刷题笔记(十四)--二叉树:层序遍历和DFS,BFS
目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 题录
-
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历
-
- BFS
- DFS_前序遍历
- 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 199. 二叉树的右视图
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 637. 二叉树的层平均值
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 429. N 叉树的层序遍历
-
- BFS
- DFS
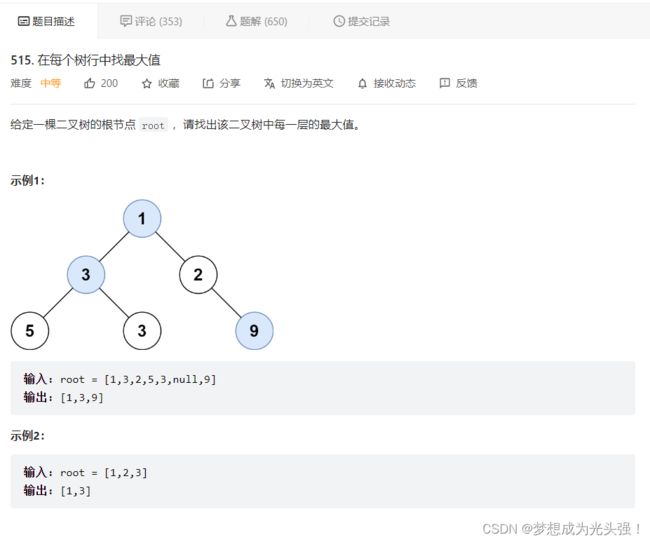
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
-
- BFS_迭代版本
- BFS_递归版本
- DFS
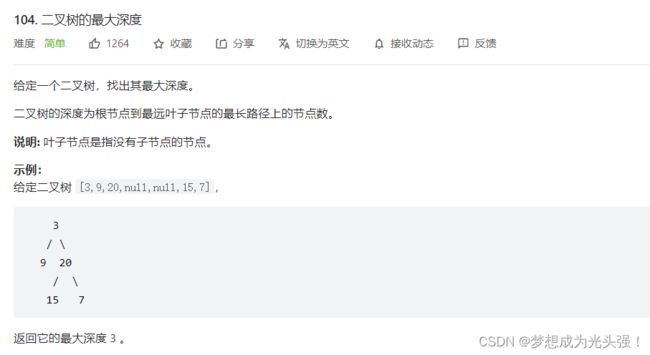
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 总结
系列文章目录
刷题笔记(一)–数组类型:二分法
刷题笔记(二)–数组类型:双指针法
刷题笔记(三)–数组类型:滑动窗口
刷题笔记(四)–数组类型:模拟
刷题笔记(五)–链表类型:基础题目以及操作
刷题笔记(六)–哈希表:基础题目和思想
刷题笔记(七)–字符串:经典题目
刷题笔记(八)–双指针:两数之和以及延伸
刷题笔记(九)–字符串:KMP算法
刷题笔记(十)–栈和队列:基础题目
刷题笔记(十一)–栈和队列:Top-K问题
刷题笔记(十二)–复习:排序算法
刷题笔记(十三)–二叉树:前中后序遍历(复习)
前言
上篇博客我们讲了二叉树的前,中和后序遍历,这是基于深度优先遍历DFS,这一篇博客,在复习深度优先遍历的同时也会扩展新的内容,也就是广度优先遍历BFS。而这种遍历的典型体现方式,就是层序遍历。层序遍历一个二叉树,要用队列来辅助我们实现,因为队列先进先出的特性刚刚好很适合层序遍历,同时也能很好的模拟广度优先遍历。当然,在这里再次感谢一下:代码随想录,给我提供的刷题路线。
题录
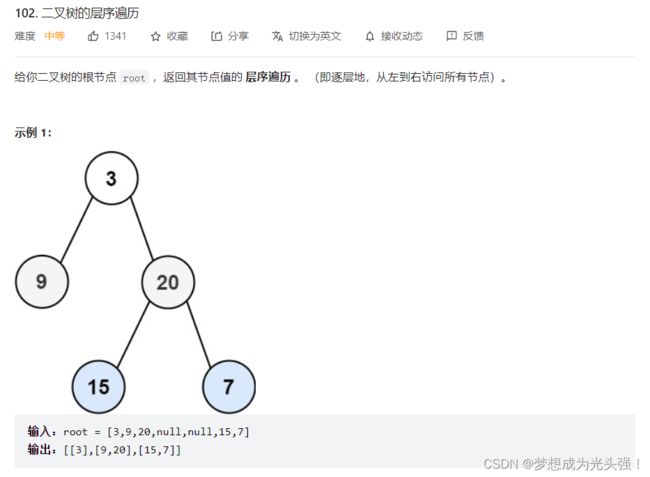
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
题目链接如下:
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
BFS
第一种就是两个队列来进行层次的控制
public class 二叉树的层序遍历 {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();//作为主队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();//作为副队列
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();//作为返回列表
if(root != null){
queue1.add(root);
}
//要保证主队列不能为空
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> mylist = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
//然后把主队列里面所有节点的左子树和右子树全部加入副队列里面
TreeNode key = queue1.poll();
