SpringBoot统一异常处理
SpringBoot统一异常处理
- 1、SpringBoot的统一异常处理自动配置类
-
- 1.1、DefaultErrorAttributes
- 1.2、BasicErrorController
-
- 1.2.1、BasicErrorController的大致运行过程
- 1.2.2、BasicErrorController的重要组件
- 1.3、DefaultErrorViewResolver
- 2、自定义SpringBoot的异常处理类
1、SpringBoot的统一异常处理自动配置类
SpringBoot的默认异常处理自动配置类的名称为ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,这个类有三个重要组件:
1.1、DefaultErrorAttributes
定义一些默认的异常属性等等,动态的扩展返回异常的属性
1.2、BasicErrorController
1.2.1、BasicErrorController的大致运行过程
我们不难看出,这里是new了一个BasicErrorController实现类
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorController.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
// ErrorViewResolver这里将错误页面以参数传进去,后面将注入到父类,后续需要用到的时候直接循环解析
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(), (List)errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
我们点击进入BasicErrorController类,代码如下所示:
这里是一个java的条件表达式:
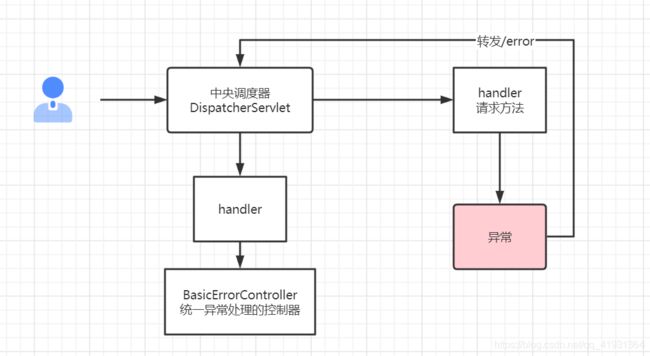
先去配置文件找server.error.path配置,如果没有,再去找error.path配置,如果再没有,则转发一个/error的请求路径,大致过程如下图所示:
@Controller
@RequestMapping({"${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}"})
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
}
1.2.2、BasicErrorController的重要组件
1、如果是浏览器请求的话,请求头中会有这个属性:Accept: text/html,
1.1、首先会走下面的代码:
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
// getErrorAttributes方法获取到所有的错误信息
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
// 去解析错误信息并绘制成错误页面
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
// 如果所有的模板都没有找到,那么返回一个SpringBoot默认的 ModelAndView 页面
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
1.2、现在我们进入resolveErrorView方法,代码如下:
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 循环 this.errorViewResolvers ,
// 拿到 DefaultErrorViewResolver东西去做解析处理,
// 因为在从统一异常处理类进来时就以参数的形式将DefaultErrorViewResolver传进来放到父类中了
Iterator var5 = this.errorViewResolvers.iterator();
ModelAndView modelAndView;
do {
if (!var5.hasNext()) {
return null;
}
ErrorViewResolver resolver = (ErrorViewResolver)var5.next();
// 调用具体类的resolveErrorView方法,目前就是 DefaultErrorViewResolver 类
modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
} while(modelAndView == null);
return modelAndView;
}
1.3、接下来我们进入DefaultErrorViewResolver 类的resolveErrorView方法:
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 进入 resolve 方法返回一个 ModelAndView
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
// 这里去找是否有 4XX或者5XX 的视图文件,去匹配视图
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = this.resolve((String)SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
1.4、进入resolve方法,代码如下:
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 默认SpringBoot可以去找到一个页面: error/404
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
// 如果模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址,就用模板引擎解析,并返回
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
// 模板引擎可用的话就返回errorViewName指定的视图地址
// 否则就去 resolveResource 找静态的地址资源
return provider != null ? new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model) : this.resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
1.5、进入getProvider方法,直接寻找是否有errorViewName 参数的请求映射方法,代码如下:–待确认,写一个映射方法。
public TemplateAvailabilityProvider getProvider(String view, Environment environment, ClassLoader classLoader, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(view, "View must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
