数据结构——二叉树遍历和常见问题
树的概念:
1.树的概念
要了解二叉树的遍历规则必须先要知道树的结构和概念。
树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由n(n>=0)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把它叫做树是因
为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。
- 根结点:根节点没有前驱结点。
- 除根节点外,其余结点被分成是一棵结构与树类似的子树。每棵子树的根结点有且只有一个前驱,可以有0个或多个后继。 因此,树是递归定义的。
- 节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度; 如上图:A的为2
- 叶节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点; 如上图:C、E、F、H节点为叶节点
- 非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点; 如上图:B、D、G节点为分支节点
- 双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点; 如上图:A是B的父节点
- 孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点; 如上图:B是A的孩子节点
- 兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点; 如上图:B、G是兄弟节点
- 树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度; 如上图:树的度为2
- 节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
- 树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次; 如上图:树的高度为4
- 堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;如上图:H、C互为兄弟节点
- 节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;如上图:A是所有节点的祖先
- 子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。如上图:所有节点都是A的子孙
- 森林:由m棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林;
特殊的二叉树:
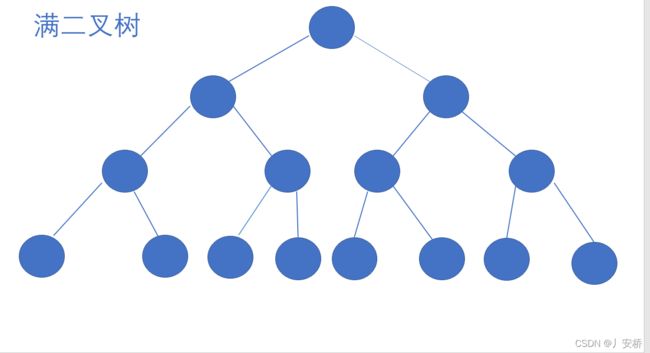
- 满二叉树:一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点数都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树。也就是说,如果一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是(2^k)-1 ,则它就是满二叉树。
- 完全二叉树:完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构,完全二叉树是由满二叉树而引出来的。对于深度为K的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点一一对应时称之为完全二叉树。 要注意的是满二叉树是一种特殊的完全二叉树。

完全二叉树其实也很好判断,在二叉树的最后一层,如果是从右向左依次缺失的满二叉树就是完全二叉树,如:

这个二叉树就不是完全二叉树,红色节点处,他先失去了左孩子,没有失去右孩子。不满足从右向左依次缺失。
二叉树遍历
概念:
所谓遍历(Traversal)是指沿着某条搜索路线,依次对树中每个结点均做一次且仅做一次访问。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问 题。 遍历是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,是二叉树上进行其它运算之基础。
前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:是根据访问结点操作发生位置命名
-
NLR:前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
-
LNR:中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。
-
LRN:后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
由于被访问的结点必是某子树的根,所以N(Node)、L(Left subtree)和R(Right
subtree)又可解释为根、根的左子树和根的右子树。NLR、LNR和LRN分别又称为先根遍历、中根遍历和后根遍历。
可能这样的解释不容易理解,下边我们画图看看二叉树的遍历方式。