if(key.left != null){
queue2.add(key.left);
}
if(key.right != null){
queue2.add(key.right);
}
mylist.add(key.val);
}
list.add(mylist);
//此时主队列为空,那么交换主队列和副队列
Queue<TreeNode> tmp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = tmp;
}
return list;
}
}
还有第二种就是只创建一个队列,然后用一个计数器来控制层次
public class 二叉树的层序遍历_BFS {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();//作为返回列表
if(root != null){
queue.add(root);
}
//要保证主队列不能为空
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int count = queue.size();//计数器来记录当前这一层有多少个节点
List<Integer> mylist = new ArrayList<>();
while(count != 0){//遍历这一层所有的节点
TreeNode key = queue.poll();
if(key.left != null){
queue.add(key.left);
}
if(key.right != null){
queue.add(key.right);
}
mylist.add(key.val);
count--;
}
list.add(mylist);
}
return list;
}
}
DFS_前序遍历
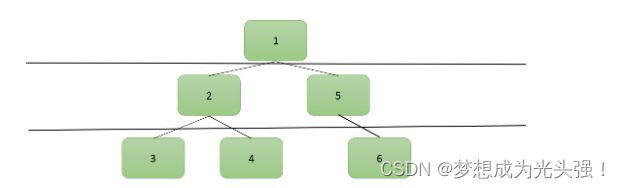
深度优先遍历其实这里不太好理解,怎么说呢?广度优先大家肯定很好理解,一层一层的嘛,遍历完当前层次的节点再去遍历它的左右子树。但是呢,深度优先遍历这里大家可能就不太好理解了,我用一个图来讲。
广度优先遍历是这样子的
深度优先遍历是这个样子的
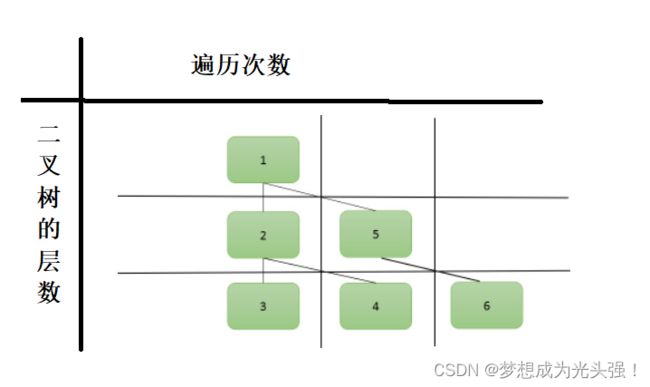
横向是每一层的层数,纵向是当前遍历的次数。
也就是说它是一条道走到黑,然后返回再去进行下一条道路的遍历,其中遇到了那一层的节点就把它往对应的list里面添加
public class 二叉树的层序遍历_DFS {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//首先排除root为null的情况
if(root==null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();//创建一个list用来存储遍历的结果
BFS(root,1,list);
return list;
}
public void BFS(TreeNode node,int index,List<List<Integer>> list){
//index用来控制层次,如果说当前到了一个新的层次,那么就要重新给list加一层,也就是加一个空数组
if(list.size() < index){
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
list.get(index - 1).add(node.val);
//然后继续往下走
if(node.left != null){
BFS(node.left,index + 1,list);
}
if(node.right != null){
BFS(node.right,index + 1,list);
}
}
}
然后可能有小伙伴来问了,那你这个标题中的前序遍历是啥意思?
