蓝桥杯 --- 双指针、BFS与图论(习题)
蓝桥杯 --- 双指针、BFS与图论(习题)
-
- 1240. 完全二叉树的权值
- 1096. 地牢大师
- 1233. 全球变暖
- 1207. 大臣的旅费
- 826. 单链表
1240. 完全二叉树的权值
给定一棵包含 N 个节点的完全二叉树,树上每个节点都有一个权值,按从上到下、从左到右的顺序依次是 A1,A2,⋅⋅⋅AN,如下图所示:
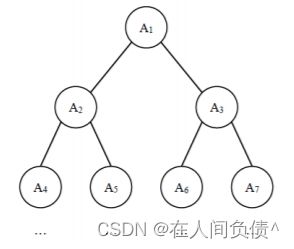
现在小明要把相同深度的节点的权值加在一起,他想知道哪个深度的节点权值之和最大?
如果有多个深度的权值和同为最大,请你输出其中最小的深度。
注:根的深度是 1。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数 N。
第二行包含 N 个整数 A1,A2,⋅⋅⋅AN。
输出格式
输出一个整数代表答案。
数据范围
1≤N≤105 ,
−105≤Ai≤105
输入样例:
7
1 6 5 4 3 2 1
输出样例:
2
#include1096. 地牢大师
你现在被困在一个三维地牢中,需要找到最快脱离的出路!
地牢由若干个单位立方体组成,其中部分不含岩石障碍可以直接通过,部分包含岩石障碍无法通过。
向北,向南,向东,向西,向上或向下移动一个单元距离均需要一分钟。
你不能沿对角线移动,迷宫边界都是坚硬的岩石,你不能走出边界范围。
请问,你有可能逃脱吗?
如果可以,需要多长时间?
输入格式
输入包含多组测试数据。
每组数据第一行包含三个整数 L,R,C 分别表示地牢层数,以及每一层地牢的行数和列数。
接下来是 L 个 R 行 C 列的字符矩阵,用来表示每一层地牢的具体状况。
每个字符用来描述一个地牢单元的具体状况。
其中, 充满岩石障碍的单元格用”#”表示,不含障碍的空单元格用”.”表示,你的起始位置用”S”表示,终点用”E”表示。
每一个字符矩阵后面都会包含一个空行。
当输入一行为”0 0 0”时,表示输入终止。
输出格式
每组数据输出一个结果,每个结果占一行。
如果能够逃脱地牢,则输出”Escaped in x minute(s).”,其中X为逃脱所需最短时间。
如果不能逃脱地牢,则输出”Trapped!”。
数据范围
1≤L,R,C≤100
输入样例:
3 4 5
S....
.###.
.##..
###.#
#####
#####
##.##
##...
#####
#####
#.###
####E
1 3 3
S##
#E#
###
0 0 0
输出样例:
Escaped in 11 minute(s).
Trapped!
#include1233. 全球变暖
你有一张某海域 N×N 像素的照片,”.”表示海洋、”#”表示陆地,如下所示:
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
其中”上下左右”四个方向上连在一起的一片陆地组成一座岛屿,例如上图就有2 座岛屿。
由于全球变暖导致了海面上升,科学家预测未来几十年,岛屿边缘一个像素的范围会被海水淹没。
具体来说如果一块陆地像素与海洋相邻(上下左右四个相邻像素中有海洋),它就会被淹没。
例如上图中的海域未来会变成如下样子:
.......
.......
.......
.......
....#..
.......
.......
请你计算:依照科学家的预测,照片中有多少岛屿会被完全淹没。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数N。
以下 N 行 N 列,包含一个由字符”#”和”.”构成的 N×N 字符矩阵,代表一张海域照片,”#”表示陆地,”.”表示海洋。
照片保证第 1 行、第 1 列、第 N 行、第 N 列的像素都是海洋。
输出格式
一个整数表示答案。
数据范围
1≤N≤1000
输入样例1:
7
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
输出样例1:
1
输入样例2:
9
.........
.##.##...
.#####...
.##.##...
.........
.##.#....
.#.###...
.#..#....
.........
输出样例2:
1
#include1207. 大臣的旅费
很久以前,T王国空前繁荣。
为了更好地管理国家,王国修建了大量的快速路,用于连接首都和王国内的各大城市。
为节省经费,T国的大臣们经过思考,制定了一套优秀的修建方案,使得任何一个大城市都能从首都直接或者通过其他大城市间接到达。
同时,如果不重复经过大城市,从首都到达每个大城市的方案都是唯一的。
J是T国重要大臣,他巡查于各大城市之间,体察民情。
所以,从一个城市马不停蹄地到另一个城市成了J最常做的事情。
他有一个钱袋,用于存放往来城市间的路费。
聪明的J发现,如果不在某个城市停下来修整,在连续行进过程中,他所花的路费与他已走过的距离有关,在走第x千米到第x+1千米这一千米中(x是整数),他花费的路费是x+10这么多。也就是说走1千米花费11,走2千米要花费23。
J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一个城市,所有可能花费的路费中最多是多少呢?
输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n,表示包括首都在内的T王国的城市数。
城市从 1 开始依次编号,1 号城市为首都。
接下来 n−1 行,描述T国的高速路(T国的高速路一定是 n−1 条)。
每行三个整数 Pi,Qi,Di,表示城市 Pi 和城市 Qi 之间有一条双向高速路,长度为 Di 千米。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示大臣J最多花费的路费是多少。
数据范围
1≤n≤105 ,
1≤Pi,Qi≤n ,
1≤Di≤1000
输入样例:
5
1 2 2
1 3 1
2 4 5
2 5 4
输出样例:
135
解题思路
由于题目说到不重复经过大城市,从首都到达每个大城市的方案都是唯一的。因此可以知道该图是一棵树,本题求的是树的直径
树的直径:树中长度最长的路径
1、任取一点x
2、找到距离x最远的点y
3、从y开始遍历,找到离y最远的点,与y最远的点的距离是树的直径
证明:AcWing 1207. 大臣的旅费
#include826. 单链表
实现一个单链表,链表初始为空,支持三种操作:
向链表头插入一个数;
删除第 k 个插入的数后面的数;
在第 k 个插入的数后插入一个数。
现在要对该链表进行 M 次操作,进行完所有操作后,从头到尾输出整个链表。
注意:题目中第 k 个插入的数并不是指当前链表的第 k 个数。例如操作过程中一共插入了 n 个数,则按照插入的时间顺序,这 n 个数依次为:第 1 个插入的数,第 2 个插入的数,…第 n 个插入的数。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 M,表示操作次数。
接下来 M 行,每行包含一个操作命令,操作命令可能为以下几种:
H x,表示向链表头插入一个数 x。
D k,表示删除第 k 个插入的数后面的数(当 k 为 0 时,表示删除头结点)。
I k x,表示在第 k 个插入的数后面插入一个数 x(此操作中 k 均大于 0)。
输出格式
共一行,将整个链表从头到尾输出。
数据范围
1≤M≤100000
所有操作保证合法。
输入样例:
10
H 9
I 1 1
D 1
D 0
H 6
I 3 6
I 4 5
I 4 5
I 3 4
D 6
输出样例:
6 4 6 5
#include