Assert.notNull(classLoader, "ClassLoader must not be null");
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
// 是否热部署
Boolean useCache = (Boolean)environment.getProperty("spring.template.provider.cache", Boolean.class, true);
// 走热部署
if (!useCache) {
return this.findProvider(view, environment, classLoader, resourceLoader);
} else {
// 走普通,直接找错误请求映射,没有找到,则返回空
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = (TemplateAvailabilityProvider)this.resolved.get(view);
if (provider == null) {
synchronized(this.cache) {
provider = this.findProvider(view, environment, classLoader, resourceLoader);
provider = provider != null ? provider : NONE;
this.resolved.put(view, provider);
this.cache.put(view, provider);
}
}
return provider != NONE ? provider : null;
}
}
1.6、如果没有映射方法,则走resolveResource方法,代码如下:
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 直接配置的几个路径,在约定的路径下放一个错误视图,则直接返回,
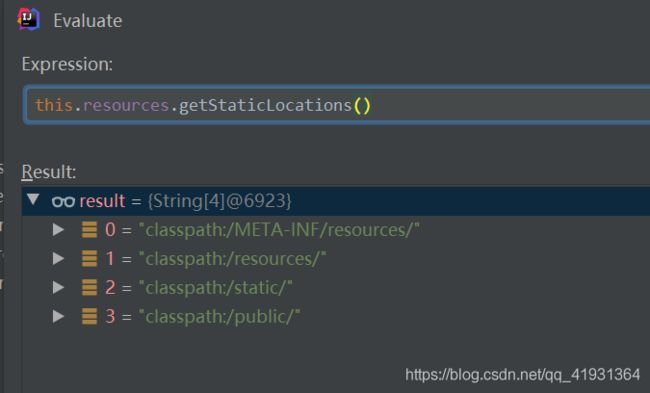
// 下面有一个图可直接看 this.resources.getStaticLocations()的值
String[] var3 = this.resources.getStaticLocations();
int var4 = var3.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String location = var3[var5];
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new DefaultErrorViewResolver.HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
} catch (Exception var8) {
}
}
return null;
}
1.7、会寻找图中的这四个路径:
1.8、在这个里面去寻找我们是否定义着400.html或者404.html文件等等,如果有直接返回,如果没有,返回到1.1,绘制一个SpringBoot默认的错误视图页面并返回。
总结:从上述分析可知,我们需要使用自定义的页面响应错误只需要在对应的路径上创建对应的错误代码的页面即可,如果想将错误记录在日志中,就需要自定义的去定制了。
2、如果是其它请求则会交给下面的error方法去处理
@RequestMapping
public <Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity(status);
} else {
// 调用 getErrorAttributes 方法将异常信息取出来放到 ResponseEntity 实体中
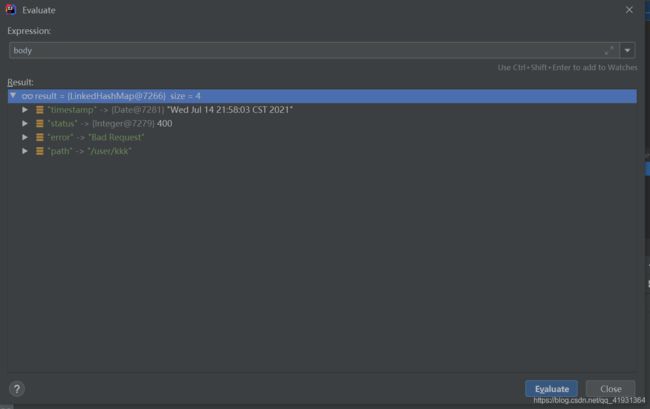
// body的信息如下图所示
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
}
1.3、DefaultErrorViewResolver
用来解析错误视图页面的
2、自定义SpringBoot的异常处理类
我们可以自定义一个SpringBoot的异常处理类,可以如下操作:
1、先写一个类继承AbstractErrorController控制类,如下所示:
1.1、创建相应的构造方法
1.2、重写errorHtml方法
1.3、重写error方法
package cool.ale.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.AbstractErrorController;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorViewResolver;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class CustomErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
// 创建相应的构造方法
public CustomErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
super(errorAttributes, errorViewResolvers);
}
/**
* 处理浏览器异常
* 加上异常日志记录
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
/**
* 用来处理ajax的
* 修改返回类型,加上异常日志记录
* @param request
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity(status);
} else {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
}
}
2、当我们将这两个方法都拷贝过来之后,就会发现,有一个 this.getErrorAttributeOptions 方法在报错,接下来我们研究一下这个方法是干什么的,为什么会报错,可不可以去掉它。
答案:可以动态的控制返回的异常属性
2.1、接下来我们看一下它是如何动态控制返回异常属性的,代码如下:
protected ErrorAttributeOptions getErrorAttributeOptions(HttpServletRequest request, MediaType mediaType) {
ErrorAttributeOptions options = ErrorAttributeOptions.defaults();
// 如果判断通过,这个EXCEPTION属性就会加上
if (this.errorProperties.isIncludeException()) {
options = options.including(new Include[]{Include.EXCEPTION});
}
// 如果判断通过,这个STACK_TRACE属性就会加上
if (this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, mediaType)) {
options = options.including(new Include[]{Include.STACK_TRACE});