这里的DFS我用的是前序遍历方式,因为图比较好画,当然你中序遍历和后序遍历也是可以的,就是调换一下add行的位置。
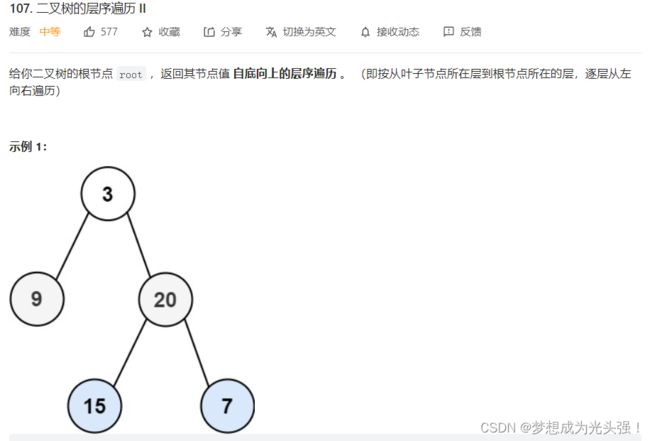
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
题目链接如下:
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
其实看第一眼就知道了,它要怎么搞呢?就是把咋们上一题拿到的答案倒转一下就行啦。就像这个样子。
BFS
public class 二叉树的层序遍历2_BFS {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.add(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int count = queue.size();
List<Integer> mylis = new ArrayList<>();
while(count > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
mylis.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
count--;
}
list.add(mylis);
}
Collections.reverse(list);//这里就新加了一行代码,倒转一下
return list;
}
}
但是这里其实有一个小小的问题,就是说,它会再重新的遍历一遍list,所以会对效率有影响,那么我们就要想办法解决这个问题,怎么解决呢?那就在每一层构建好之后把对应的集合插在list前端不就好了
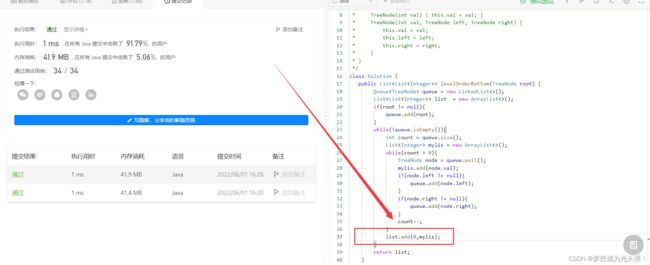
public class 二叉树的层序遍历2_BFS {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.add(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int count = queue.size();
List<Integer> mylis = new ArrayList<>();
while(count > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
mylis.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
count--;
}
list.add(0,mylis);
}
return list;
}
}
DFS
public class 二叉树的层序遍历2_DFS {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
DFS(root,1,list);
return list;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode node,int index,List<List<Integer>> list){
//如果说来到了一个新的层次,那么就要给list前面新加一个arraylist
if(list.size() < index ){
list.add(0,new ArrayList<>());
}
//这里添加元素不能是正向添加了,就要从后往前添加
list.get(list.size() - index).add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
DFS(node.left,index+1,list);
}
if(node.right != null){
DFS(node.right,index+1,list);
}
}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
题目链接如下:
199. 二叉树的右视图
题目截屏如下:
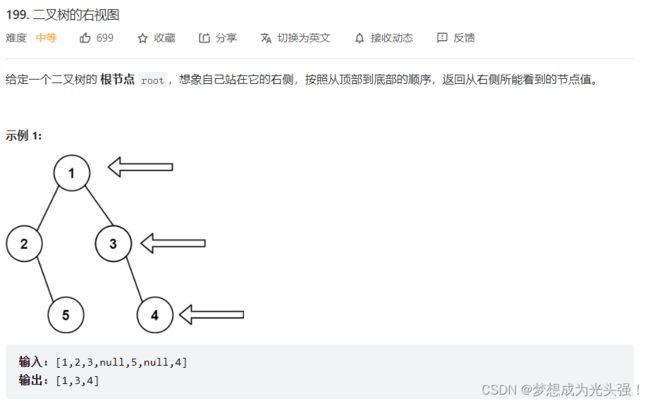
这道题怎么说呢?其实就是层序遍历,保存每一层最后的值就好啦。
BFS
public class 二叉树的右视图_BFS {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();//创建一个队列用来广度遍历二叉树
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();//用来接收每一层的最后一个值
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//获得每一层的数量个数
int size = queue.size();
//注意我这里对于节点的操作是先peek然后是Poll,不是以上来就是poll
