iOS-底层原理 17:类的加载(上)
iOS 底层原理 文章汇总
在上一篇iOS-底层原理 16:dyld与objc的关联文章中,我们理解了dyld与objc是如何关联的,本文的主要目的是理解类的相关信息是如何加载到内存的,其中重点关注map_images和load_images
-
map_images:主要是管理文件中和动态库中的所有符号,即class、protocol、selector、category等 -
load_images:加载执行load方法
其中代码通过编译,读取到Mach-O可执行文件中,再从Mach-O中读取到内存,如下图所示
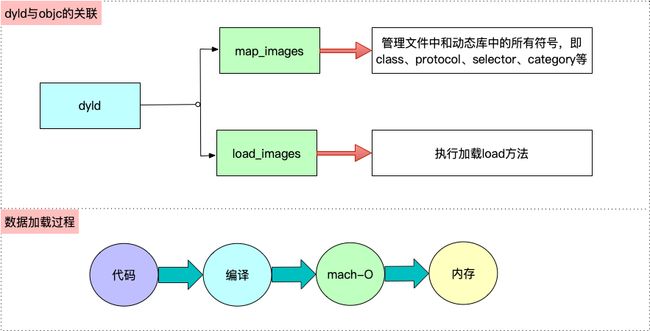
map_images:加载镜像文件到内存
在查看源码之前,首先需要说明为什么map_images有&,而load_images没有
map_images是引用类型,外界变了,跟着变。load_images是值类型,不传递值
map_images源码流程
map_images方法的主要作用是将Mach-O中的类信息加载到内存
- 进入
map_images的源码
void
map_images(unsigned count, const char * const paths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
return map_images_nolock(count, paths, mhdrs);
}
- 进入
map_images_nolock源码,其关键代码是_read_images
void
map_images_nolock(unsigned mhCount, const char * const mhPaths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
//...省略
// Find all images with Objective-C metadata.查找所有带有Objective-C元数据的映像
hCount = 0;
// Count classes. Size various table based on the total.计算类的个数
int totalClasses = 0;
int unoptimizedTotalClasses = 0;
//代码块:作用域,进行局部处理,即局部处理一些事件
{
//...省略
}
//...省略
if (hCount > 0) {
//加载镜像文件
_read_images(hList, hCount, totalClasses, unoptimizedTotalClasses);
}
firstTime = NO;
// Call image load funcs after everything is set up.一切设置完成后,调用镜像加载功能。
for (auto func : loadImageFuncs) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < mhCount; i++) {
func(mhdrs[i]);
}
}
}
_read_images 源码实现
_read_images主要是主要是加载类信息,即类、分类、协议等,进入_read_images源码实现,主要分为以下几部分:
- 1、条件控制进行的一次加载
- 2、修复预编译阶段的@selector的混乱问题
- 3、错误混乱的类处理
- 4、修复重映射一些没有被镜像文件加载进来的类
- 5、修复一些消息
- 6、当类里面有协议时:readProtocol 读取协议
- 7、修复没有被加载的协议
- 8、分类处理
- 9、类的加载处理
- 10、没有被处理的类,优化那些被侵犯的类
1、条件控制进行的一次加载
在doneOnce流程中通过NXCreateMapTable 创建表,存放类信息,即创建一张类的哈希表``gdb_objc_realized_classes,其目的是为了类查找方便、快捷
if (!doneOnce) {
//...省略
// namedClasses
// Preoptimized classes don't go in this table.
// 4/3 is NXMapTable's load factor
int namedClassesSize =
(isPreoptimized() ? unoptimizedTotalClasses : totalClasses) * 4 / 3;
//创建表(哈希表key-value),目的是查找快
gdb_objc_realized_classes =
NXCreateMapTable(NXStrValueMapPrototype, namedClassesSize);
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: first time tasks");
}
查看gdb_objc_realized_classes的注释说明,这个哈希表用于存储不在共享缓存且已命名类,无论类是否实现,其容量是类数量的4/3
// This is a misnomer: gdb_objc_realized_classes is actually a list of
// named classes not in the dyld shared cache, whether realized or not.
//gdb_objc_realized_classes实际上是不在dyld共享缓存中的已命名类的列表,无论是否实现
NXMapTable *gdb_objc_realized_classes; // exported for debuggers in objc-gdb.h
2、修复预编译阶段的@selector的混乱问题
主要是通过通过_getObjc2SelectorRefs拿到Mach_O中的静态段__objc_selrefs,遍历列表调用sel_registerNameNoLock将SEL添加到namedSelectors哈希表中
// Fix up @selector references 修复@selector引用
//sel 不是简单的字符串,而是带地址的字符串
static size_t UnfixedSelectors;
{
mutex_locker_t lock(selLock);
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (hi->hasPreoptimizedSelectors()) continue;
bool isBundle = hi->isBundle();
//通过_getObjc2SelectorRefs拿到Mach-O中的静态段__objc_selrefs
SEL *sels = _getObjc2SelectorRefs(hi, &count);
UnfixedSelectors += count;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) { //列表遍历
const char *name = sel_cname(sels[i]);
//注册sel操作,即将sel添加到
SEL sel = sel_registerNameNoLock(name, isBundle);
if (sels[i] != sel) {//当sel与sels[i]地址不一致时,需要调整为一致的
sels[i] = sel;
}
}
}
}
- 其中
_getObjc2SelectorRefs的源码如下,表示获取Mach-O中的静态段__objc_selrefs,后续通过_getObjc2开头的Mach-O静态段获取,都对应不同的section name
// function name content type section name
GETSECT(_getObjc2SelectorRefs, SEL, "__objc_selrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2MessageRefs, message_ref_t, "__objc_msgrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ClassRefs, Class, "__objc_classrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2SuperRefs, Class, "__objc_superrefs");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ClassList, classref_t const, "__objc_classlist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2NonlazyClassList, classref_t const, "__objc_nlclslist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2CategoryList, category_t * const, "__objc_catlist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2CategoryList2, category_t * const, "__objc_catlist2");
GETSECT(_getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList, category_t * const, "__objc_nlcatlist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ProtocolList, protocol_t * const, "__objc_protolist");
GETSECT(_getObjc2ProtocolRefs, protocol_t *, "__objc_protorefs");
GETSECT(getLibobjcInitializers, UnsignedInitializer, "__objc_init_func");
sel_registerNameNoLock源码路径如下:sel_registerNameNoLock -> __sel_registerName,如下所示,其关键代码是auto it = namedSelectors.get().insert(name);,即将sel插入namedSelectors哈希表
SEL sel_registerNameNoLock(const char *name, bool copy) {
return __sel_registerName(name, 0, copy); // NO lock, maybe copy
}
static SEL __sel_registerName(const char *name, bool shouldLock, bool copy)
{
SEL result = 0;
if (shouldLock) selLock.assertUnlocked();
else selLock.assertLocked();
if (!name) return (SEL)0;
result = search_builtins(name);
if (result) return result;
conditional_mutex_locker_t lock(selLock, shouldLock);
auto it = namedSelectors.get().insert(name);//sel插入表
if (it.second) {
// No match. Insert.
*it.first = (const char *)sel_alloc(name, copy);
}
return (SEL)*it.first;
}
3、错误混乱的类处理
主要是从Mach-O中取出所有类,在遍历进行处理
//3、错误混乱的类处理
// Discover classes. Fix up unresolved future classes. Mark bundle classes.
bool hasDyldRoots = dyld_shared_cache_some_image_overridden();
//读取类:readClass
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (! mustReadClasses(hi, hasDyldRoots)) {
// Image is sufficiently optimized that we need not call readClass()
continue;
}
//从编译后的类列表中取出所有类,即从Mach-O中获取静态段__objc_classlist,是一个classref_t类型的指针
classref_t const *classlist = _getObjc2ClassList(hi, &count);
bool headerIsBundle = hi->isBundle();
bool headerIsPreoptimized = hi->hasPreoptimizedClasses();
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
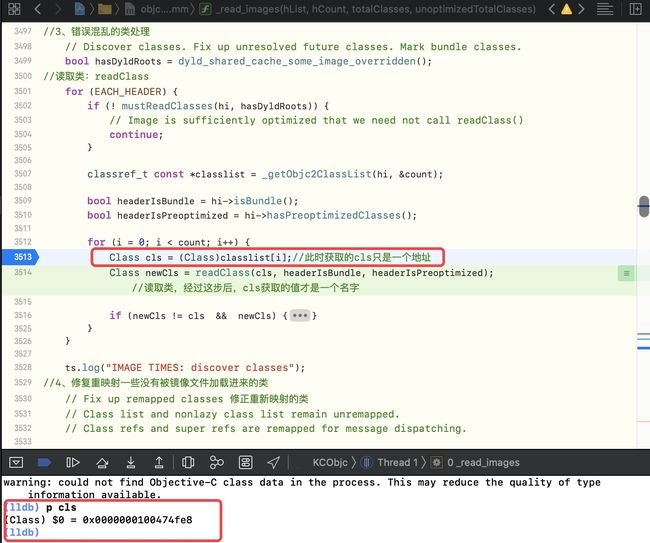
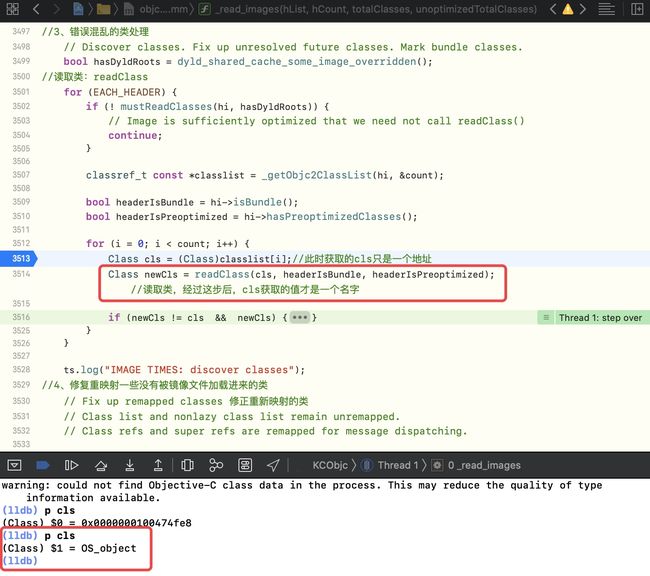
Class cls = (Class)classlist[i];//此时获取的cls只是一个地址
Class newCls = readClass(cls, headerIsBundle, headerIsPreoptimized); //读取类,经过这步后,cls获取的值才是一个名字
//经过调试,并未执行if里面的流程
//初始化所有懒加载的类需要的内存空间,但是懒加载类的数据现在是没有加载到的,连类都没有初始化
if (newCls != cls && newCls) {
// Class was moved but not deleted. Currently this occurs
// only when the new class resolved a future class.