}
// 如果判断通过,这个MESSAGE属性就会加上
if (this.isIncludeMessage(request, mediaType)) {
options = options.including(new Include[]{Include.MESSAGE});
}
// 如果判断通过,这个BINDING_ERRORS属性就会加上
if (this.isIncludeBindingErrors(request, mediaType)) {
options = options.including(new Include[]{Include.BINDING_ERRORS});
}
return options;
}
2.2、然而 this.errorProperties 和 this.isIncludeBindingErrors 是从哪来的呢,首先我们点击 this.errorProperties 或者 this.isIncludeBindingErrors ,都会跟踪到这个类的下面这句代码:
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
2.3、然而这个属性是在 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 类去new BasicErrorController的时候在构造参数中传的值,这个时候我们就可以来到ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration来看一下,就是下面这句代码:
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
// this.serverProperties.getError()东西是通过注解注入进来的
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(), (List)errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
2.4、接下来我们看 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 类的注解,如下所示:
下面这个注解相当于@Component加@ConfigurationProperties,就是将一个配置文件注册到IOC容器中,这个时候我们就看到了两个配置文件,ServerProperties 和 WebMvcProperties。
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class})
2.5、接下来我们分析其中的一个类,ServerProperties.class ,这个文件:
进来之后我们可以看到它的配置注解为下面所示:
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "server",
ignoreUnknownFields = true
)
2.6、加了一个前缀server,然后又是getError,我们去搜索它,代码如下所示:
public ErrorProperties getError() {
return this.error;
}
2.7、所以我们就可以在application.yml文件里面去配置一些属性,使得上面的说法,说这些返回的属性是动态的,可以控制,就比如下面所示:
server.error.include-exception=true
3、我们是需要自定义SpringBoot的返回属性的,所以,就不需要它来动态控制了。
下面是我写的一个简易版的统一异常处理,代码如下:
package cool.ale.controller;
import cool.ale.entity.Result;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.AbstractErrorController;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorViewResolver;
import org.springframework.boot.web.error.ErrorAttributeOptions;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/error")
public class CustomErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomErrorController.class);
// 创建相应的构造方法
public CustomErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
super(errorAttributes, errorViewResolvers);
}
/**
* 处理浏览器异常
* 加上异常日志记录
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions()));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
logger.info(model.get("trace").toString());
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
/**
* 用来处理ajax的
* 修改返回类型,加上异常日志记录
* @param request
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody
public Result error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new Result(204,"NO_CONTENT");
} else {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions());
String code = body.get("status").toString();
String message = body.get("message").toString();
logger.info(body.get("trace").toString());
return new Result(Integer.parseInt(code), message);
}
}
protected ErrorAttributeOptions getErrorAttributeOptions() {
ErrorAttributeOptions options = ErrorAttributeOptions.of(
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.EXCEPTION,
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.STACK_TRACE,
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.MESSAGE,
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.BINDING_ERRORS
);
return options;
}
}