while(size > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.peek();
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
if(size == 1){
list.add(node.val);
}
queue.poll();
size--;
}
}
return list;
}
}
当然如果说觉得麻烦的话,对于while循环可以换成for循环来做的。
DFS
深度优先遍历的话,就先从右子树开始遍历就好啦,这样可以保证当前层次遍历的第一个值就是正常层序遍历的最后一个值。
public class 二叉树的右视图_DFS {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();//用来存储每一层最后一个元素
DFS(root,1,list);
return list;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode node,int deepth,List<Integer> list){
//如果为空直接返回
if(node == null){
return;
}
//如果说当前的层数 == list的层数+1,就代表当前层次是第一个被遍历的元素,然后这里的层次遍历时从右到左
if(deepth == list.size() + 1){
list.add(node.val);
}
DFS(node.right,deepth+1,list);
DFS(node.left,deepth+1,list);
}
}
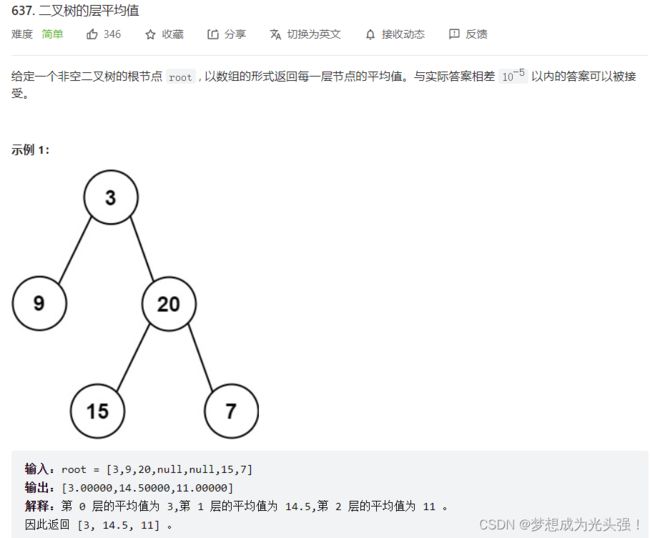
637. 二叉树的层平均值
题目链接如下:
637. 二叉树的层平均值
BFS
public class 二叉树的层平均值 {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
int len = size;
Double sum = 0.0;
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
sum += node.val;
}
list.add(sum / len);
}
return list;
}
}
DFS
说一下大致思路哈,就是求每一层的总和,然后用一个list记录下来,记录之后遍历list再除每一层的长度,这里每一层的长度用另外一个list来保存。
public class 二叉树的层平均值_DFS {
List<Double> list1 = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一层的总和
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一层的长度
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
DFS(root,0);
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
//要把每一层的总和除去每一层的元素个数
list1.set(i, list1.get(i)/list2.get(i));
}
return list1;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode node,int deepth){
if(node == null){
return;
}
//这里这样写是为了对于list的调用
if(deepth == list1.size()){//如果当前深度等于list1的长度,那么当前遍历就是这个层次的第一个碰到的元素
list1.add((double) node.val);
list2.add(1);
}else{
list1.set(deepth,list1.get(deepth) + node.val);
list2.set(deepth, list2.get(deepth)+1);
}
DFS(node.left,deepth+1);
DFS(node.right,deepth+1);
}
}
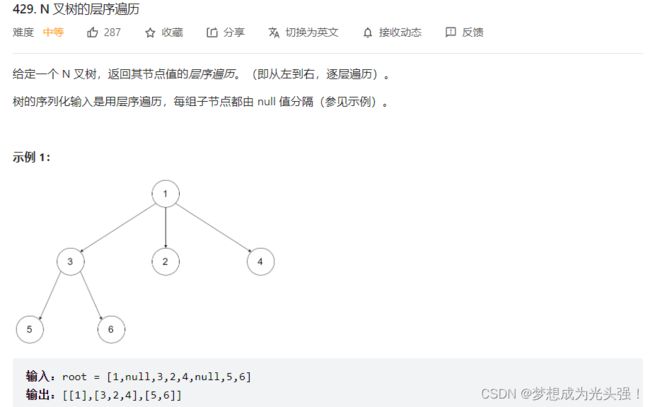
429. N 叉树的层序遍历
题目链接如下:
429. N 叉树的层序遍历
这种题目和上面的题目没啥很大的区别,就是不能再有左右子树了,要遍历当前节点的所有子节点。
BFS
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();//用来遍历每一层的节点
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> mylist = new ArrayList<>();
while(size-- > 0){
Node node = queue.poll();
mylist.add(node.val);
//把当前节点的所有子节点加入当前层次的mylist当中