// Non-lazily realize the class below.
//将懒加载的类添加到数组中
resolvedFutureClasses = (Class *)
realloc(resolvedFutureClasses,
(resolvedFutureClassCount+1) * sizeof(Class));
resolvedFutureClasses[resolvedFutureClassCount++] = newCls;
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover classes");
所以到这步为止,类的信息目前仅存储了地址+名称
4、修复重映射一些没有被镜像文件加载进来的类
主要是将未映射的Class 和Super Class进行重映射,其中
-
_getObjc2ClassRefs是获取Mach-O中的静态段__objc_classrefs即类的引用 -
_getObjc2SuperRefs是获取Mach-O中的静态段__objc_superrefs即父类的引用 -
通过注释可以得知,被
remapClassRef的类都是懒加载的类,所以最初经过调试时,这部分代码是没有执行的
//4、修复重映射一些没有被镜像文件加载进来的类
// Fix up remapped classes 修正重新映射的类
// Class list and nonlazy class list remain unremapped.类列表和非惰性类列表保持未映射
// Class refs and super refs are remapped for message dispatching.类引用和超级引用将重新映射以进行消息分发
//经过调试,并未执行if里面的流程
//将未映射的Class 和 Super Class重映射,被remap的类都是懒加载的类
if (!noClassesRemapped()) {
for (EACH_HEADER) {
Class *classrefs = _getObjc2ClassRefs(hi, &count);//Mach-O的静态段 __objc_classrefs
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapClassRef(&classrefs[i]);
}
// fixme why doesn't test future1 catch the absence of this?
classrefs = _getObjc2SuperRefs(hi, &count);//Mach_O中的静态段 __objc_superrefs
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapClassRef(&classrefs[i]);
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: remap classes");
5、修复一些消息
主要是通过_getObjc2MessageRefs 获取Mach-O的静态段 __objc_msgrefs,并遍历通过fixupMessageRef将函数指针进行注册,并fix为新的函数指针
#if SUPPORT_FIXUP
//5、修复一些消息
// Fix up old objc_msgSend_fixup call sites
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// _getObjc2MessageRefs 获取Mach-O的静态段 __objc_msgrefs
message_ref_t *refs = _getObjc2MessageRefs(hi, &count);
if (count == 0) continue;
if (PrintVtables) {
_objc_inform("VTABLES: repairing %zu unsupported vtable dispatch "
"call sites in %s", count, hi->fname());
}
//经过调试,并未执行for里面的流程
//遍历将函数指针进行注册,并fix为新的函数指针
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
fixupMessageRef(refs+i);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up objc_msgSend_fixup");
#endif
6、当类里面有协议时:readProtocol 读取协议
//6、当类里面有协议时:readProtocol 读取协议
// Discover protocols. Fix up protocol refs. 发现协议。修正协议参考
//遍历所有协议列表,并且将协议列表加载到Protocol的哈希表中
for (EACH_HEADER) {
extern objc_class OBJC_CLASS_$_Protocol;
//cls = Protocol类,所有协议和对象的结构体都类似,isa都对应Protocol类
Class cls = (Class)&OBJC_CLASS_$_Protocol;
ASSERT(cls);
//获取protocol哈希表 -- protocol_map
NXMapTable *protocol_map = protocols();
bool isPreoptimized = hi->hasPreoptimizedProtocols();
// Skip reading protocols if this is an image from the shared cache
// and we support roots
// Note, after launch we do need to walk the protocol as the protocol
// in the shared cache is marked with isCanonical() and that may not
// be true if some non-shared cache binary was chosen as the canonical
// definition
if (launchTime && isPreoptimized && cacheSupportsProtocolRoots) {
if (PrintProtocols) {
_objc_inform("PROTOCOLS: Skipping reading protocols in image: %s",
hi->fname());
}
continue;
}
bool isBundle = hi->isBundle();
//通过_getObjc2ProtocolList 获取到Mach-O中的静态段__objc_protolist协议列表,
//即从编译器中读取并初始化protocol
protocol_t * const *protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//通过添加protocol到protocol_map哈希表中
readProtocol(protolist[i], cls, protocol_map,
isPreoptimized, isBundle);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover protocols");
- 通过
NXMapTable *protocol_map = protocols();创建protocol哈希表,表的名称为protocol_map
/***********************************************************************
* protocols
* Returns the protocol name => protocol map for protocols.
* Locking: runtimeLock must read- or write-locked by the caller
**********************************************************************/
static NXMapTable *protocols(void)
{
static NXMapTable *protocol_map = nil;
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
INIT_ONCE_PTR(protocol_map,
NXCreateMapTable(NXStrValueMapPrototype, 16),
NXFreeMapTable(v) );
return protocol_map;
}
- 通过
_getObjc2ProtocolList获取到Mach-O中的静态段__objc_protolist协议列表,即从编译器中读取并初始化protocol
protocol_t * const *protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolList(hi, &count);
- 循环遍历协议列表,通过
readProtocol方法将协议添加到protocol_map哈希表中
readProtocol(protolist[i], cls, protocol_map,
isPreoptimized, isBundle);
7、修复没有被加载的协议
主要是通过 _getObjc2ProtocolRefs 获取到Mach-O的静态段 __objc_protorefs(与6中的__objc_protolist并不是同一个东西),然后遍历需要修复的协议,通过remapProtocolRef比较当前协议和协议列表中的同一个内存地址的协议是否相同,如果不同则替换
//7、修复没有被加载的协议
// Fix up @protocol references
// Preoptimized images may have the right
// answer already but we don't know for sure.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// At launch time, we know preoptimized image refs are pointing at the
// shared cache definition of a protocol. We can skip the check on
// launch, but have to visit @protocol refs for shared cache images
// loaded later.
if (launchTime && cacheSupportsProtocolRoots && hi->isPreoptimized())
continue;
//_getObjc2ProtocolRefs 获取到Mach-O的静态段 __objc_protorefs
protocol_t **protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {//遍历
//比较当前协议和协议列表中的同一个内存地址的协议是否相同,如果不同则替换
remapProtocolRef(&protolist[i]);//经过代码调试,并未执行
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up @protocol references");
其中remapProtocolRef的源码实现如下
/***********************************************************************
* remapProtocolRef
* Fix up a protocol ref, in case the protocol referenced has been reallocated.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be read- or write-locked by the caller
**********************************************************************/
static size_t UnfixedProtocolReferences;
static void remapProtocolRef(protocol_t **protoref)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
//获取协议列表中统一内存地址的协议
protocol_t *newproto = remapProtocol((protocol_ref_t)*protoref);
if (*protoref != newproto) {//如果当前协议 与 同一内存地址协议不同,则替换
*protoref = newproto;
UnfixedProtocolReferences++;
}
}
8、分类处理
主要是处理分类,需要在分类初始化并将数据加载到类后才执行,对于运行时出现的分类,将分类的发现推迟推迟到对_dyld_objc_notify_register的调用完成后的第一个load_images调用为止
//8、分类处理
// Discover categories. Only do this after the initial category 发现分类
// attachment has been done. For categories present at startup,
// discovery is deferred until the first load_images call after
// the call to _dyld_objc_notify_register completes. rdar://problem/53119145
if (didInitialAttachCategories) {
for (EACH_HEADER) {
load_categories_nolock(hi);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover categories");
