2.JDBC必知必会
文章目录
- 2.0 JDBC
- 2.1 配置单数据源
-
- 项目一:尝试Spring Boot自动装配数据源
-
- 创建
- 查看应用程序有哪些bean
- 原理
- 问题
- 项目二:SpringMVC手动配置数据源
- Spring Boot自动装配原理与数据源相关配置
- 项目三:尝试Spring Boot自动装配+参数配置
- 2.2.配置多数据源
-
- 1.排除Spring Boot依赖,使用Spring手工配置两组DataSource
- 2.与SpringBoot结合
- 留言
- 2.3 HikariCP(日语:光)
-
- HikariCP为什么快
- Spring Boot 2.x 自动配置HikariCP作为数据源的源码
- 常用HikariCP配置参数
- 留言
- 2.4 Alibaba Druid
-
- 项目一:手动配置Druid数据源
- 项目二:druid-spring-boot-starter自动配置
-
- Druid Filter
- Druid密码加密解密
- 2.5 数据库连接池的选择
- 2.6 Spring的JDBC操作类
-
- spring-jdbc
- 通过注解定义Bean
- 简单的JDBC操作
-
- JdbcTemplete
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
- 项目代码
-
- 配置数据源参数
- schema.sql
- 单条语句执行
- 实体类Foo
- 批处理操作
- 启动类
- 2.7 Spring的事务抽象
-
- 事务抽象的核心接口
-
- PlatformTransactionManager(interface)
- TransactionDefinition(class)
- 事务的传播特性
- 事务的隔离性
- 2.8 事务抽象实例
-
- 编程式事务
-
- (1)PlatformTransactionManager
- (2)transactionTemplate
- 声明式事务
-
- 基于注解的配置方式
- 实例
- 2.8 Spring的JDBC异常抽象
-
- Spring是怎么认识错误码的
- 2.9 课程答疑
-
- 开发环境
-
- (1)Lombok插件
- (2)Maven Helper插件
- (3)Cygwin
- (4)Docker
- Spring常用注解
-
- (1)配置类与配置的注入
- (2)Bean的定义
- (3)注入相关
- Actuator提供的Endpoint(端点)
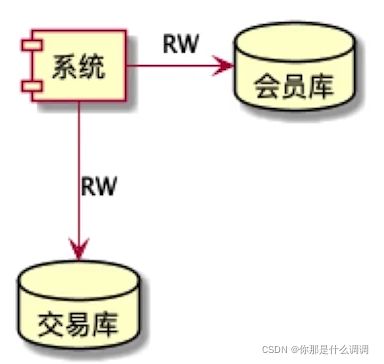
- 多数据源、读写分离、分库分表
-
- 访问几个完全不同的数据库:配置两个完全不同的DataSource
- 访问同一个库的主库与从库:主库做读写操作,从库做读操作
- 访问一组做了分库分表的数据库
- 事务
-
- 常用传播特性
- 测试代码
- Alibaba Druid开启慢SQL日志
- 注意事项
2.0 JDBC
JDBC小结
2.1 配置单数据源
项目一:尝试Spring Boot自动装配数据源
创建
- 访问https://start.spring.io/
- 增加Spring Boot Actuator(健康检查、beans),H2 Database(H2数据库驱动),JDBC API(简化JDBC使用),Lombok(@Slf4j、@Data),Spring Web依赖(访问actuator)。
package com.example.demo;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j // lombok
@Order(value = 2)
public class DemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired // 先根据类型查找,再根据名称查找
private DataSource dataSource;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
/**
* CommandLineRunner接口的run方法会在Spring Beans都初始化之后,
* SpringApplication.run() 之前执行,适合应用程序启动之初的数据初始化工作。
* 也可以用ApplicationRunner接口,只是run方法的参数是ApplicationArguments对象
* 可以用@Order(value = 1)指定执行顺序
*/
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
showConnection();
}
private void showConnection() throws SQLException {
log.info("====================================================");
log.info(dataSource.toString());
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
log.info("====================================================");
log.info(conn.toString());
conn.close();
}
}
package com.example.SingleDataSource1;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Order(value = 1)
@Slf4j
public class AAA implements CommandLineRunner {
public void run(String... args) {
log.info("AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");
}
}
查看应用程序有哪些bean
访问(安装JSON Viewer插件):
http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
"dataSource": {
"aliases": [
],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource",
"resource": "class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/jdbc/DataSourceConfiguration$Hikari.class]",
"dependencies": [
"org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceConfiguration$Hikari",
"spring.datasource-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties"
]
}
原理
spring-boot-starter-actuator会引入spring-boot-starter。
spring-boot-starter会引入spring-boot-autoconfigure。
spring-boot-autoconfigure中的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceConfiguration类会自动注入HikariDataSource。
问题
如何添加修改数据源的配置
如何手动配置数据源
如何配置多个数据源
项目二:SpringMVC手动配置数据源
配置依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>geektime.spring.datagroupId>
<artifactId>pure-spring-datasource-demoartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<spring.version>5.1.3.RELEASEspring.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2databasegroupId>
<artifactId>h2artifactId>
<version>RELEASEversion>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2artifactId>
<version>RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
可以选择在配置文件中写bean
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="org.h2.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:h2:mem:testdb"/>
<property name="username" value="SA"/>
<property name="password" value="SA"/>
bean>
或者用java代码生成
package geektime.spring.data.datasourcedemo;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Properties;
// 标识为配置类,相当于Spring Boot自动装配原理与数据源相关配置
项目三:尝试Spring Boot自动装配+参数配置
SpringBoot默认采⽤资源根⽬录下schema.sql⽂件进⾏创建表的初始化,使⽤data.sql进⾏插⼊初始化数据的⼯作。
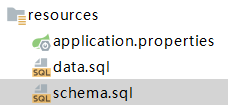
data.sql:
INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (1, 'aaa');
INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (2, 'bbb');
schema.sql:
CREATE TABLE FOO (ID INT IDENTITY, BAR VARCHAR(64));
配置文件:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:tested
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=5
spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=5
spring.datasource.hikari.idleTimeout=600000
spring.datasource.hikari.connectionTimeout=30000
spring.datasource.hikari.maxLifetime=1800000
#------初始化内嵌数据库(springboot不配置以下内容,也会自动加载以下配置)-------
spring.datasource.initialization-mode=always
# 指定Schema (DDL)脚本
spring.datasource.schema=classpath:schema.sql
# 指定Data (DML)脚本
spring.datasource.data=classpath:data.sql
# 指定schema要使用的Platform
spring.datasource.platform=h2
# 是否启用h2控制台
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
# 配置h2控制台访问地址,http://localhost:8080/h2
spring.h2.console.path=/h2
package geektime.spring.data.datasourcedemo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class DataSourceDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DataSourceDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
showConnection();
showData();
}
private void showConnection() throws SQLException {
log.info(dataSource.toString());
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
log.info(conn.toString());
conn.close();
}
private void showData() {
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT * FROM FOO");
log.info("========================================================");
for (Map m : maps) {
log.info("" + m);
}
// .forEach(row -> log.info(row.toString()));
}
}
2.2.配置多数据源
(1)不同数据源的配置要分开(即使数据源之间有很多配置是相同的)
(2)告诉系统、对应的设施(事务,ORM)使用哪个DataSource
1.排除Spring Boot依赖,使用Spring手工配置两组DataSource
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>DoubleDataSource1artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<spring.version>5.1.3.RELEASEspring.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2artifactId>
<version>RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2databasegroupId>
<artifactId>h2artifactId>
<version>RELEASEversion>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example" />
beans>
package com.example.DoubleDataSource1;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Properties;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DoubleDataSource1Application {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dataSource1") // 当多个bean类名冲突,名字无法判断时,根据指定的别名注入
DataSource dataSource;
@Bean(destroyMethod = "close")
public DataSource dataSource1() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("driverClassName", "org.h2.Driver");
properties.setProperty("url", "jdbc:h2:mem:testdb1");
properties.setProperty("username", "sa");
return BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); // dbcp
}
@Bean(destroyMethod = "close")
public DataSource dataSource2() throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("driverClassName", "org.h2.Driver");
properties.setProperty("url", "jdbc:h2:mem:testdb2");
properties.setProperty("username", "sa");
return BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); // dbcp
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager1() throws Exception {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource1());
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager2() throws Exception {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource2());
}
public void showDataSource1() throws SQLException {
System.out.println(dataSource1.toString());
Connection conn = dataSource1.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn.toString());
conn.close();
}
public void showDataSource2() throws SQLException {
System.out.println(dataSource2.toString());
Connection conn = dataSource2.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn.toString());
conn.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext*.xml");
showBeans(applicationContext);
dataSourceDemo(applicationContext);
}
private static void showBeans(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()));
}
private static void dataSourceDemo(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws SQLException {
DoubleDataSource1Application demo = applicationContext.getBean("doubleDataSource1Application", DoubleDataSource1Application.class);
}
}
2.与SpringBoot结合
SpringBoot的自动配置多数都是针对只有一个DataSource的,所以我在课程中提了,要么给主要的DataSource Bean增加@Primary注解,要么就把几个自动配置类排除掉。
(1)配置@Primary类型的Bean(两个Bean有主次之分)
(2)排除Spring Boot的自动配置,通过spring-boot-autoconfigure手动构建数据源(没有主次之分)(与使用Sring手动配置相比优点是:参数写在properties里,同一套代码使用多个数据库连接池)
package com.example.DoubleDataSource2;
import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariConfig;
import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class,
JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration.class})
@Slf4j
public class DoubleDataSource2Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
HikariDataSource fooDataSource;
@Autowired
BasicDataSource barDataSource;
@Autowired
RuoYiConfig ruoYiConfig;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DoubleDataSource2Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