for(Node chileNode:node.children){
queue.offer(chileNode);
}
}
list.add(mylist);
}
return list;
}
DFS
public class N叉树的层序遍历_DFS {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();//用list来保存每一层次的节点
DFS(root,list,0);
return list;
}
public void DFS(Node node,List<List<Integer>> list,int deepth){
if(node == null){
return;
}
if(list.size() == deepth){//如果来到了一个新的层次,那就要new一个新的arraylist出来啦
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
list.get(deepth).add(node.val);//把当前节点加入对应的层次
//遍历每个节点的child数组
for(Node mynode:node.children){
DFS(mynode,list,deepth+1);
}
}
}
515.在每个树行中找最大值
题目链接如下:
515.在每个树行中找最大值
BFS
public class 在每个树行中找最大值_BFS {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int size = queue.size();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.val > max){
max = node.val;
}
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
list.add(max);
}
return list;
}
}
DFS
public class 在每个树行中找最大值_DFS {
//要不就是遍历所有节点,然后遍历之后一个个的筛选
//但是这里我觉得根据层次来决定更好
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
DFS(root,0,list);
return list;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode node,int deepth,List<Integer> list){
if(node == null){
return;
}
//根据deepth来选择每一个层次的最大值
if(deepth == list.size()){
list.add(node.val);
}else{
if(list.get(deepth) < node.val){
list.set(deepth,node.val);
}
}
DFS(node.left,deepth+1,list);
DFS(node.right,deepth+1,list);
}
}
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
题目链接如下:
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
BFS_迭代版本
public class 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针_BFS {
public Node connect(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
while(size > 0){
Node mynode = queue.poll();
//如果说不是当前层次的最后一个节点,就把当前节点的next指针指向队列头结点
//如果是当前层次的最后一个节点,那就不用管它
if(size != 1){
mynode.next = queue.peek();
}
if(mynode.left != null){
queue.offer(mynode.left);
}
if(mynode.right != null){
queue.offer(mynode.right);
}
size--;
}
}
return root;
}
}
BFS_递归版本
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root == null) return root;
//首先连接当前节点的左子树和右子树
if(root.left != null) {
root.left.next = root.right;
//再接着连接当前节点的右子树和下一个节点的左子树
if (root.next != null) {
root.right.next = root.next.left;
}
}
connect(root.left);