9、类的加载处理
主要是实现类的加载处理,实现非懒加载类
-
通过
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList获取Mach-O的静态段__objc_nlclslist非懒加载类表 -
通过
addClassTableEntry将非懒加载类插入类表,存储到内存,如果已经添加就不会载添加,需要确保整个结构都被添加 -
通过
realizeClassWithoutSwift实现当前的类,因为前面3中的readClass读取到内存的仅仅只有地址+名称,类的data数据并没有加载出来
// Realize non-lazy classes (for +load methods and static instances) 初始化非懒加载类,进行rw、ro等操作:realizeClassWithoutSwift
//懒加载类 -- 别人不动我,我就不动
//实现非懒加载的类,对于load方法和静态实例变量
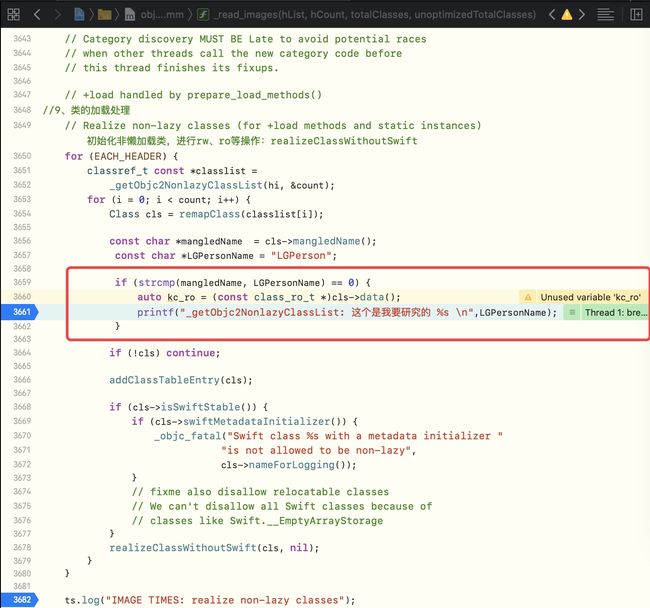
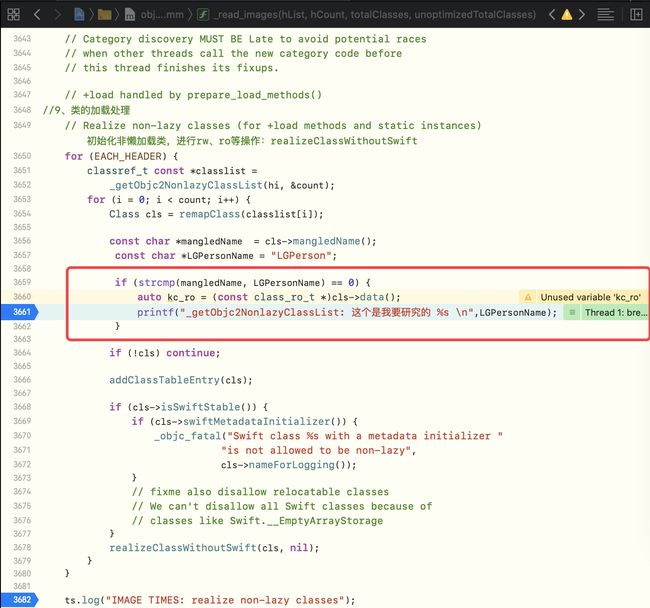
for (EACH_HEADER) {
//通过_getObjc2NonlazyClassList获取Mach-O的静态段__objc_nlclslist非懒加载类表
classref_t const *classlist =
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Class cls = remapClass(classlist[i]);
const char *mangledName = cls->mangledName();
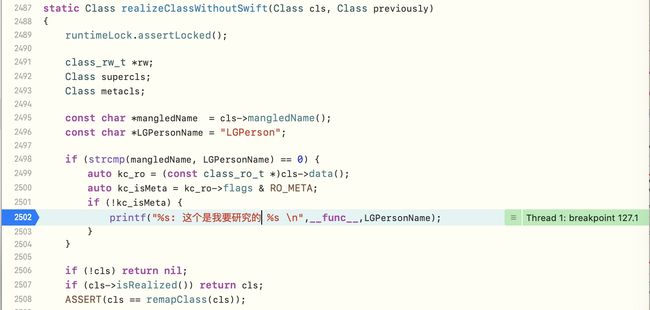
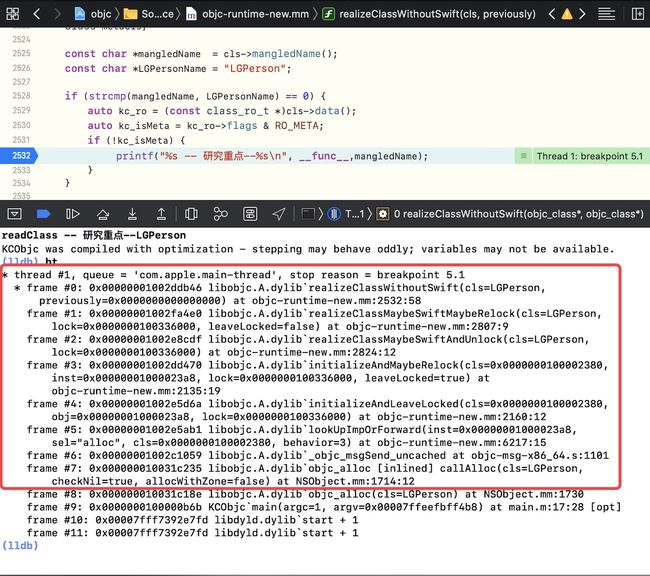
const char *LGPersonName = "LGPerson";
if (strcmp(mangledName, LGPersonName) == 0) {
auto kc_ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();
printf("_getObjc2NonlazyClassList: 这个是我要研究的 %s \n",LGPersonName);
}
if (!cls) continue;
addClassTableEntry(cls);//插入表,但是前面已经插入过了,所以不会重新插入
if (cls->isSwiftStable()) {
if (cls->swiftMetadataInitializer()) {
_objc_fatal("Swift class %s with a metadata initializer "
"is not allowed to be non-lazy",
cls->nameForLogging());
}
// fixme also disallow relocatable classes
// We can't disallow all Swift classes because of
// classes like Swift.__EmptyArrayStorage
}
//实现当前的类,因为前面readClass读取到内存的仅仅只有地址+名称,类的data数据并没有加载出来
//实现所有非懒加载的类(实例化类对象的一些信息,例如rw)
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: realize non-lazy classes");
10、没有被处理的类,优化那些被侵犯的类
主要是实现没有被处理的类,优化被侵犯的类
// Realize newly-resolved future classes, in case CF manipulates them
if (resolvedFutureClasses) {
for (i = 0; i < resolvedFutureClassCount; i++) {
Class cls = resolvedFutureClasses[i];
if (cls->isSwiftStable()) {
_objc_fatal("Swift class is not allowed to be future");
}
//实现类
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);
cls->setInstancesRequireRawIsaRecursively(false/*inherited*/);
}
free(resolvedFutureClasses);
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: realize future classes");
if (DebugNonFragileIvars) {
//实现所有类
realizeAllClasses();
}
我们需要重点关注的是3中的readClass以及9中realizeClassWithoutSwift两个方法
readClass:读取类
readClass主要是读取类,在未调用该方法前,cls只是一个地址,执行该方法后,cls是类的名称,其源码实现如下,关键代码是addNamedClass和addClassTableEntry,源码实现如下
/***********************************************************************
* readClass
* Read a class and metaclass as written by a compiler. 读取编译器编写的类和元类
* Returns the new class pointer. This could be: 返回新的类指针,可能是:
* - cls
* - nil (cls has a missing weak-linked superclass)
* - something else (space for this class was reserved by a future class)
*
* Note that all work performed by this function is preflighted by
* mustReadClasses(). Do not change this function without updating that one.
*
* Locking: runtimeLock acquired by map_images or objc_readClassPair
**********************************************************************/
Class readClass(Class cls, bool headerIsBundle, bool headerIsPreoptimized)
{
const char *mangledName = cls->mangledName();//名字
// **CJL写的** ----如果想进入自定义,自己加一个判断
const char *LGPersonName = "LGPerson";
if (strcmp(mangledName, LGPersonName) == 0) {
auto kc_ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();
printf("%s -- 研究重点--%s\n", __func__,mangledName);
}
//当前类的父类中若有丢失的weak-linked类,则返回nil
if (missingWeakSuperclass(cls)) {
// No superclass (probably weak-linked).
// Disavow any knowledge of this subclass.
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING class '%s' with "
"missing weak-linked superclass",
cls->nameForLogging());
}
addRemappedClass(cls, nil);
cls->superclass = nil;
return nil;
}
cls->fixupBackwardDeployingStableSwift();
//判断是不是后期要处理的类
//正常情况下,不会走到popFutureNamedClass,因为这是专门针对未来待处理的类的操作
//通过断点调试,不会走到if流程里面,因此也不会对ro、rw进行操作
Class replacing = nil;
if (Class newCls = popFutureNamedClass(mangledName)) {
// This name was previously allocated as a future class.
// Copy objc_class to future class's struct.
// Preserve future's rw data block.
if (newCls->isAnySwift()) {
_objc_fatal("Can't complete future class request for '%s' "
"because the real class is too big.",
cls->nameForLogging());
}
//读取class的data,设置ro、rw
//经过调试,并不会走到这里
class_rw_t *rw = newCls->data();
const class_ro_t *old_ro = rw->ro();
memcpy(newCls, cls, sizeof(objc_class));
rw->set_ro((class_ro_t *)newCls->data());
newCls->setData(rw);
freeIfMutable((char *)old_ro->name);
free((void *)old_ro);
addRemappedClass(cls, newCls);
replacing = cls;
cls = newCls;
}
//判断是否类是否已经加载到内存
if (headerIsPreoptimized && !replacing) {
// class list built in shared cache
// fixme strict assert doesn't work because of duplicates
// ASSERT(cls == getClass(name));
ASSERT(getClassExceptSomeSwift(mangledName));
} else {
addNamedClass(cls, mangledName, replacing);//加载共享缓存中的类
addClassTableEntry(cls);//插入表,即相当于从mach-O文件 读取到 内存 中
}
// for future reference: shared cache never contains MH_BUNDLEs
if (headerIsBundle) {
cls->data()->flags |= RO_FROM_BUNDLE;
cls->ISA()->data()->flags |= RO_FROM_BUNDLE;
}
return cls;
}
通过源码实现,主要分为以下几步:
- 通过
mangledName获取类的名字,其中mangledName方法的源码实现如下
const char *mangledName() {
// fixme can't assert locks here
ASSERT(this);
if (isRealized() || isFuture()) { //这个初始化判断在lookupImp也有类似的
return data()->ro()->name;//如果已经实例化,则从ro中获取name
} else {
return ((const class_ro_t *)data())->name;//反之,从mach-O的数据data中获取name
}
}
-
当前类的父类中若有丢失的
weak-linked类,则返回nil -
判断是不是后期需要处理的类,在正常情况下,不会走到
popFutureNamedClass,因为这是专门针对未来待处理的类的操作,也可以通过断点调试,可知不会走到if流程里面,因此也不会对ro、rw进行操作-
data是mach-O的数据,并不在class的内存中 -
ro的赋值是从mach-O中的data强转赋值的 -
rw里的ro是从ro复制过去的
-
-
通过
addNamedClass将当前类添加到已经创建好的gdb_objc_realized_classes哈希表,该表用于存放所有类
/***********************************************************************
* addNamedClass 加载共享缓存中的类 插入表
* Adds name => cls to the named non-meta class map. 将name=> cls添加到命名的非元类映射
* Warns about duplicate class names and keeps the old mapping.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be held by the caller
**********************************************************************/
static void addNamedClass(Class cls, const char *name, Class replacing = nil)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
Class old;
if ((old = getClassExceptSomeSwift(name)) && old != replacing) {
inform_duplicate(name, old, cls);
// getMaybeUnrealizedNonMetaClass uses name lookups.