showConnection();
}
public void showConnection() throws SQLException {
log.info("============================================开始");
log.info(fooDataSource.toString());
log.info("poolname:" + fooDataSource.getPoolName());
Connection conn1 = fooDataSource.getConnection();
log.info(conn1.toString());
conn1.close();
log.info("============================================");
log.info(barDataSource.toString());
log.info("username:" + barDataSource.getUsername());
Connection conn2 = barDataSource.getConnection();
log.info(conn2.toString());
conn2.close();
log.info("============================================");
log.info("" + ruoYiConfig.getName() + "," + ruoYiConfig.getVersion());
log.info("============================================结束");
}
}
package com.example.DoubleDataSource2;
import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("foo.datasource")
public DataSourceProperties fooDataSourceProperties() {
return new DataSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.hikari")
public HikariDataSource fooDataSource() {
DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties = fooDataSourceProperties();
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
@Bean
@Resource
public PlatformTransactionManager fooTxManager(DataSource fooDataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(fooDataSource);
}
@Bean
@Resource
public JdbcTemplate foojdbcTemplate(DataSource fooDataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(fooDataSource);
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("bar.datasource")
public DataSourceProperties barDataSourceProperties() {
return new DataSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.dbcp2")
public BasicDataSource barDataSource() {
DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties = barDataSourceProperties();
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(BasicDataSource.class).build();
}
@Bean
@Resource
public PlatformTransactionManager barTxManager(DataSource barDataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(barDataSource);
}
@Bean
@Resource
public JdbcTemplate barjdbcTemplate(DataSource barDataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(barDataSource);
}
}
使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “ruoyi”)从配置文件获取参数
package com.example.DoubleDataSource2;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ruoyi")
public class RuoYiConfig
{
public String name;
public String version;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
}
}
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
spring.output.ansi.enabled=ALWAYS
foo.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:foo
foo.datasource.username=sa
foo.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.hikari.poolName=hikari-aaaa
bar.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:bar
bar.datasource.username=Root
bar.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.dbcp2.userName=Root
ruoyi.name = Han
ruoyi.version = 1.1.0
增加dbcp2依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2artifactId>
<version>RELEASEversion>
dependency>
留言
Bean简单来讲就是由Spring容器创建并托管的实例。
@Resource是说我这个方法的参数要按照名字来注入其他的Bean。
2.3 HikariCP(日语:光)
HikariCP为什么快
(1)字节码级别优化(很多方法通过JavaAssist生成)。
(2)大量的小改进。用FastStatementList代替ArrayList,无锁集合ConcurrentBag,代理类的优化(用invokestatic代替了invokervirtual)
Spring Boot 2.x 自动配置HikariCP作为数据源的源码
Spring Boot 1.x 默认使用Tomcat连接池,因此需要移除tomcat-jdbc依赖,同时引入HikariCP依赖,spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource指定数据源类型
Spring Boot 2.x 默认使用 HikariCP。配置 spring.datasource.hikari.*
查看spring-boot-autoconfigure2.6.7.jar 中 DataSourceConfiguration.class源码
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
// class Path中有HikariDataSource.class
@ConditionalOnClass({HikariDataSource.class})
// Spring上下文中没有配置DataSource的Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"},
havingValue = "com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource",
matchIfMissing = true
)
static class Hikari {
Hikari() {
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.datasource.hikari"
)
HikariDataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
HikariDataSource dataSource = (HikariDataSource)DataSourceConfiguration.createDataSource(properties, HikariDataSource.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getName())) {
dataSource.setPoolName(properties.getName());
}
return dataSource;
}
}
常用HikariCP配置参数
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:tested
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=10
spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=10
spring.datasource.hikari.idle-timeout=600000
spring.datasource.hikari.connection-timeout=30000
spring.datasource.hikari.max-lifetime=1800000
留言
数据库连接池应该设多大?
