qml实现Json可视化(头脑风暴、思维导图)
本demo来自 https://github.com/cjmdaixi/QuickJSONViewer
代码上传到了 https://download.csdn.net/download/u011942101/85005519
文章目录
- Json杂谈
- 实现的思路
- 核心代码
- 从中学习到了什么
- 感谢无私奉献的人
Json杂谈
JSON是一个序列化的对象或数组,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于 ECMAScript (欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范)的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
很多Json数据解析工具。例如在线的 [https://www.sojson.com/simple_json.html],

此demo确实用图表的方式来展示Json结构,通过借鉴此代码,也可以快速的实现类似Xml等数据的图标展示。效果如图:
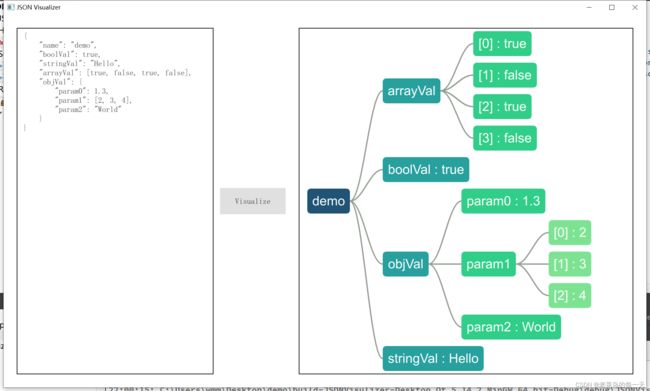
实现的思路
核心问题包括下面几个方面:
- 对JSON数据进行解析,我使用的是递归方法,比较容易理解。
- 同层级的节点放进一个ColumnLayout中,轻松实现均匀排布。
- 对JSON的数据类型需要判断,在JS中不好做,所以放在C++中实现,这里就涉及到如何在C++中构造QML对象以及设置属性。
核心代码
递归创建节点
para1 : 父节点 ,para2 : 节点的文本, para3 : josn数据 ,pare4 : 层级关系
QQuickItem * FluxHub::createObjectNode(QQuickItem *currentItem, const QString &key, const QJsonObject &jsonObj, int level)
{
auto objectNode = createLevelItem(level, currentItem);
setNodeText(objectNode, key);
for(auto it = jsonObj.begin(); it != jsonObj.end(); ++it){
auto child = it.value();
auto childName = it.key();
auto childType = it.value().type();
QQuickItem *rt = nullptr;
if(childType == QJsonValue::Object){
rt = createObjectNode(objectNode, childName, child.toObject(), level + 1);
}
else if(childType == QJsonValue::Array){
rt = createArrayNode(objectNode, childName, child.toArray(), level + 1);
}
else{
rt = createLeafNode(objectNode, childName, child, level + 1);
}
if(rt == nullptr){
qWarning()<<"Create child node error!"<<childName<<childType;
return nullptr;
}
}
return objectNode;
}
QQuickItem *FluxHub::createLevelItem(int level, QQuickItem *parentItem)
{
auto *component = level >= m_levelComponents.count()?
m_levelComponents.back() : m_levelComponents[level];
auto item = qobject_cast<QQuickItem*>(component->create());
if(item == nullptr){
qWarning()<<"Create level item error!"<<component->errorString();
return nullptr;
}
QQmlProperty layoutProp(parentItem, "childrenLayout");
if(layoutProp.type() == QQmlProperty::Invalid){
item->setParentItem(parentItem);
}else{
auto layout = layoutProp.read().value<QQuickItem*>();
Q_ASSERT(layout);
item->setParentItem(layout);
}
QQmlProperty colorProp(item, "color");
colorProp.write(levelColor(level));
return item;
}
//节点Node.qml
import QtQuick 2.7
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.3
Item{
id: root
implicitWidth: childrenRect.width
implicitHeight: childrenRect.height
property alias nodeRect: nodeContentRect
property alias text: nodeText.text
property alias childrenLayout: childrenLayout
property string color
RowLayout {
id: rowLayout
spacing: 50
Rectangle{
id: nodeContentRect
implicitWidth: nodeText.contentWidth + 15
implicitHeight: nodeText.contentHeight + 15
color: root.color
radius: 5
Text{
id: nodeText
anchors.fill: parent
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
font{
family: "Arial"
pointSize: 15
}
color: "white"
}
}
ColumnLayout{
id: childrenLayout
spacing: 10
onHeightChanged: lineCanvas.requestPaint();
onWidthChanged: lineCanvas.requestPaint();
}
}
Canvas{
id: lineCanvas
anchors.fill: parent
onPaint: {
var ctx = getContext("2d");
ctx.reset();
var pt1 = mapFromItem(nodeContentRect, nodeContentRect.width, nodeContentRect.height / 2);
for(var i = 0; i !== childrenLayout.children.length; ++i){
var item = childrenLayout.children[i];
var pt2 = mapFromItem(item.nodeRect, 0, item.nodeRect.height / 2);
ctx.moveTo(pt1.x, pt1.y);
//ctx.lineTo(pt2.x, pt2.y);
ctx.bezierCurveTo(pt1.x + 20, pt1.y, pt2.x - 20, pt2.y, pt2.x, pt2.y);
}
ctx.strokeStyle = "#969f95";
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.stroke();
}
}
}
从中学习到了什么
- c++ 中构造Qml对象,相关类 QQmlComponent
- c++中读取qml对象的属性,比如
QQmlProperty layoutProp(parentItem, "childrenLayout");
if(layoutProp.type() == QQmlProperty::Invalid){
item->setParentItem(parentItem);
}else{
auto layout = layoutProp.read().value<QQuickItem*>();
Q_ASSERT(layout);
item->setParentItem(layout);
}
QQmlProperty colorProp(item, "color");
colorProp.write(levelColor(level));
- qml Canvas 画线,位置的定位
Canvas{
id: lineCanvas
anchors.fill: parent
onPaint: {
var ctx = getContext("2d");
ctx.reset();
var pt1 = mapFromItem(nodeContentRect, nodeContentRect.width, nodeContentRect.height / 2);
for(var i = 0; i !== childrenLayout.children.length; ++i){
var item = childrenLayout.children[i];
var pt2 = mapFromItem(item.nodeRect, 0, item.nodeRect.height / 2);
ctx.moveTo(pt1.x, pt1.y);
//ctx.lineTo(pt2.x, pt2.y);
ctx.bezierCurveTo(pt1.x + 20, pt1.y, pt2.x - 20, pt2.y, pt2.x, pt2.y);
}
ctx.strokeStyle = "#969f95";
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.stroke();
}
}