// Classes not found by name lookup must be in the
// secondary meta->nonmeta table.
addNonMetaClass(cls);
} else {
//添加到gdb_objc_realized_classes哈希表
NXMapInsert(gdb_objc_realized_classes, name, cls);
}
ASSERT(!(cls->data()->flags & RO_META));
// wrong: constructed classes are already realized when they get here
// ASSERT(!cls->isRealized());
}
- 通过
addClassTableEntry,将初始化的类添加到allocatedClasses表,这个表在iOS-底层原理 16:dyld与objc的关联文章中提及过,是在_objc_init中的runtime_init就创建了allocatedClasses表
/***********************************************************************
* addClassTableEntry 将一个类添加到所有类的表中
* Add a class to the table of all classes. If addMeta is true,
* automatically adds the metaclass of the class as well.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be held by the caller.
**********************************************************************/
static void
addClassTableEntry(Class cls, bool addMeta = true)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// This class is allowed to be a known class via the shared cache or via
// data segments, but it is not allowed to be in the dynamic table already.
auto &set = objc::allocatedClasses.get();//开辟的类的表,在objc_init中的runtime_init就创建了表
ASSERT(set.find(cls) == set.end());
if (!isKnownClass(cls))
set.insert(cls);
if (addMeta)
//添加到allocatedClasses哈希表
addClassTableEntry(cls->ISA(), false);
}
如果我们想在readClass源码中想定位到自定义的类,可以自定义加if判断

总结
所以综上所述,readClass的主要作用就是将Mach-O中的类读取到内存,即插入表中,但是目前的类仅有两个信息:地址以及名称,而mach-O的其中的data数据还未读取出来
realizeClassWithoutSwift:实现类
realizeClassWithoutSwift方法中有ro、rw的相关操作,这个方法在消息流程的慢速查找中有所提及,方法路径为:慢速查找(lookUpImpOrForward) – realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked – realizeClassMaybeSwiftMaybeRelock – realizeClassWithoutSwift(实现类)
realizeClassWithoutSwift方法主要作用是实现类,将类的data数据加载到内存中,主要有以下几部分操作:
- 【第一步】读取
data数据,并设置ro、rw - 【第二步】递归调用
realizeClassWithoutSwift完善继承链 - 【第三步】通过
methodizeClass方法化类
第一步:读取data数据
读取class的data数据,并将其强转为ro,以及rw初始化和ro拷贝一份到rw中的ro
-
ro表示readOnly,即只读,其在编译时就已经确定了内存,包含类名称、方法、协议和实例变量的信息,由于是只读的,所以属于Clean Memory,而Clean Memory是指加载后不会发生更改的内存 -
rw表示readWrite,即可读可写,由于其动态性,可能会往类中添加属性、方法、添加协议,在最新的2020的WWDC的对内存优化的说明Advancements in the Objective-C runtime - WWDC 2020 - Videos - Apple Developer中,提到rw,其实在rw中只有10%的类真正的更改了它们的方法,所以有了rwe,即类的额外信息。对于那些确实需要额外信息的类,可以分配rwe扩展记录中的一个,并将其滑入类中供其使用。其中rw就属于dirty memory,而dirty memory是指在进程运行时会发生更改的内存,类结构一经使用就会变成ditry memory,因为运行时会向它写入新数据,例如 创建一个新的方法缓存,并从类中指向它
// fixme verify class is not in an un-dlopened part of the shared cache?
//读取class的data(),以及ro/rw创建
auto ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data(); //读取类结构的bits属性、//ro -- clean memory,在编译时就已经确定了内存
auto isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META; //判断元类
if (ro->flags & RO_FUTURE) {
// This was a future class. rw data is already allocated.
rw = cls->data(); //dirty memory 进行赋值
ro = cls->data()->ro();
ASSERT(!isMeta);
cls->changeInfo(RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING, RW_FUTURE);
} else { //此时将数据读取进来了,也赋值完毕了
// Normal class. Allocate writeable class data.
rw = objc::zalloc(); //申请开辟zalloc -- rw
rw->set_ro(ro);//rw中的ro设置为临时变量ro
rw->flags = RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING|isMeta;
cls->setData(rw);//将cls的data赋值为rw形式
}
【第二步】递归调用 realizeClassWithoutSwift 完善 继承链
递归调用realizeClassWithoutSwift完善继承链,并设置当前类、父类、元类的rw
-
递归调用
realizeClassWithoutSwift设置父类、元类 -
设置
父类和元类的isa指向 -
通过
addSubclass 和 addRootClass设置父子的双向链表指向关系,即父类中可以找到子类,子类中可以找到父类
// Realize superclass and metaclass, if they aren't already.
// This needs to be done after RW_REALIZED is set above, for root classes.
// This needs to be done after class index is chosen, for root metaclasses.
// This assumes that none of those classes have Swift contents,
// or that Swift's initializers have already been called.
// fixme that assumption will be wrong if we add support
// for ObjC subclasses of Swift classes. --
//递归调用realizeClassWithoutSwift完善继承链,并处理当前类的父类、元类
//递归实现 设置当前类、父类、元类的 rw,主要目的是确定继承链 (类继承链、元类继承链)
//实现元类、父类
//当isa找到根元类之后,根元类的isa是指向自己的,不会返回nil从而导致死循环——remapClass中对类在表中进行查找的操作,如果表中已有该类,则返回一个空值;如果没有则返回当前类,这样保证了类只加载一次并结束递归
supercls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->superclass), nil);
metacls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->ISA()), nil);
...
// Update superclass and metaclass in case of remapping -- class 是 双向链表结构 即父子关系都确认了
// 将父类和元类给我们的类 分别是isa和父类的对应值
cls->superclass = supercls;
cls->initClassIsa(metacls);
...
// Connect this class to its superclass's subclass lists
//双向链表指向关系 父类中可以找到子类 子类中也可以找到父类
//通过addSubclass把当前类放到父类的子类列表中去
if (supercls) {
addSubclass(supercls, cls);
} else {
addRootClass(cls);
}
这里有一个问题,realizeClassWithoutSwift递归调用时,isa找到根元类之后,根元类的isa是指向自己,并不会返回nil,所以有以下递归终止条件,其目的是保证类只加载一次
- 在
realizeClassWithoutSwift中-
如果类
不存在,则返回nil -
如果类
已经实现,则直接返回cls
-
static Class realizeClassWithoutSwift(Class cls, Class previously)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
//如果类不存在,则返回nil
if (!cls) return nil;
如果类已经实现,则直接返回cls
if (cls->isRealized()) return cls;
ASSERT(cls == remapClass(cls));
...
}
- 在
remapClass方法中,如果cls不存在,则直接返回nil
/***********************************************************************
* remapClass
* Returns the live class pointer for cls, which may be pointing to
* a class struct that has been reallocated.