连接数 = ((核心数 * 2) + 有效磁盘数)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/133996025
利用@ConfigurationProperties将属性的赋值放到配置文件中
https://blog.csdn.net/u014486725/article/details/124090043
https://blog.csdn.net/YooFale/article/details/84869869
2.4 Alibaba Druid
详细的监控
ExceptionSorter,针对主流数据库的返回码都有支持
SQL防注入
内置加密配置
众多拓展点,方便进行定制
项目一:手动配置Druid数据源
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.1.10version>
dependency>
创建Druid数据源bean
package com.example.DruidDemo;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@Bean(name = "druidDataSource")
public DruidDataSource druidDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:h2:mem:foo");
dataSource.setUsername("Sa");
dataSource.setPassword("n/z7PyA5cvcXvs8px8FVmBVpaRyNsvJb3X7YfS38DJrIg25EbZaZGvH4aHcnc97Om0islpCAPc3MqsGvsrxVJw==");
dataSource.setInitialSize(5);
dataSource.setMaxActive(5);
dataSource.setMinIdle(5);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcTemplate")
@Resource
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DruidDataSource druidDataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(druidDataSource);
}
}
package com.example.DruidDemo;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure.class)
@Slf4j
public class DruidDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
DruidDataSource druidDataSource;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DruidDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("=========================================");
log.info(druidDataSource.getUrl());
log.info(druidDataSource.getUsername());
log.info(druidDataSource.getPassword());
log.info("" +druidDataSource.getInitialSize());
log.info("" + druidDataSource.getMaxActive());
log.info("" + druidDataSource.getMinIdle());
log.info(druidDataSource.toString()); // 没有创建
DruidPooledConnection connection = druidDataSource.getConnection();
log.info(druidDataSource.toString()); // 第一次使用的时候Druid会自己调用init()
}
}
项目二:druid-spring-boot-starter自动配置
spring-boot-autoconfigure不支持对druid自动配置
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion> // 排除HikariCP
<artifactId>HikariCPartifactId>
<groupId>com.zaxxergroupId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.1.10version>
dependency>
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class DruidDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DruidDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("=========================================");
log.info(dataSource.toString());
}
}
Druid Filter
- 用于定制连接池操作的各种环节
- 可以继承FilterEventAdapter以便方便地实现Filter
- 在resources目录下增加META-INF/druid-filter.properties文件(配置filter类地址和对应地名称)

@Slf4j
public class ConnectionLogFilter extends FilterEventAdapter { // 继承FilterEventAdapter
@Override
// 连接前打日志
public void connection_connectBefore(FilterChain chain, Properties info) {
log.info("BEFORE CONNECTION!");
}
@Override
// 连接后打日志
public void connection_connectAfter(ConnectionProxy connection) {
log.info("AFTER CONNECTION!");
}
}
spring.output.ansi.enabled=ALWAYS
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:foo
spring.datasource.username=sa
# 密码加密
spring.datasource.druid.filter.config.enabled=true
// 加密后地密码
spring.datasource.password=n/z7PyA5cvcXvs8px8FVmBVpaRyNsvJb3X7YfS38DJrIg25EbZaZGvH4aHcnc97Om0islpCAPc3MqsGvsrxVJw==
// 解密用的公钥
spring.datasource.druid.connection-properties=config.decrypt=true;config.decrypt.key=${public-key}
// 公钥
public-key=MFwwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADSwAwSAJBALS8ng1XvgHrdOgm4pxrnUdt3sXtu/E8My9KzX8sXlz+mXRZQCop7NVQLne25pXHtZoDYuMh3bzoGj6v5HvvAQ8CAwEAAQ==
# Filter配置
# conn是自己实现地filter, config可以实现密码加解密功能, stat统计功能, 日志通过slf4j输出
spring.datasource.druid.filters=conn,config,stat,slf4j
# SQL防注入
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.db-type=h2
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.config.delete-allow=false // 不能做删除操作
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.config.drop-table-allow=false // 不能做删表操作
# 连接池属性
spring.datasource.druid.initial-size=5
spring.datasource.druid.max-active=5
spring.datasource.druid.min-idle=5
# 做检查
spring.datasource.druid.test-on-borrow=true
spring.datasource.druid.test-on-return=true
spring.datasource.druid.test-while-idle=true
# 配置可执行sql
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statementExecutableSqlLogEnable=true
