【C++】map和set的模拟实现
文章目录
- 1、map、set和红黑树源码的截取
- 2、红黑树的迭代器
- 3、代码部分
-
- 3-1、Set.h
- 3-2、Map.h
- 3-3、RBTee.h
- 3-4、测试代码
1、map、set和红黑树源码的截取
我们红黑树的节点只需要用到value值就够了,value是什么,节点就存什么。但是,红黑树的源码为什么也要key值呢?
这是因为我们插入的时候,要用到接口
bool insert(const Value& v)
但是我们查找的时候,接口iterator find(const Key& k)是通过key值来查找的,所以,红黑树源码要key值是为了查找等操作的需求
2、红黑树的迭代器
迭代器的好处是可以方便遍历,是数据结构的底层实现与用户透明。如果想要给红黑树增加迭代器,需要考虑以前问题:
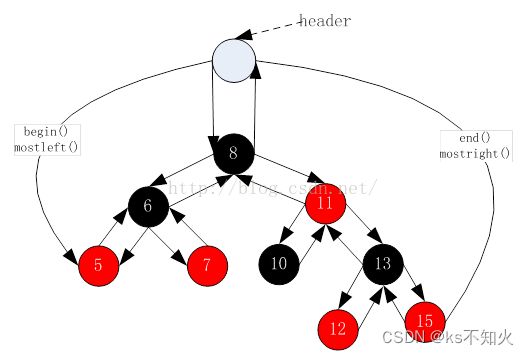
begin()与end()
STL明确规定,begin()与end()代表的是一段前闭后开的区间,而对红黑树进行中序遍历后,可以得到一个有序的序列,因此:begin()可以放在红黑树中最小节点(即最左侧节点)的位置,end()放在最大节点(最右侧节点)的下一个位置,关键是最大节点的下一个位置在哪块?能否给成nullptr呢?答案是行不通的,因为对end()位置的迭代器进行–操作,必须要能找最后一个元素,此处就不行,因此最好的方式是将end()放在头结点的位置:
但是,上面这样过于麻烦了,我们实现的时候不需要加入header节点,正常实现即可!
3、代码部分
3-1、Set.h
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace bzh
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator iterator;
//迭代器和const迭代器底层都是const迭代器,这样一来,迭代器就不能够被更改数据了
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
//模板没有实例化,编译器区分不清这里是静态变量还是类型
//编译器不会编译类模板,只会编译实例化的类型
//typename先告诉编译器RBTree::iterator是个类型,等模板实例化再来取
iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)//上面迭代器和const迭代器都是const的
{
//return _t.Insert(key);//这里的insert是普通迭代器
pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT>::iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(key);
return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);
//ret.first就是ret的迭代器,这是一个普通迭代器,这里用普通迭代器构建一个const迭代器!!!
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyofT> _t;
};
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
for (const auto& e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
//*it += 10;加了const报错,不加const不报错
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
3-2、Map.h
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace bzh
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT> _t;//map的v可以改变,所以不加const
};
void test_map()
{
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
map<int, int> m;
for (const auto& e : a)
{
m.insert(make_pair(e,e));
}
map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
//it->first++;
it->second++;
cout << it->first << " : " << it->second << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
3-3、RBTee.h
#pragma once
#include q;
//for (auto e : a)
//{
// q.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
//}
//q.Inorder();
//cout << q.IsBalance();
srand(time(0));
/*const size_t N = 10;
RBTree t;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
size_t x = rand();
t.Insert(make_pair(x, x));
cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
}
t.Inorder();
cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;*/
}
3-4、测试代码
#include us;
// us.insert(3);
// us.insert(1);
// us.insert(3);
// us.insert(2);
// us.insert(0);
//
// unordered_set::iterator it = us.begin();
// while (it != us.end())
// {
// cout << *it << " ";
// ++it;
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// string arr[] = { "ƻ", "", "㽶", "ݮ", "ƻ", "", "ƻ", "ƻ", "", "ƻ", "㽶", "ƻ", "㽶" };
//
// unordered_map countMap;
// for (auto& e : arr)
// {
// //map::iterator it = countMap
// /* auto it = countMap.find(e);
// if (it == countMap.end())
// {
// countMap.insert(make_pair(e, 1));
// }
// else
// {
// it->second++;
// }*/
//
// countMap[e]++;
// }
//
// for (const auto& kv : countMap)
// {
// cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// const size_t N = 1000000;
//
// unordered_set us;
// set s;
//
// vector v;
// v.reserve(N);
// srand(time(0));
// for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
// {
// //v.push_back(rand());
// //v.push_back(rand()+i);
// v.push_back(i);
// }
//
// size_t begin1 = clock();
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// s.insert(e);
// }
// size_t end1 = clock();
// cout << "set insert:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;
//
// size_t begin2 = clock();
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// us.insert(e);
// }
// size_t end2 = clock();
// cout << "unordered_set insert:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;
//
//
// size_t begin3 = clock();
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// s.find(e);
// }
// size_t end3 = clock();
// cout << "set find:" << end3 - begin3 << endl;
//
// size_t begin4 = clock();
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// us.find(e);
// }
// size_t end4 = clock();
// cout << "unordered_set find:" << end4 - begin4 << endl;
//
// cout << s.size() << endl;
// cout << us.size() << endl;
//
// size_t begin5 = clock();
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// s.erase(e);
// }
// size_t end5 = clock();
// cout << "set erase:" << end5 - begin5 << endl;
//
// size_t begin6 = clock();
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// us.erase(e);
// }
// size_t end6 = clock();
// cout << "unordered_set erase:" << end6 - begin6 << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
int main()
{
return 0;
}