* Returns nil if cls is ignored because of weak linking.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be read- or write-locked by the caller
**********************************************************************/
static Class remapClass(Class cls)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
if (!cls) return nil;//如果cls不存在,则返回nil
auto *map = remappedClasses(NO);
if (!map)
return cls;
auto iterator = map->find(cls);
if (iterator == map->end())
return cls;
return std::get<1>(*iterator);
}
【第三步】通过 methodizeClass 方法化类
通过methodizeClass方法,从ro中读取方法列表(包括分类中的方法)、属性列表、协议列表赋值给rw,并返回cls
// Attach categories 附加类别 -- 疑问:ro中也有方法列表 rw中也有方法列表,下面这个方法可以说明
//将ro数据写入到rw
methodizeClass(cls, previously);
return cls;
断点调试 realizeClassWithoutSwift
如果我们需要跟踪自定义类,同样需要_read_images方法中的第九步的realizeClassWithoutSwift调用前,以及realizeClassWithoutSwift方法中增加自定义逻辑,主要是为了方便调试自定义类
下面,开启我们的断点调试
-
继续在
auto ro =加断点,继续运行,断住 – 这部分主要是读取data

查看ro,其中auto isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META; //判断元类
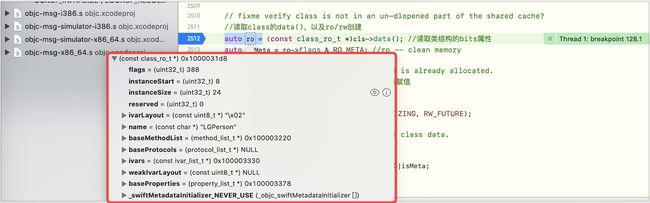
-
在else里面的
rw->set_ro(ro);处加断点,断住,查看rw,此时的rw是0x0,查看rw,其中包括ro和rwe
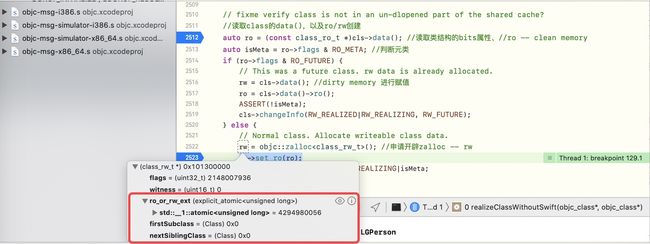
-
继续运行,然后查看
x/4gx cls,此时还是为0x0

这里我们需要去查看set_ro的源码实现,其路径为:set_ro–set_ro_or_rwe(找到get_ro_or_rwe,是通过ro_or_rw_ext_t类型从ro_or_rw_ext中获取) –ro_or_rw_ext_t中的ro

通过源码可知ro的获取主要分两种情况:有没有运行时,- 如果
有运行时,从rw中读取 - 反之,如果没有运行时,从
ro中读取
- 如果
-
在
if (supercls && !isMeta)处加断点,继续运行断住,此时断点的cls是地址,猜测cls可能是元类
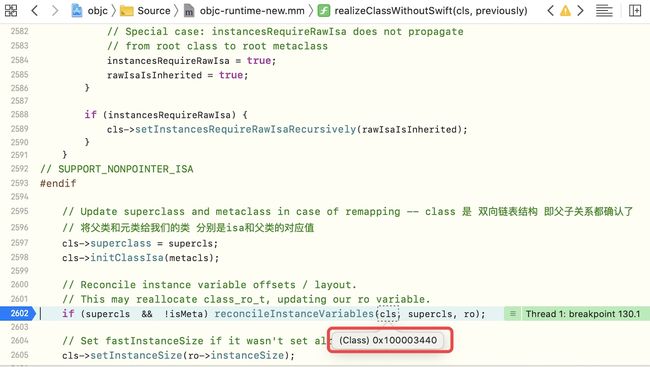
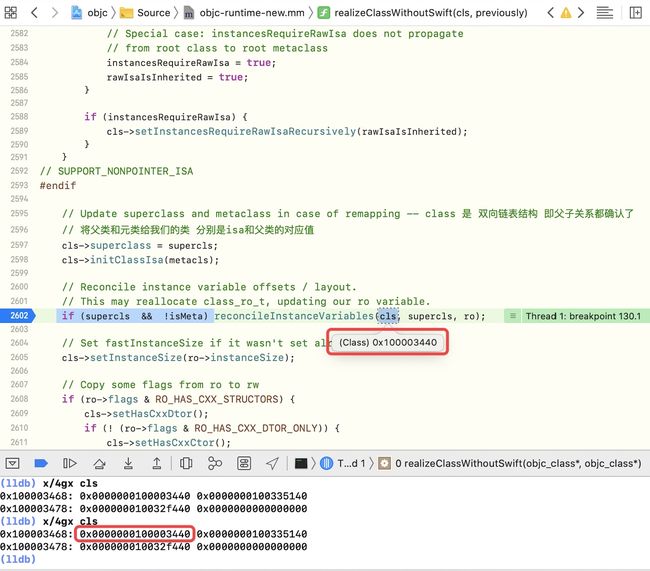
下面来进行验证:通过cls的isa指针地址来验证,是同一个地址,这个是存在一个递归(在supercls = 、metacls =部分递归)
methodizeClass:方法化类
其中methodizeClass的源码实现如下,主要分为几部分:
-
将
属性列表、方法列表、协议列表等贴到rwe中 -
附加
分类中的方法(将在下一篇文章中进行解释说明)
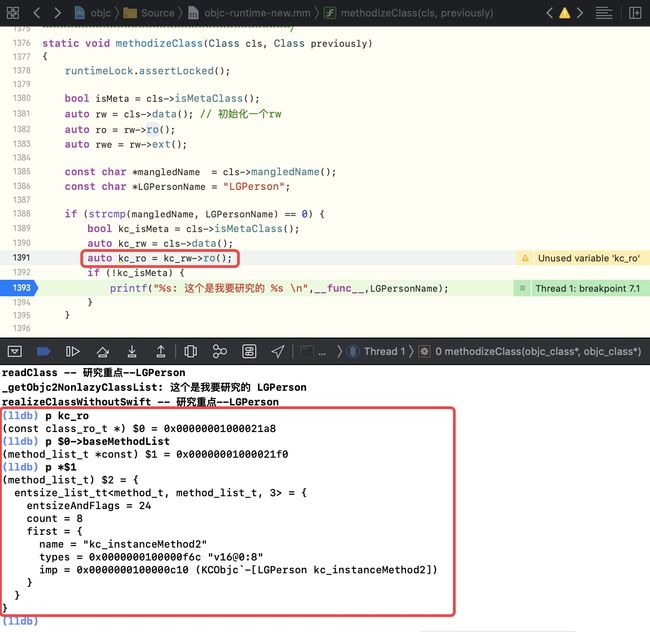
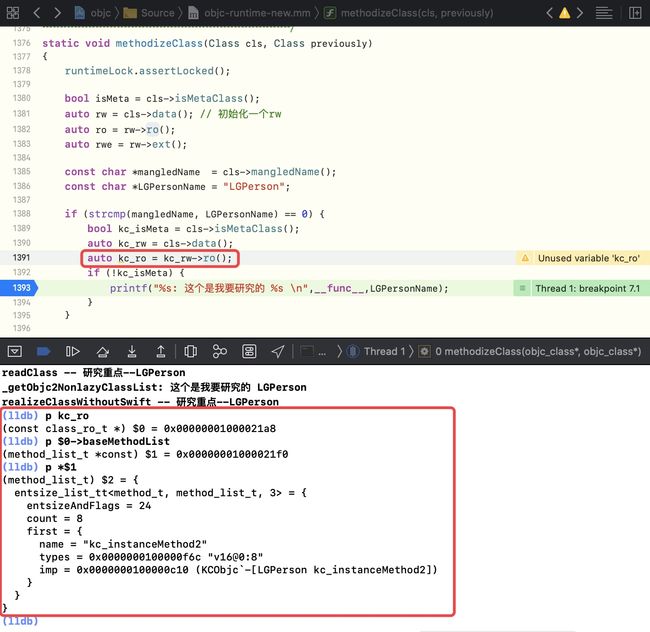
static void methodizeClass(Class cls, Class previously)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
auto rw = cls->data(); // 初始化一个rw
auto ro = rw->ro();
auto rwe = rw->ext();
...
// Install methods and properties that the class implements itself.
//将属性列表、方法列表、协议列表等贴到rw中
// 将ro中的方法列表加入到rw中
method_list_t *list = ro->baseMethods();//获取ro的baseMethods
if (list) {
prepareMethodLists(cls, &list, 1, YES, isBundleClass(cls));//methods进行排序
if (rwe) rwe->methods.attachLists(&list, 1);//对rwe进行处理
}
// 加入属性
property_list_t *proplist = ro->baseProperties;
if (rwe && proplist) {
rwe->properties.attachLists(&proplist, 1);
}
// 加入协议
protocol_list_t *protolist = ro->baseProtocols;
if (rwe && protolist) {
rwe->protocols.attachLists(&protolist, 1);
}
// Root classes get bonus method implementations if they don't have
// them already. These apply before category replacements.
if (cls->isRootMetaclass()) {
// root metaclass
addMethod(cls, @selector(initialize), (IMP)&objc_noop_imp, "", NO);
}
// Attach categories.
// 加入分类中的方法
if (previously) {
if (isMeta) {
objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, previously,
ATTACH_METACLASS);
} else {
// When a class relocates, categories with class methods
// may be registered on the class itself rather than on
// the metaclass. Tell attachToClass to look for those.
objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, previously,
ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS);
}
}
objc::unattachedCategories.attachToClass(cls, cls,
isMeta ? ATTACH_METACLASS : ATTACH_CLASS);
....
}
rwe的逻辑
方法列表加入rwe的逻辑如下:
-
获取
ro的baseMethods -
通过
prepareMethodLists方法排序 -
对
rwe进行处理即通过attachLists插入
方法如何排序
在消息流程的慢速查找流程iOS-底层原理 13:消息流程分析之慢速查找文章中,方法的查找算法是通过二分查找算法,说明sel-imp是有排序的,那么是如何排序的呢?
- 进入
prepareMethodLists的源码实现,其内部是通过fixupMethodList方法排序
static void
prepareMethodLists(Class cls, method_list_t **addedLists, int addedCount,
bool baseMethods, bool methodsFromBundle)
{
...
// Add method lists to array.
// Reallocate un-fixed method lists.
// The new methods are PREPENDED to the method list array.
for (int i = 0; i < addedCount; i++) {
method_list_t *mlist = addedLists[i];
ASSERT(mlist);
// Fixup selectors if necessary
if (!mlist->isFixedUp()) {
fixupMethodList(mlist, methodsFromBundle, true/*sort*/);//排序
}
}
...
}
- 进入
fixupMethodList源码实现,是根据selector address排序
static void
fixupMethodList(method_list_t *mlist, bool bundleCopy, bool sort)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
ASSERT(!mlist->isFixedUp());
// fixme lock less in attachMethodLists ?
// dyld3 may have already uniqued, but not sorted, the list
if (!mlist->isUniqued()) {
mutex_locker_t lock(selLock);
// Unique selectors in list.