# 把druid.sql的日志级别设置为DEBUG
logging.level.druid.sql=debug
Druid密码加密解密
String password = "123456";
String[] arr = ConfigTools.genKeyPair(512); // 获取私钥密钥
LOG.debug("privateKey:" + arr[0]);
LOG.debug("publicKey:" + arr[1]);
LOG.debug("password:" + ConfigTools.encrypt(arr[0], password)); // 用私钥对密码加密
https://vimsky.com/examples/detail/java-class-com.alibaba.druid.filter.config.ConfigTools.html
2.5 数据库连接池的选择
可靠性
性能
功能(SQL防注入)
可运维性(密码加密)
可拓展性(服务追踪中,执行SQL前打印TraceId和SpanId)
其他
2.6 Spring的JDBC操作类
spring-jdbc
- core,JdbcTemplete等相关核心接口和类(RowMapper)
- datasource,数据源相关的辅助类
- object,将基本的JDBC操作封装成对象
- support,错误码等其他辅助工具
通过注解定义Bean
- @Componet 通用的Bean
- @Repository 对数据库的操作
- @Service 对业务的服务
- @Controller
- @RestController 方便开发RESTFUL Web Service
简单的JDBC操作
JdbcTemplete
- query
- queryForObject
- queryForList
- queryForMap
- update 插入、删除、修改
- execute 通用方法
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
在使用JdbcTemplate的使用实例中,SQL语句中的参数占位符都是?,当参数只有一个的时候,也许我们看不出什么问题,但是,当参数有了多个,很容易搞错参数的赋值顺序。
为了解决这个问题,Spring JDBC提供了NamedParameterJdbcTemplate,使用命名化的参数来替代原先的问号占位符。
项目代码
配置数据源参数
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,beans
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:tested
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=5
spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=5
spring.datasource.hikari.idleTimeout=600000
spring.datasource.hikari.connectionTimeout=30000
spring.datasource.hikari.maxLifetime=1800000
#------初始化内嵌数据库(springboot不配置以下内容,也会自动加载以下配置)-------
spring.datasource.initialization-mode=always
# 指定Schema (DDL)脚本
spring.datasource.schema=classpath:schema.sql
# 指定Data (DML)脚本
spring.datasource.data=classpath:data.sql
# 指定schema要使用的Platform
spring.datasource.platform=h2
# 是否启用h2控制台
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
# 配置h2控制台访问地址,http://localhost:8080/h2
spring.h2.console.path=/h2
schema.sql
CREATE TABLE FOO (ID INT IDENTITY, BAR VARCHAR(64));
单条语句执行
@Repository
@Slf4j
public class FooDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 查询操作
*/
public void queryData() {
// 返回一行、一列
log.info("==================Count: {}", jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM FOO", Long.class));
// 返回一行、多列
List<String> list = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT BAR FROM FOO", String.class);
list.forEach(s -> log.info("==================Bar: {}", s));
// 返回多行、多列,结果转换为Map
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT ID, BAR FROM FOO");
log.info(maps.toString());
maps.forEach(m -> {
log.info("==================id-{}, bar-{}", m.get("ID"), m.get("BAR"));
});
// 返回多行、多列,结果映射为对象
List<Foo> fooList = jdbcTemplate.query("SELECT * FROM Foo", new RowMapper<Foo>() {
@Override
public Foo mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return Foo.builder()
.id(rs.getLong(1))
.bar(rs.getString(2))
.build();
}
});
fooList.forEach(f -> log.info("==================Foo: {}", f));
}
/**
* 插入操作
*/
public void insertData() {
Arrays.asList("insert1", "insert2").forEach(bar -> {
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES (?)", bar);
});
}
}
实体类Foo
@Data
@Builder
public class Foo {
private long id;
private String bar;
}
批处理操作
@Repository
public class BatchFooDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
public void batchInsert() {
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("batch1", "batch2"));
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES (?)",
new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1, list1.get(i));
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return list1.size();
}
});
List<Foo> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(Foo.builder().id(100L).bar("batch3").build());
list.add(Foo.builder().id(101L).bar("batch4").build());
namedParameterJdbcTemplate
.batchUpdate("INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (:id, :bar)",
SqlParameterSourceUtils.createBatch(list));
}
}
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class SingleDataSource1Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private FooDao fooDao;
@Autowired
private BatchFooDao batchFooDao;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SingleDataSource1Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
fooDao.insertData();
batchFooDao.batchInsert();
fooDao.queryData();
}
}
2.7 Spring的事务抽象
Spring提供了一致的事务模型:
不管是使用JBDC、Hibernate还是Mybatis来操作数据,也不管使用的是DataSoure还是JTA的事务。在事务抽象里都能很好的把它统一在一起。
事务抽象的核心接口
PlatformTransactionManager(interface)
- DataSourceTransactionManager(class)
- HibernateTransactionManager(class)
- JtaTransactionManager(class)
public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
TransactionDefinition(class)
通过TransactionDefinition可以取得TransactionStatus。
- Propagation 传播特性
- Isolation 隔离性
- Timeout 事务的超时
- Read-only status 是否是只读
事务的传播特性
事务的隔离性
2.8 事务抽象实例
编程式事务
(1)PlatformTransactionManager
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class SingleDataSource1Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SingleDataSource1Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
/* 事务定义类 */
DefaultTransactionDefinition transactionDefinition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
transactionDefinition.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED);
/* 返回事务对象 */
TransactionStatus status = platformTransactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
try {
log.info("====================================================");
log.info("COUNT BEFORE TRANSACTION: {}", getCount());
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES ('AAAA')");
/* BAR1会报错 */
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR1) VALUES ('BBBB')");
platformTransactionManager.commit(status);
} catch (Exception e) {
platformTransactionManager.rollback(status);
}
log.info("COUNT AFTER TRANSACTION: {}", getCount());
log.info("====================================================");
}
private long getCount() {
Long query = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("SELECT COUNT(*) AS CNT FROM FOO", Long.class);
return query;
}
}
(2)transactionTemplate
public class TransactionTemplate extends DefaultTransactionDefinition implements TransactionOperations, InitializingBean {
/**
* 有返回值:TransactionCallback
* 没有返回值:TransactionCallbackWithoutResult
*/
public <T> T execute(TransactionCallback<T> action) throws TransactionException {
.....
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class SingleDataSource1Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SingleDataSource1Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("====================================================");
log.info("COUNT BEFORE TRANSACTION: {}", getCount());
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
try {
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (1, 'aaa')");
log.info("COUNT IN TRANSACTION: {}", getCount());
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionStatus.setRollbackOnly();
}
}
});
log.info("COUNT AFTER TRANSACTION: {}", getCount());
log.info("====================================================");
}
private long getCount() {
Long query = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("SELECT COUNT(*) AS CNT FROM FOO", Long.class);
return query;
}
}
声明式事务
Spring AOP:Java默认的动态代理方式做AOP。封装了AspectJ。
Spring的声明式事务是利用了AOP的Proxy,它在目标方法上做了一个封装。操作开始前启动事务,方法执行结束之后commit或者rollback。
基于注解的配置方式
@EnableTransactionManagement注解在Spring Boot工程中可以不用加
proxyTargetClass:false——基于接口的代理(JDK)。true——基于类的代理(CGLIB)。SpringBoot中有很多自动配置的,已经把proxyTargetClass设置为true了。
order:指定事务AOP的拦截的顺序,默认是最低的优先级。
在类上加@Transacational注解,则类里的public方法都会带上事务。而且属性都是用同一个。

实例
需要调用代理类才能执行到被代理增强的那些方法,如果是在方法内部调用的话,因为invokeInsertThenRollback本身是没有事务的,因此调用insertThenRollBack也不会有事务支持。
Spring Bean注入给其他人时,注入的不是A,而是B。所以通过Bean来调用时,调用的是B.xxx(),在A自身内部调用内部方法时,调用的还是A.xxx()
在自动注入的Bean上面加上@Lazy注解,防止循环依赖。
public interface FooService {
void insertRecord();
void insertThenRollback() throws RollbackException;
void invokeInsertThenRollback() throws RollbackException;
}
@Component
public class FooServiceImpl implements FooService {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
@Lazy
FooService fooService;
@Override
@Transactional
public void insertRecord() {
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES ('AAA')"); // 插入一条
}
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RollBackException.class)
public void insertThenRollBack() throws RollBackException {
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES ('BBB')"); // 被回滚
throw new RollBackException();
}
@Override
public void invokeInsertThenRollback() throws RollBackException {
/* 同级无法创建代理对象. 插入一条 */
insertThenRollBack();
/* (1)直接调用注入的实例,回滚 */
// fooService.insertThenRollBack();
