([str(label_id), str(x_center), str(y_center), str(box_w), str(box_h),str(x0),str(y0),str(x1),str(y1),str(x2),str(y2),str(x3),str(y3)])
with open(save_path, 'w') as f:
for label_info in label_info_list:
label_str = ' '.join(label_info)
f.write(label_str)
f.write('\n')
# debug
# plt.figure(0)
# plt.imshow(im)
# plt.show()
# print("xxx")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 图像文件夹
image_dir = "4_labeled/4"
# labelme 的标注结果
json_dir = "4_labeled/4"
# yolo 使用的 txt 结果
save_dir = "output_txt"
# yolo 使用的 jpg 结果
save_jpg_dir = "output_jpg"
labelme_to_yolo(image_dir, json_dir, save_dir,save_jpg_dir)
3.2. labelme分割(polygon)和点(points)两种模式区别
对于polygon格式标出的json文件(标签信息主要在"shapes"中),shapes对应一个列表,其中每一个目标是一个字典(比如两个装甲板对应两个字典)。
字典中有labels + points + group_id + shape_type + flags
如"labels" : "R3"
points对应一个列表,有这个目标所有标注点的信息,每个标注点以[x,y]的形式保存
"points" : [ [x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], [x4, y4] ]
"shape_type" : "polygon"
{
"version": "4.6.0",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "R3",
"points": [
[
527.3333333333334,
732.2222222222222
],
[
514.0,
814.4444444444445
],
[
716.8888888888889,
817.3333333333334
],
[
725.7777777777778,
725.1111111111111
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "B5",
"points": [
[
300.0,
727.7777777777778
],
[
294.22222222222223,
802.6666666666666
],
[
470.8888888888889,
800.2222222222222
],
[
471.55555555555554,
714.6666666666666
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {}
}
],
"imagePath": "Pic_2020_10_24_173228_28.jpeg",
"imageData": "/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD",
"imageHeight": 1024,
"imageWidth": 1280
}point格式标注:
shapes中格式和上面一样,points中只存放一个点,几个点shapes中就有几个字典
labels + points + group_id + shape_type + flags
"shape_type" : point
{
"version": "4.6.0",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "R4",
"points": [
[
637.8737541528238,
644.8504983388704
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "R4",
"points": [
[
641.1960132890365,
688.704318936877
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "R4",
"points": [
[
740.531561461794,
687.3754152823919
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
},
{
"label": "R4",
"points": [
[
737.8737541528238,
642.8571428571428
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "point",
"flags": {}
}
],
"imagePath": "1779.jpg",
"imageData": "/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/Ha",
"imageHeight": 1024,
"imageWidth": 1280
}3.3. labelme_point_2yolo代码
# coding:utf-8
# labeme中point格式标注,转化成yolo格式
import os
import cv2 as cv2
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""
1. One row per object
2. Each row is class x_center y_center width height format.
3. Box coordinates must be in normalized xywh format (from 0 - 1).
If your boxes are in pixels, divide x_center and width by image width, and y_center and height by image height.
4. Class numbers are zero-indexed (start from 0).
"""
# labelme 中预设的类别名和类别 id 的对应关系
# 在这个point模式转换的代码中因为有RS,BS,Rs,Bs哨兵大小写标错,所以对应字典中大小写都有
label_idx_map = {"B1": 0, "B2": 1, "B3": 2, "B4": 3, "B5": 4, "BO": 5, "Bs": 6, "Bb": 7,"R1": 8, "R2": 9, "R3": 10, "R4": 11, "R5": 12, "RO": 13, "Rs": 14, "Rb": 15, "RS" : 14, "BS" : 6}
color_list = [[200, 0, 0], [0, 200, 0], [0, 0, 200], [200, 200, 0], [0, 200, 200], [200, 0, 200], [0, 0, 0],
[128, 128, 0],[200, 0, 0], [70, 20, 0], [100, 0, 200], [200, 200, 200], [0, 20, 200], [200, 0, 200], [0, 0, 0],
[128, 128, 0]]
def labelme_to_yolo(img_dir, json_dir, save_dir,save_jpg_dir):
name_list = os.listdir(json_dir) # 可以和图片是同一个文件夹
count = 0
for name in name_list:
if name.endswith('.json'):
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, name.replace(".json", ".txt")) # 创建txt路径
im_path = os.path.join(img_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpg")) # 拼装图片路径
json_path = os.path.join(json_dir, name) # 拼装json路径
if(os.path.exists(im_path)):
im = cv2.imread(im_path) # 读取图片
name_jpg = os.path.join(save_jpg_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpg")) # 保存图片的路径
else:
im_path = os.path.join(img_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpeg")) # 如果找不到jpg,就去找jpeg
im = cv2.imread(im_path) # 读取图片
name_jpg = os.path.join(save_jpg_dir, name.replace(".json", ".jpeg")) # 创建保存图片的路径
label_dict = json.load(open(json_path, 'r')) # 读取json文件
height = label_dict["imageHeight"]
width = label_dict["imageWidth"]
loc_info_list = label_dict["shapes"] # shapes列表中point格式一个点是一个字典
label_info_list = list()
count_point = 0
point = []
for loc_info in loc_info_list: # 取出每个点
count_point += 1
obj_name = loc_info.get("label") # obj_name = 标签
label_id = label_idx_map.get(obj_name)# 检索标签对应的数字
# print(label_id)
loc = loc_info.get("points")
x0, y0 = loc[0] # 取出一个点
point.append([x0,y0])
# x1, y1 = loc[1] # 左下角点
# x2, y2 = loc[2] # 右下角点
# x3, y3 = loc[3] # 右上角点
# if x2<=x0 or y2<=y0:
# print("error:",name)
if count_point == 4:
count_point = 0
x_max = max(point[0][0],point[1][0],point[2][0],point[3][0])
x_min = min(point[0][0],point[1][0],point[2][0],point[3][0])
y_max = max(point[0][1],point[1][1],point[2][1],point[3][1])
y_min = min(point[0][1],point[1][1],point[2][1],point[3][1])
# cv2.rectangle(im, (int(x_max), int(y_max)), (int(x_min), int(y_min)), color_list[label_id], 2)
cv2.imwrite(name_jpg, im)
x_center = (x_max + x_min) / 2 / width
y_center = (y_max + y_min ) / 2 / height
box_w = (abs(x_max - x_min)) / width
box_h = (abs(y_max - y_min)) / height
x0 = point[0][0] / width
x1 = point[1][0] / width
x2 = point[2][0] / width
x3 = point[3][0] / width
y0 = point[0][1] / height
y1 = point[1][1] / height
y2 = point[2][1] / height
y3 = point[3][1] / height
label_info_list.append([str(label_id), str(x_center), str(y_center), str(box_w), str(box_h),str(x0),str(y0),str(x1),str(y1),str(x2),str(y2),str(x3),str(y3)])
print(save_path)
count += 1
print(count)
with open(save_path, 'w') as f: # 每四次就进来写一下,如果两个标签,第二个四次重写文件
for label_info in label_info_list:
label_str = ' '.join(label_info)
f.write(label_str)
f.write('\n')
# debug
# plt.figure(0)
# plt.imshow(im)
# plt.show()
# print("xxx")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 图像文件夹
image_dir = "1 (1)"
# labelme 的标注结果
json_dir = "1 (1)"
# yolo 使用的 txt 结果
save_dir = "1_output_txt"
# yolo 使用的 jpg 结果
save_jpg_dir = "1_output_jpg"
labelme_to_yolo(image_dir, json_dir, save_dir,save_jpg_dir)