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
const char *name = sel_cname(meth.name);
meth.name = sel_registerNameNoLock(name, bundleCopy);
}
}
// Sort by selector address.根据sel地址排序
if (sort) {
method_t::SortBySELAddress sorter;
std::stable_sort(mlist->begin(), mlist->end(), sorter);
}
// Mark method list as uniqued and sorted
mlist->setFixedUp();
}
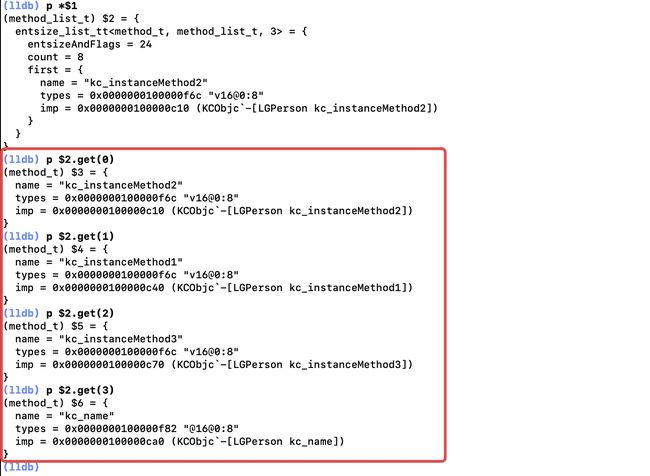
验证方法排序
下面我们可以通过调试来验证方法的排序
-
读取
ro中的methodlist -
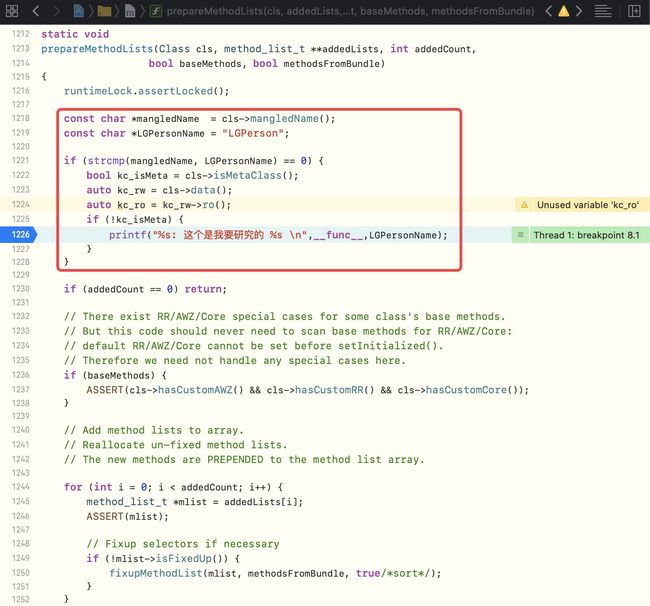
进入
prepareMethodLists源码,加自定义断点(主要是为了针对性研究),执行断点,运行到自定义逻辑并断住(这里加kc_isMeta,主要是用于过滤掉同名的元类中的methods)
-
进入
fixupMethodList源码实现,(sel 根据selAdress 排序) ,再次断点,来到下图部分,即方法经过了一层排序

所以 排序前后的methodlist对比如下,所以总结如下:methodizeClass方法中实现类中方法(协议等)的序列化

attachToClass方法
在methodlist方法主要是将分类添加到主类中,其源码实现如下
void attachToClass(Class cls, Class previously, int flags)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
ASSERT((flags & ATTACH_CLASS) ||
(flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) ||
(flags & ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS));
const char *mangledName = cls->mangledName();
const char *LGPersonName = "LGPerson";
if (strcmp(mangledName, LGPersonName) == 0) {
bool kc_isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
auto kc_rw = cls->data();
auto kc_ro = kc_rw->ro();
if (!kc_isMeta) {
printf("%s: 这个是我要研究的 %s \n",__func__,LGPersonName);
}
}
auto &map = get();
auto it = map.find(previously);//找到一个分类进来一次,即一个个加载分类,不要混乱
if (it != map.end()) {//这里会走进来:当主类没有实现load,分类开始加载,迫使主类加载,会走到if流程里面
category_list &list = it->second;
if (flags & ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS) {//判断是否是元类
int otherFlags = flags & ~ATTACH_CLASS_AND_METACLASS;
attachCategories(cls, list.array(), list.count(), otherFlags | ATTACH_CLASS);//实例方法
attachCategories(cls->ISA(), list.array(), list.count(), otherFlags | ATTACH_METACLASS);//类方法
} else {
//如果不是元类,则只走一次 attachCategories
attachCategories(cls, list.array(), list.count(), flags);
}
map.erase(it);
}
}
因为attachToClass中的外部循环是找到一个分类就会进到attachCategories一次,即找一个就循环一次
attachCategories方法
在attachCategories 方法中准备分类的数据,其源码实现如下
static void
attachCategories(Class cls, const locstamped_category_t *cats_list, uint32_t cats_count,
int flags)
{
if (slowpath(PrintReplacedMethods)) {
printReplacements(cls, cats_list, cats_count);
}
if (slowpath(PrintConnecting)) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: attaching %d categories to%s class '%s'%s",
cats_count, (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) ? " existing" : "",
cls->nameForLogging(), (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) ? " (meta)" : "");
}
/*
* Only a few classes have more than 64 categories during launch.
* This uses a little stack, and avoids malloc.
*
* Categories must be added in the proper order, which is back
* to front. To do that with the chunking, we iterate cats_list
* from front to back, build up the local buffers backwards,
* and call attachLists on the chunks. attachLists prepends the
* lists, so the final result is in the expected order.
*/
constexpr uint32_t ATTACH_BUFSIZ = 64;
method_list_t *mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];
property_list_t *proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];
protocol_list_t *protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];
uint32_t mcount = 0;
uint32_t propcount = 0;
uint32_t protocount = 0;
bool fromBundle = NO;
bool isMeta = (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS);
/*
rwe的创建,
那么为什么要在这里进行`rwe的初始化`?因为我们现在要做一件事:往`本类`中`添加属性、方法、协议`等
*/
auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();
//mlists 是一个二维数组
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cats_count; i++) {
auto& entry = cats_list[i];
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);
if (mlist) {
if (mcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {//mcount = 0,ATTACH_BUFSIZ= 64,不会走到if里面的流程
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle);//准备排序
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
mcount = 0;
}
mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++mcount] = mlist;
fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();
}
property_list_t *proplist =
entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi);
if (proplist) {
if (propcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {
rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount);
propcount = 0;
}
proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++propcount] = proplist;
}
protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocolsForMeta(isMeta);
if (protolist) {
if (protocount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {
rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount);
protocount = 0;
}
protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++protocount] = protolist;
}
}
if (mcount > 0) {
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount, NO, fromBundle);//排序
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount);//mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount 为内存平移
if (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) flushCaches(cls);
}
rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - propcount, propcount);
rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - protocount, protocount);
}
- 在
auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();是进行rwe的创建,那么为什么要在这里进行rwe的初始化??因为我们现在要做一件事:往本类中添加属性、方法、协议等,即对原来的 clean memory要进行处理了-
进入
extAllocIfNeeded方法的源码实现,判断rwe是否存在,如果存在则直接获取,如果不存在则开辟 -
进入
extAlloc源码实现,即对rwe 0-1的过程,在此过程中,就将本类的data数据加载进去了
-
class_rw_ext_t *extAllocIfNeeded() {
auto v = get_ro_or_rwe();
if (fastpath(v.is())) { //判断rwe是否存在
return v.get();//如果存在,则直接获取
} else {
return extAlloc(v.get());//如果不存在则进行开辟
}
}
//extAlloc源码实现
class_rw_ext_t *
class_rw_t::extAlloc(const class_ro_t *ro, bool deepCopy)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
//此时只有rw,需要对rwe进行数据添加,即0-1的过程
auto rwe = objc::zalloc();//创建
rwe->version = (ro->flags & RO_META) ? 7 : 0;
method_list_t *list = ro->baseMethods();
if (list) {
if (deepCopy) list = list->duplicate();
rwe->methods.attachLists(&list, 1);
}
// See comments in objc_duplicateClass
// property lists and protocol lists historically
// have not been deep-copied
//
// This is probably wrong and ought to be fixed some day
property_list_t *proplist = ro->baseProperties;
if (proplist) {
rwe->properties.attachLists(&proplist, 1);
}
protocol_list_t *protolist = ro->baseProtocols;
if (protolist) {
rwe->protocols.attachLists(&protolist, 1);
}
set_ro_or_rwe(rwe, ro);
return rwe;
}
-
其中关键代码是
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount);即存入mlists的末尾,mlists的数据来源前面的for循环 -
在调试运行时,发现
category_t中的name编译时是LGPerson(参考clang编译时的那么),运行时是LGA即分类的名字 -
代码
mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++mcount] = mlist;,经过调试发现此时的mcount等于1,即可以理解为倒序插入,64的原因是允许容纳64个(最多64个分类)
总结:本类 中 需要添加属性、方法等,所以需要初始化rwe,rwe的初始化主要涉及:分类、addMethod、addProperty、addprotocol , 即对原始类进行修改或者处理时,才会进行rwe的初始化
attachLists方法:插入
- 其中
方法、属性继承于entsize_list_tt,协议则是类似entsize_list_tt实现,都是二维数组
struct method_list_t : entsize_list_tt
struct property_list_t : entsize_list_tt
struct protocol_list_t {
// count is pointer-sized by accident.
uintptr_t count;
protocol_ref_t list[0]; // variable-size
size_t byteSize() const {
return sizeof(*this) + count*sizeof(list[0]);
}
protocol_list_t *duplicate() const {
return (protocol_list_t *)memdup(this, this->byteSize());
}
...