/* (2)获取当前类的代理对象,再调用的代理对象的方法(其实是增强后的方法),回滚 */
// FooService fooService = (FooService) AopContext.currentProxy();
// fooService.insertThenRollBack();
}
}
public class RollBackException extends Exception {
}
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class SingleDataSource1Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
FooService fooService;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SingleDataSource1Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
fooService.insertRecord();
log.info("AAA {}", getCount());
try {
fooService.insertThenRollBack();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("BBB {}", getCount());
}
try {
fooService.invokeInsertThenRollback();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("BBB {}", getCount());
}
}
private long getCount() {
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("SELECT COUNT(*) AS CNT FROM FOO", Integer.class);
}
}
2.8 Spring的JDBC异常抽象
Spring会将数据库操作的异常操作转换为DataAccessException。
无论使用何种数据访问方式,都能使用一样的异常。

Spring是怎么认识错误码的
(1)通过SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator类解析错误码
(2)在org/springframework/jdbc/support/sql-error-codes.xml定义各个数据库的errorCode。可以自己在classpath下定义sql-error-codes.xml,会覆盖掉官方文件
resources下新增sql-error-codes.xml
DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd">
<beans>
<bean id="H2" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes">
<property name="badSqlGrammarCodes">
<value>42000,42001,42101,42102,42111,42112,42121,42122,42132value>
property>
<property name="duplicateKeyCodes">
<value>23001,23505value>
property>
<property name="dataIntegrityViolationCodes">
<value>22001,22003,22012,22018,22025,23000,23002,23003,23502,23503,23506,23507,23513value>
property>
<property name="dataAccessResourceFailureCodes">
<value>90046,90100,90117,90121,90126value>
property>
<property name="cannotAcquireLockCodes">
<value>50200value>
property>
<property name="customTranslations">
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslation">
<property name="errorCodes" value="23001,23505" />
<property name="exceptionClass"
value="com.example.SingleDataSource1.CustomDuplicatedKeyException" />
bean>
property>
bean>
beans>
package com.example.SingleDataSource1;
import org.springframework.dao.DuplicateKeyException;
public class CustomDuplicatedKeyException extends DuplicateKeyException {
public CustomDuplicatedKeyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
public CustomDuplicatedKeyException(String msg, Throwable cause) {
super(msg, cause);
}
}
package com.example.SingleDataSource1;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class SingleDataSource1ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test(expected = CustomDuplicatedKeyException.class)
public void testThrowingCustomException() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (1, 'a')");
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (1, 'b')");
}
}
package com.example.SingleDataSource1;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class SingleDataSource1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SingleDataSource1Application.class, args);
}
}
2.9 课程答疑
开发环境
(1)Lombok插件
如果IDEA版本在2020.3以上,不需要安装Lombok插件。
(2)Maven Helper插件
(3)Cygwin
(4)Docker
用于在本地启动一些演示用的依赖设施,MongoDB或Redis
Spring常用注解
(1)配置类与配置的注入
- @Configuration:标注一个类是配置类
- @Bean:将方法的返回对象变为Bean
- @ConfigurationProperties:将配置文件中的变量注入返回对象中
- @PropertySource:引入*.Properties或者 .yml
- @ImportResource:将xml配置文件中的bean加载到Application Context中。
/**
- 写在启动类上
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@ImportResource({"classpath*:applicationContext.xml"})
public class ProductApplication {
}
/**
- 创建一个单独的配置类来加载此XML bean定义文件。
*/
@Configuration
@ImportResource({"classpath*:applicationContext.xml"})
public class XmlConfiguration {
}
- @ComponentScan:
@SpringBootApplication包含了@ComponentScan
默认自动扫描加载启动类所在包及其子包。因此下图中A1、A2能加载到,B1加载不到

将B1也加入路径
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan({"com.demo.zhujie1.aaaaa", "com.demo.zhujie1.bbbbb"}) // 加入B2路径,A1、A2路径也需要
@Slf4j
public class Zhujie1Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
A1 a1;
@Autowired
A2 a2;
@Autowired
B1 b1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Zhujie1Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
log.info(a1.getName());
log.info(a2.getName());
log.info(b1.getName());