不管是哪种遍历规则,所走的路径就是这样,区别是对双亲节点的读取顺序。
就拿先序遍历举例,先序遍历是先读取双亲节点,再读取左右节点,从根节点A进入,读取A,遍历他的左子树,到达B点,读取B点,以此类推。上图先序遍历为:ABCDEFGH
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再读取双亲节点,再遍历右子树上图中序遍历为:CBEDFAGH
后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,再读取双亲节点,上图后序遍历为:CEFDBHGA
实现:
然后就是代码实现了。
首先是节点类型:
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BtNode // BinaryTreeNode
{
ElemType data;
struct BtNode* leftchild;
struct BtNode* rightchild;
}BtNode, * BinaryTree;
先序遍历(递归实现):
void PreOrder(BtNode* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
cout << p->data << " ";
PreOrder(p->leftchild);
PreOrder(p->rightchild);
}
}
先序遍历(非递归实现):
void NicePreOreder(BtNode* ptr)//非递归先序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
std::stack<BtNode*>st;
while (ptr != NULL || !st.empty())
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);
cout << ptr->data;
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
cout << endl;
}
中序遍历(递归实现):
void InOrder(BtNode* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
InOrder(p->leftchild);
cout << p->data << " ";
InOrder(p->rightchild);
}
}
中序遍历(非递归实现):
void NiceInOreder(BtNode* ptr)//非递归中序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
std::stack<BtNode*>st;
while(ptr!=NULL || !st.empty())
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
cout << ptr->data;
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
cout << endl;
}
后序遍历(递归实现):
void PastOrder(BtNode* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
PastOrder(p->leftchild);
PastOrder(p->rightchild);
cout << p->data << " ";
}
}
后序遍历(非递归实现):
void NicePastOrder(BtNode* ptr)//非递归后序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL)return;
std::stack<BtNode*>st;
BtNode* tag = NULL;//用于解决右子树是有被访问过
while (ptr != NULL || !st.empty())
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
if (ptr->rightchild == NULL || ptr->rightchild == tag)
{
cout << ptr->data;
tag = ptr;
ptr = NULL;
}
else
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
}
}
二叉树常见问题:
1.节点个数:
递归:
int Cout(BtNode* ptr)//节点个数
{
if (ptr == NULL)return 0;
else return (Cout(ptr->leftchild) + Cout(ptr->rightchild) + 1);
}
非递归:
通过队列来记录导入的节点,每次导入一层的所有节点数,每导入一次节点,节点数+1。
int Cout1(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == 0)return 0;
deque<BtNode*>qu;
qu.push_back(ptr);
int num = 0;
while (!qu.empty())
{
int n = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ptr = qu.front(); qu.pop_front();
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
{
qu.push_back(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
{
qu.push_back(ptr->rightchild);
}
num++;
}
}
return num;
}
2.二叉树的深度:
递归:
int depth(BtNode* ptr)//深度
{
if (ptr == NULL)return 0;
else return max(depth(ptr->leftchild), depth(ptr->rightchild)) + 1;
}
非递归:
通过队列来记录导入的节点,每次导入一层的所有节点数,深度+1。
int depth1(BtNode* ptr)//深度(非递归)
{
if (ptr == 0)return 0;
deque<BtNode*>qu;
qu.push_back(ptr);
int num = 0;
while (!qu.empty())
{
int n = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ptr = qu.front(); qu.pop_front();
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
{
qu.push_back(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
{
qu.push_back(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
num++;
}
return num;
}
3. Z字打印:
利用两个栈来回进行导入子树节点,要注意的一点就是两个栈导入节点时,因为要进行Z字打印,一个栈先导入左子树,一个栈先导入右子树。
void Zprintf(BtNode* ptr)//Z字打印,利用两个栈来回导出数据
{
if (ptr == NULL)return;
std::stack<BtNode*>ast;
std::stack<BtNode*>bst;
ast.push(ptr);
while (!ast.empty() || !bst.empty())
{
while (!ast.empty())
{
ptr = ast.top(); ast.pop();
cout << ptr->data;
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
{
bst.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
{
bst.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
while (!bst.empty())
{
ptr = bst.top(); bst.pop();
cout<<ptr->data;
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
{
ast.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
{
ast.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
}
}
}
4.判断是否是满二叉树:
判断是否是满二叉树,利用两个队列,如果每两层的差值是第一层的两倍是满二叉树。
bool IS_fullTree(BtNode* ptr)//判断是否是满二叉树,利用两个队列,如果每两层的差值是第一层的两倍是满二叉树。
{
bool tag = true;
if (ptr == NULL)return tag;
std::queue<BtNode*>aqu;
std::queue<BtNode*>bqu;
int s = 1;
aqu.push(ptr);
while (!aqu.empty() || !bqu.empty())
{
if (s != aqu.size())
{
tag = false;
break;
}
while (!aqu.empty())
{
ptr = aqu.front(); aqu.pop();
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
{
bqu.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
{
bqu.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
s += s;
if (s != bqu.size())
{
tag = false;
break;
}
while (!bqu.empty())
{
ptr = bqu.front(); aqu.pop();
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
{
aqu.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
{
aqu.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
}
return tag;
}
5.判断是否是完全二叉树:
判断是不是完全二叉树,用队列来,保证最后一层保存的节点的后边全是空
bool IS_Comptree(BtNode* ptr)//判断是不是完全二叉树,用队列来,保证最后全是空
{
bool tag = true;
if (ptr == NULL)return true;
queue<BtNode*>qu;
qu.push(ptr);
while (!qu.empty())
{
ptr = qu.front(); qu.pop();
if (ptr == NULL)break;
qu.push(ptr->leftchild);
qu.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
while (!qu.empty())
{
if (ptr != NULL)
{
tag = false;
break;
}
qu.pop();
}
return tag;
}
6.任选两种遍历顺序构建二叉树
先写出两个重要的函数,构造节点的函数和查找节点的函数。
构造节点:
BtNode* Buynode()
{
BtNode* s = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (NULL == s)exit(1);
memset(s, 0, sizeof(BtNode));
return s;
}
查找节点:
int FindIs(const char* is, int n, char ch)
{
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (is[i] == ch)
{
pos = i;
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
前中构建:
BtNode* CreatePI(const char* ps, const char* is, int n)//前中构建
{
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n >= 1)
{
s = Buynode();
s->data = ps[0];
int pos = FindIs(is, n, ps[0]);
if (pos == -1) exit(1);
s->leftchild = CreatePI(ps + 1, is, pos);
s->rightchild = CreatePI(ps + pos + 1, is + pos + 1, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}
中后构建:
BtNode* CreateIL(const char* is, const char* ls, int n)//中后构建
{
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0)
{
s = Buynode();
s->data = ls[n - 1];
int pos = FindIs(is, n, ls[n - 1]);
s->leftchild = CreateIL(is,ls,pos);
s->rightchild = CreateIL(is+pos+1,ls+pos,n-pos-1);
}
return s;
}
写在最后:
二叉树的大部分问题解决并不困难,一定要有自己的想法,对所有问题都要基于他特殊的树形结构来解决。二叉树特有的结构使他很多问题都可以使用递归方式解决,而能使用递归解决,同时也可以使用栈和队列来实现非递归解决。加粗样式面试时,很多问题考虑递归的同时,也需要有非递归解决的思路。