}
- 进入
attachLists方法的源码实现
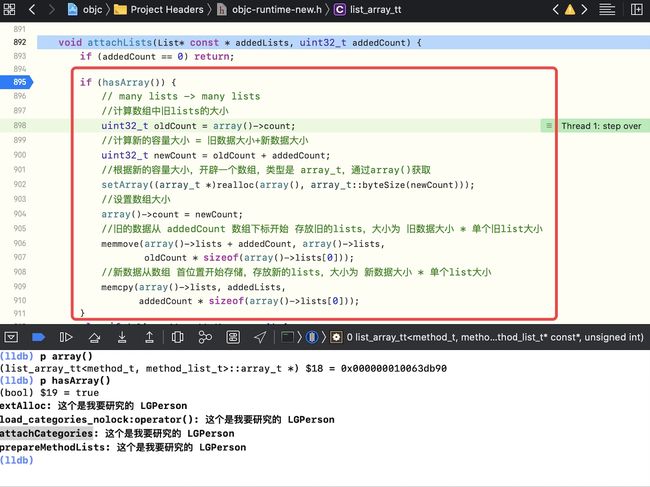
void attachLists(List* const * addedLists, uint32_t addedCount) {
if (addedCount == 0) return;
if (hasArray()) {
// many lists -> many lists
//计算数组中旧lists的大小
uint32_t oldCount = array()->count;
//计算新的容量大小 = 旧数据大小+新数据大小
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
//根据新的容量大小,开辟一个数组,类型是 array_t,通过array()获取
setArray((array_t *)realloc(array(), array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
//设置数组大小
array()->count = newCount;
//旧的数据从 addedCount 数组下标开始 存放旧的lists,大小为 旧数据大小 * 单个旧list大小
memmove(array()->lists + addedCount, array()->lists,
oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
//新数据从数组 首位置开始存储,存放新的lists,大小为 新数据大小 * 单个list大小
memcpy(
array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
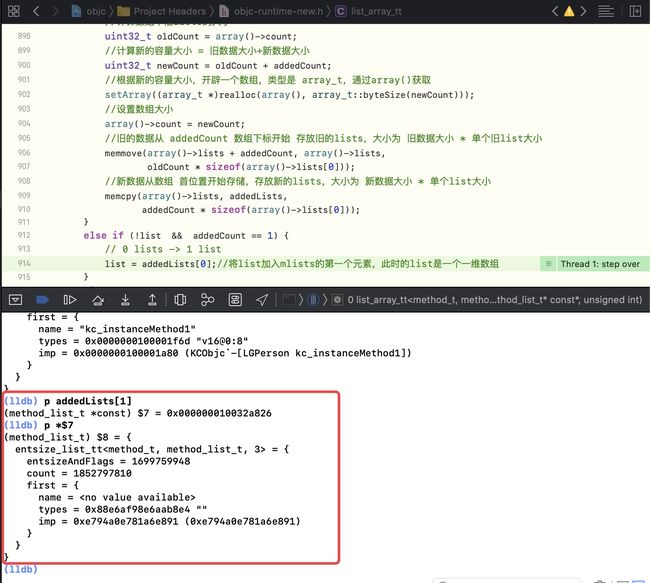
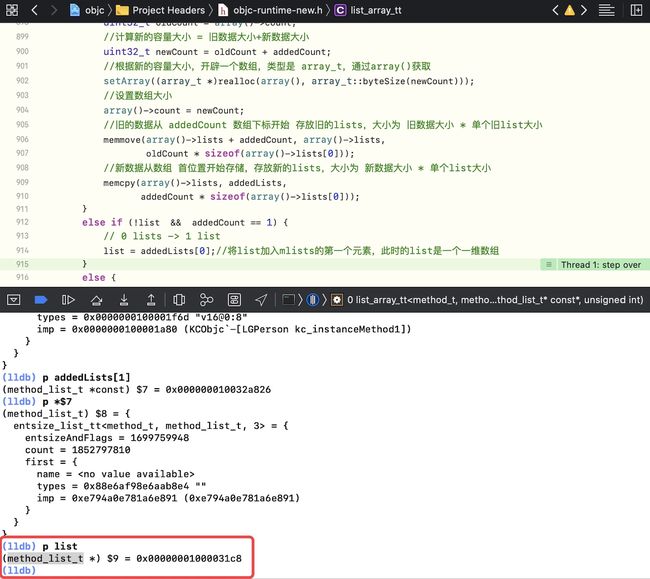
else if (!list && addedCount == 1) {
// 0 lists -> 1 list
list = addedLists[0];//将list加入mlists的第一个元素,此时的list是一个一维数组
}
else {
// 1 list -> many lists 有了一个list,有往里加很多list
//新的list就是分类,来自LRU的算法思维,即最近最少使用
//获取旧的list
List* oldList = list;
uint32_t oldCount = oldList ? 1 : 0;
//计算容量和 = 旧list个数+新lists的个数
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
//开辟一个容量和大小的集合,类型是 array_t,即创建一个数组,放到array中,通过array()获取
setArray((array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
//设置数组的大小
array()->count = newCount;
//判断old是否存在,old肯定是存在的,将旧的list放入到数组的末尾
if (oldList) array()->lists[addedCount] = oldList;
// memcpy(开始位置,放什么,放多大) 是内存平移,从数组起始位置存入新的list
//其中array()->lists 表示首位元素位置
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
}
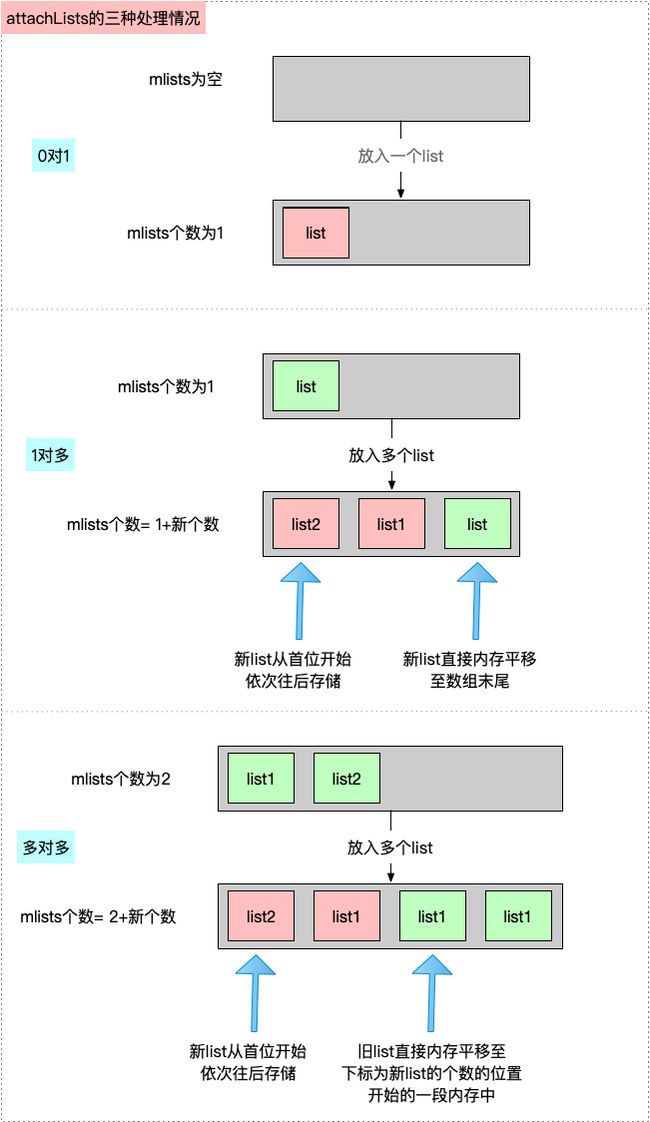
从源码可以得知,插入表主要分为三种情况:
-
【情况1:
多对多】如果当前调用attachLists的list_array_tt二维数组中有多个一维数组-
计算数组中
旧lists的大小 -
计算新的容量大小 =
旧数据大小+新数据大小 -
根据新的容量大小,开辟一个数组,类型是
array_t,通过array()获取 -
设置数组大小
-
旧的数据
从 addedCount 数组下标开始 存放旧的lists,大小为旧数据大小 * 单个旧list大小,即整段平移,可以简单理解为原来的数据移动到后面,即指针偏移 -
新数据
从数组 首位置开始存储,存放新的lists,大小为新数据大小 * 单个list大小,可以简单理解为越晚加进来,越在前面,越在前面,调用时则优先调用
-
-
【情况2:
0对一】如果调用attachLists的list_array_tt二维数组为空且新增大小数目为 1- 直接赋值
addedList的第一个list
- 直接赋值
-
【情况3:
一对多】如果当前调用attachLists的list_array_tt二维数组只有一个一维数组-
获取旧的list
-
计算
容量和 = 旧list个数+新lists的个数 -
开辟一个容量和大小的集合,类型是
array_t,即创建一个数组,放到array中,通过array()获取 -
设置数组的大小
-
判断old是否存在,old肯定是存在的,将
旧的list放入到数组的末尾 -
memcpy(开始位置,放什么,放多大)是内存平移,从数组起始位置开始存入新的list,其中array()->lists表示首位元素位置
-
针对情况3,这里的lists是指分类
-
这是日常开发中,为什么
子类实现父类方法会把父类方法覆盖的原因 -
同理,对于同名方法,
分类方法覆盖类方法的原因 -
这个操作来自一个算法思维
LRU即最近最少使用,加这个newlist的目的是由于要使用这个newlist中的方法,这个newlist对于用户的价值要高,即优先调用 -
会来到