}
}
(2)Bean的定义
- @Component
- @Repository
- @Service
- @Controller
- @RestController
(3)注入相关
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier
- @Resource
- @Value
Actuator提供的Endpoint(端点)
- /actuator:展示所有端点
- /actuator/health:健康检查
- /actuator/info
- /actuator/beans:查看Beans
- /actuator/mappings:Web的URL映射
- /actuator/env:环境信息
- /actuator/conditions:查看代码某个配置在什么条件下生效
- /actuator/threaddump:当前线程活动的快照
(1)默认:
/actuator/health和/actuator/info可Web访问
(2)解禁所有Endpoint:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
(3)开启/actuator/shutdown:
management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/actuator/shutdown"
多数据源、读写分离、分库分表
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1687119939271468578&wfr=spider&for=pc
访问几个完全不同的数据库:配置两个完全不同的DataSource
访问同一个库的主库与从库:主库做读写操作,从库做读操作
配置三个数据源(缺点是主从复制有延迟)。

使用中间件:淘宝TDDL,ShardingSphere client版本。

使用缓存:

访问一组做了分库分表的数据库
- 垂直分表:热门数据、冷门数据分开存储,大字段放在冷门数据表中。
- 垂直分库:按业务拆分,放到不同的库中,这些库分别部署在不同的服务器,解决单一服务器性能的- 瓶颈,同时提升整体架构的业务清晰度。
- 水平分表:解决单一表数据量过大的问题
- 水平分库:解决单一服务器数据量过大的问题
使用ShardingSphere
事务
Spring的声明式事务本质上是通过AOP增强了类的功能。
Spring的AOP本质上就是为了类做了一个代理,看似在调用自己写的类,实际用的是增强后的代理类。
常用传播特性
测试代码
@Component
@Slf4j
public class FooServiceImpl implements FooService {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
FooService fooService;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RollbackException.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void insertThenRollBack() throws RollbackException {
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES ('BBB')");
throw new RollbackException();
}
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RollbackException.class)
public void invokeInsertThenRollback() throws RollbackException {
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO FOO (BAR) VALUES ('AAA')");
try {
fooService.insertThenRollBack();
} catch (RollbackException e) {
}
// throw new RollbackException();
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement(mode = AdviceMode.PROXY) // 启动类上开启事务,默认开启
@Slf4j
public class DeclarativeTransactionDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
FooService fooService;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeclarativeTransactionDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
try {
fooService.invokeInsertThenRollback();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
log.info("AAA: {}", getCount1());
log.info("BBB: {}", getCount2());
}
private long getCount1() {
return (long) jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT COUNT(*) AS CNT FROM FOO WHERE BAR = 'AAA'")
.get(0).get("CNT");
}
private long getCount2() {
return (long) jdbcTemplate.queryForList("SELECT COUNT(*) AS CNT FROM FOO WHERE BAR = 'BBB'")
.get(0).get("CNT");
}
}
Alibaba Druid开启慢SQL日志
@Repository
public class FooService {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Transactional
public void selectForUpdate() {
// 在where 后面查询条件是主键索引,唯一索引时候是行锁。查询条件是普通字段时候加的是表锁
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select id from foo where id = 1 for update", Long.class);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class DruidDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private FooService fooService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DruidDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("=========================================");
new Thread(() -> fooService.selectForUpdate()).start();
new Thread(() -> fooService.selectForUpdate()).start();
}
}
spring.output.ansi.enabled=ALWAYS
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:foo
spring.datasource.username=sa
# spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.enabled=true
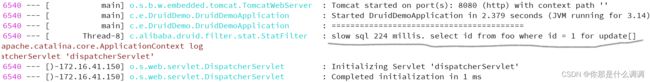
spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.log-slow-sql=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.slow-sql-millis=100 // 超过100ms抓出来
CREATE TABLE FOO (ID INT IDENTITY, BAR VARCHAR(64));
INSERT INTO FOO (ID, BAR) VALUES (1, 'AAA');
注意事项
(1)没有特殊情况,不要在生产环境打开监控的Servlet
(2)removeAbandoned用于移除被遗弃的连接。ORM和JdbcTemplate不会发生连接泄露,不要开启removeAbandoned。
(3)testXxxx的使用需要注意(testOnBorrow和testOnReturn关闭、testWhileIdle开启 连接有一段时间不用会检查)
# 做检查
spring.datasource.druid.test-on-borrow = false
spring.datasource.druid.test-on-return = false
spring.datasource.druid.test-while-idle = true
(4)务必配置合理的超时时间