connect(root.right);
return root;
}
DFS
public class 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针_DFS {
public Node connect(Node root) {
DFS(root);
return root;
}
public void DFS(Node node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
//先连接当前节点的左右子树
if(node.left != null){
node.left.next = node.right;
//然后把右子树和下一个对应节点连接起来
if(node.next != null){
node.right.next = node.next.left;
}
}
DFS(node.left);
DFS(node.right);
}
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目链接如下:
104. 二叉树的最大深度
BFS
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
queue.offer(root);
int count = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
count++;
int size = queue.size();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return count;
}
DFS
public class 二叉树的最大深度_DFS {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
int deepth = DFS(root);
return deepth;
}
public int DFS(TreeNode root){
return root == null ? 0 : Math.max(DFS(root.left),DFS(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目链接如下:
111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目截图如下:
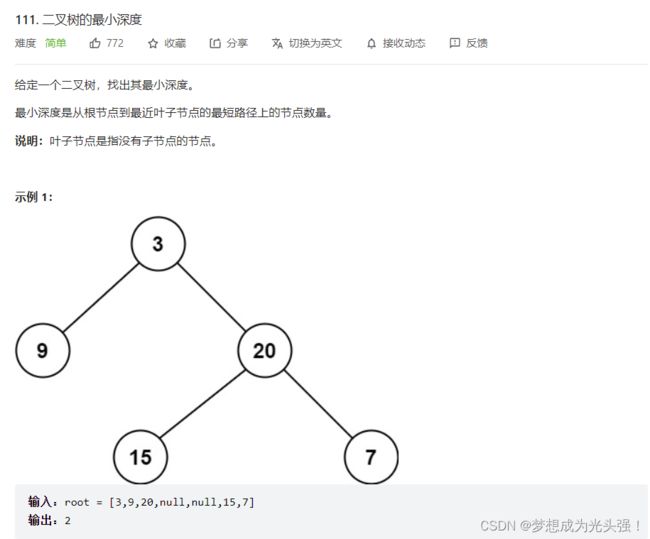
这个题也没什么特别好说的,和上面的区别不大,掌握了层序遍历的核心思想就行。
BFS
public class 二叉树的最小深度_BFS {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
queue.offer(root);
int count = 0;
boolean flag = false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//如果此时队列里面有元素,那么就证明当前层次不为空
count++;
int size = queue.size();
while(size-- > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
//如果说一个节点的左右子节点都为null,那么他就是最短的路径
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
//每次while循环完之后检测一样,如果出现了叶子结点就直接返回count就好
if(flag){
return count;
}
}
return count;
}
}
DFS
public class 二叉树的最大深度_DFS {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
int deepth = DFS(root);
return deepth;
}
public int DFS(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
//这里首先要排除就是左右子树有一个为空的情况,因为这个时候它不算是叶子结点
//如果右子树为空就从左子树往下走
if(root.right == null && root.left != null){
return DFS(root.left) + 1;
}
//如果左子树为空就从右子树往下走
if(root.left == null && root.right != null){
return DFS(root.right) + 1;
}
//如果左右子树都不为空那么就找短的哪一个
return Math.min(DFS(root.left),DFS(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
总结
多多复习,这里的题目都是大同小异,掌握核心思想基本问题不大。