1对多的原因 ,主要是有分类的添加,即旧的元素在后面,新的元素在前面 ,究其根本原因主要是优先调用category,这也是分类的意义所在
memmove和memcpy的区别
-
在不知道需要平移的内存大小时,需要
memmove进行内存平移,保证安全 -
memcpy从原内存地址的起始位置开始拷贝若干个字节到目标内存地址中,速度快
rwe 数据加载
rwe – 本类的数据加载【重点!!!】
下面通过调试来验证rwe数据0-1的过程,即添加类的方法列表
-
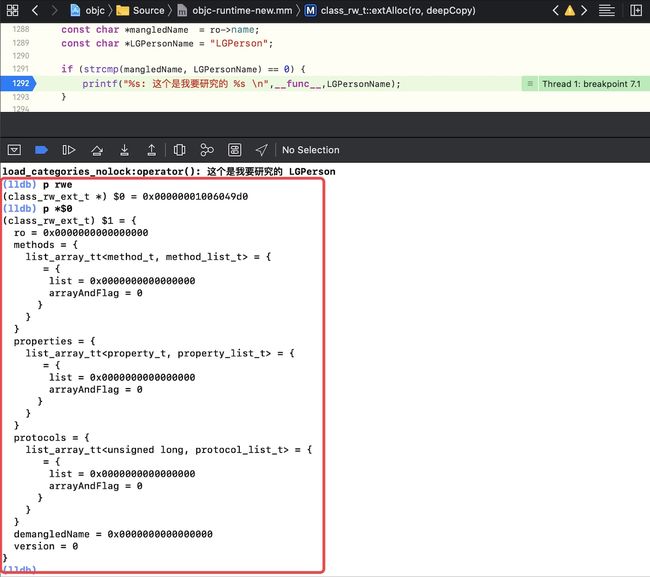
在
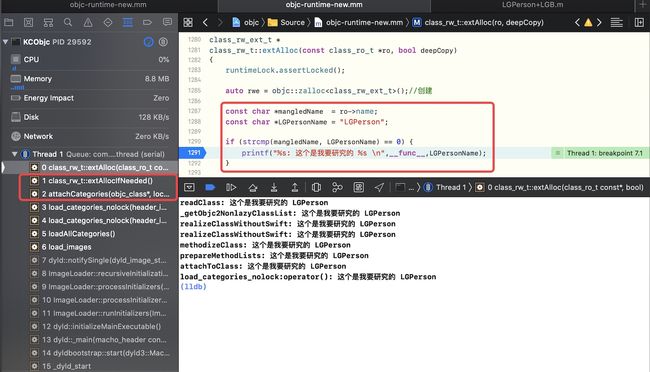
attachCategories -> extAllocIfNeeded -> extAlloc增加自定义逻辑,运行,并断住,从堆栈信息可以看出是从attachCategories方法中auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();过来的,这里的作用是开辟rwe, -
继续往下执行到
if (list) {断住 -
在
attachLists方法中的if (hasArray()) {处设置断点,并运行断住,继续往下执行,会走到 else-if流程,即0对1 –LGPerson本类的方法列表的添加会走0对1流程
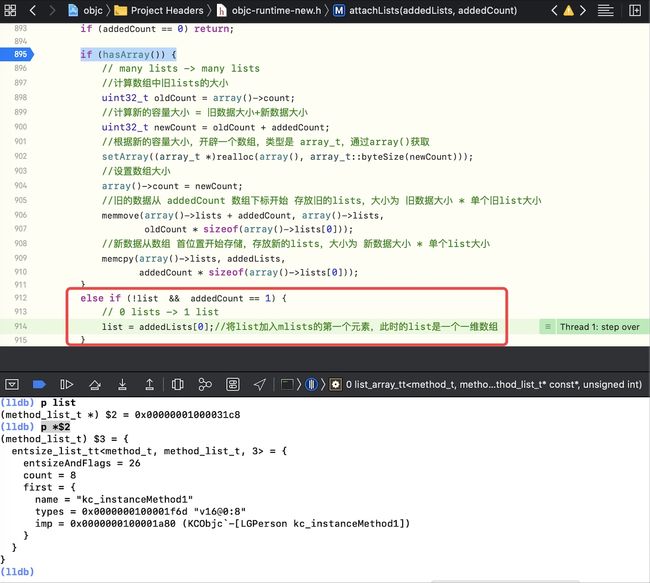
总结 :所以 0对1是一种一维赋值,函数路径为:map_images -> _read_images -> readClass -> realizeClassWithoutSwift -> methodizeClass -> prepareMethodLists -> fixupMethodList -> attachToClass -> load_categories_nolock -> attachCategories -> extAllocIfNeeded -> extAlloc -> attachLists
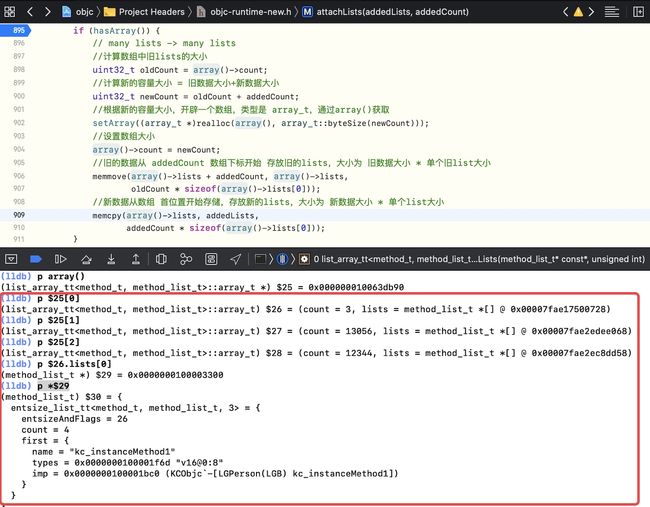
rwe – LGA分类数据加载【重点!!!】
-
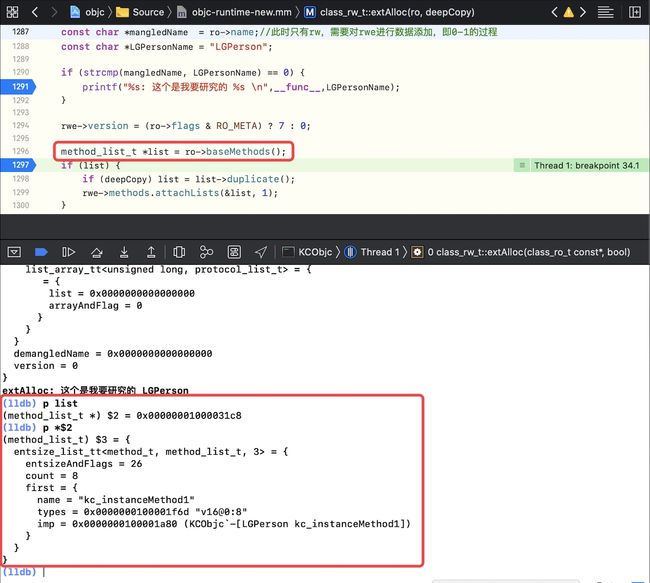
继续执行一步,打印list
-
接上面,继续往下执行,走到
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);, -
其中
mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount为内存平移 -
进入
attachLists方法, 在if (hasArray()) {处加断点,继续执行,由于已经有了一个list,所以 会走到1对多的流程
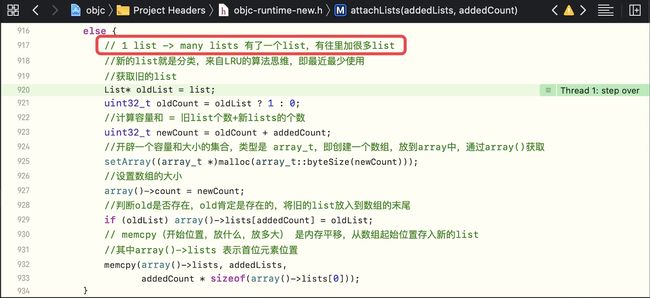
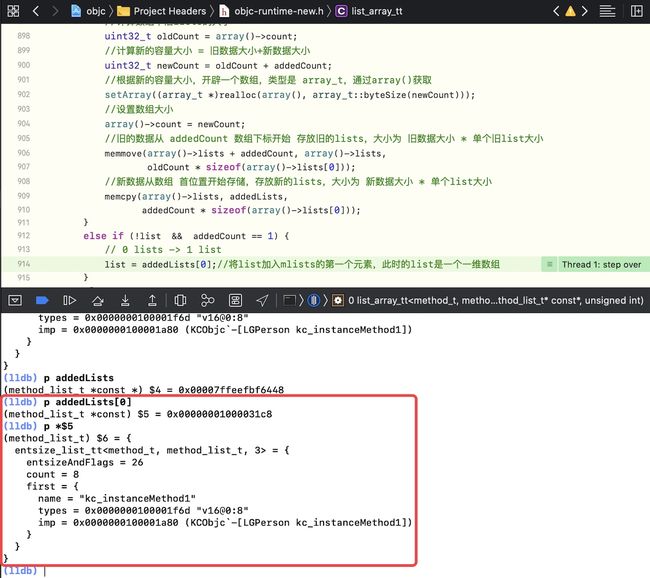
-
执行到最后,输出当前的array 即
p array()

这个list_array_tt表示 array中会放很多的 method_list_t,method_list_t中会放很多method_t
总结:如果本类只有一个分类,则会走到情况3,即1对多的情况
rwe – LGB分类数据加载【重点!!!】
如果再加一个分类LGB,走到第三种情况,即多对多
其输出的顺序是
总结
综上所述,attachLists方法主要是将类 和 分类 的数据加载到rwe中
-
首先
加载本类的data数据,此时的rwe没有数据为空,走0对1流程 -
当
加入一个分类时,此时的rwe仅有一个list,即本类的list,走1对多流程 -
再加入一个分类时,此时的
rwe中有两个list,即本类+分类的list,走多对多流程
懒加载类 和 非懒加载类
在这里,尽管方法处理完毕,但是并没有从rw中存储到rwe中,那么问题来了,到目前为止,从data -> ro -> rw -> 看到了rwe,即realizeClassWithoutSwift(ro、rw操作)-> methodizeClass,但是并没有走if里面的流程,为什么?
究其根本原因是_read_images方法中的第九步 实现非懒加载类,那么我们是如何将 懒加载类 变成 非懒加载类的呢?
主要是在运行objc源码前,我们在LGPerson中实现了一个+load方法,反之,如果去掉+load方法,是懒加载类,不会走到第九步的for循环中
所以,综上所述,懒加载类和 非懒加载类的区别 就是 是否实现了+load方法
实现+load,则是非懒加载类,- 反之,是
懒加载类
为什么实现load方法就会变成非懒加载类?
- 主要是因为
load会提前加载(load方法会在load_images调用,前提是类存在)
懒加载类在什么时候加载?
- 在
调用方法的时候加载
调试验证 懒加载类加载的时机
下面通过代码调试来验证
-
在
_read_images的第九步 for循环加一个断点 –readClass -- main的断点处 -
继续往下执行,走到
realizeClassWithoutSwift -- methodizeClass -- prepareMethodLists -- [person kc_instanceMethod1];

堆栈信息验证
也可以通过bt 堆栈信息查看,方法为什么能来?其本质是因为 走到realizeClassWithoutSwift,其本质是调用alloc,即消息的发送
总结
readClass主要是读取类,即此时的类仅有地址+名称,还没有data数据realizeClassWithoutSwift主要是实现类,即将类的data数据读取到内存中-
methodizeClass方法中实现类中方法(协议等)的`序列化 -
attachCategories方法中实现类以及分类的数据加载
-