Why String is immutable in Java ?--reference
String is an immutable class in Java. An immutable class is simply a class whose instances cannot be modified. All information in an instance is initialized when the instance is created and the information can not be modified. There are many advantages of immutable classes. This article summarizes whyString is designed to be immutable. A good answer depends on deep understanding of memory, synchronization, data structures, etc.
1. Requirement of String Pool
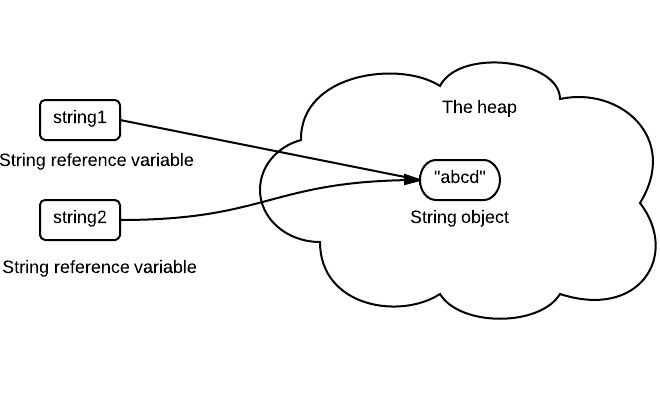
String pool (String intern pool) is a special storage area in Method Area. When a string is created and if the string already exists in the pool, the reference of the existing string will be returned, instead of creating a new object and returning its reference.
The following code will create only one string object in the heap.
String string1 = "abcd"; String string2 = "abcd"; |
If string is not immutable, changing the string with one reference will lead to the wrong value for the other references.
2. Caching Hashcode
The hashcode of string is frequently used in Java. For example, in a HashMap. Being immutable guarantees that hashcode will always the same, so that it can be cashed without worrying the changes.That means, there is no need to calculate hashcode every time it is used. This is more efficient.
In String class, it has the following code:
private int hash;//this is used to cache hash code. |
3. Facilitating the Use of Other Objects
To make this concrete, consider the following program:
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>(); set.add(new String("a")); set.add(new String("b")); set.add(new String("c")); for(String a: set) a.value = "a"; |
In this example, if String is mutable, it's value can be changed which would violate the design of set (set contains unduplicated elements). This example is designed for simplicity sake, in the real Stringclass there is no value field.
4. Security
String is widely used as parameter for many java classes, e.g. network connection, opening files, etc. Were String not immutable, a connection or file would be changed and lead to serious security threat. The method thought it was connecting to one machine, but was not. Mutable strings could cause security problem in Reflection too, as the parameters are strings.
Here is a code example:
boolean connect(string s){ if (!isSecure(s)) { throw new SecurityException(); } //here will cause problem, if s is changed before this by using other references. causeProblem(s); } |
5. Immutable objects are naturally thread-safe
Because immutable objects can not be changed, they can be shared among multiple threads freely. This eliminate the requirements of doing synchronization.
In summary, String is designed to be immutable for the sake of efficiency and security. This is also the reason why immutable classes are preferred in general.
reference from:http://www.programcreek.com/2013/04/why-string-is-immutable-in-java/