如何理解线程池
线程池的核心状态
核心状态说明
在线程池的核心类ThreadPoolExecutor中,定义了几个线程池在运行过程中的核心状态,源码如下:
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
从源码中可以看出,线程池在运行过程中涉及的核心状态包括:RUNNING,SHUTDOWN,STOP,TIDYING,TERMINATED.具体含义解释如下:
- RUNNING:表示线程池处于运行状态,此时线程池能够接受新提交的任务,并且能够处理阻塞队列中的任务。
- SHUTDOWN:表示线程池处于关闭状态,此时线程池不能接受新提交的任务,但是不会中断正在执行的线程,能够继续执行正在执行的任务,也能够处理阻塞队列中已经保存的任务。如果线程池处于RUNNING状态,那么调用线程池的shutdown()方法会使线程池进入SHURDOWN状态。
- STOP:表示线程池处于停止状态,此时线程池不能够接受新提交的任务,也不能继续处理阻塞队列中的任务,同时会中断正在执行任务的线程,使得正在执行的任务被中断。如果线程池处于RUNNING状态或者SHUTDOWN状态,那么调用线程池的shutdownNow()方法会使线程池进入STOP状态。
- TIDYING:如果线程池中所有的任务都已经停止,有效线程数为0,线程池就会进入TIDYING状态。换句话说,如果线程池中已经没有正在执行的任务,并且线程池中的阻塞队列为空,同时线程池中的工作线程数量为0,线程池就会进入TIDYING状态。
- TERMINATED:如果线程池处于TIDYING状态,此时调用线程池的terminated()方法,线程池就会进入TERMINATED状态。
核心状态的流转过程
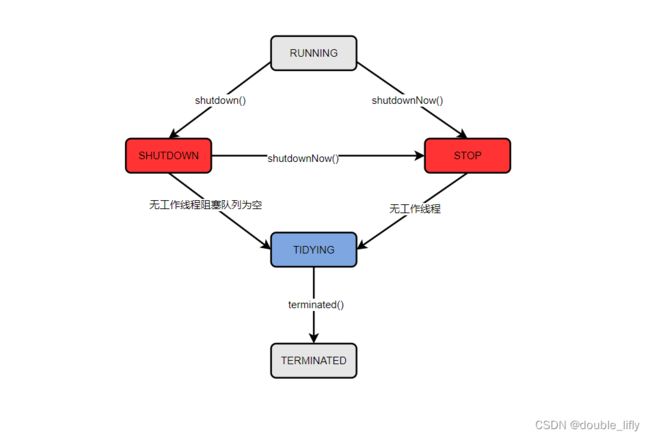
由上图可知,线程池由RUNNING状态转换成TERMINATED状态需要经历过如下流程。
- 当线程池处于RUNNING状态时,显示调用线程池的shutdown()方法,或者隐式调用finalize()方法,线程池会由RUNNING状态转换为SHUTDOWN状态。
- 当线程池处于RUNNING状态时,显示调用线程池的shutdownNow()方法,线程池会有RUNNING状态转换为STOP状态。
- 当线程池处于SHUTDOWN状态时,显示调用shutdownNow()方法,线程池会由SHUTDOWN状态转换为STOP状态。
- 当线程池处于SHUTDOWN状态时,如果线程池中无工作线程,并且阻塞队列为空,则线程池会有SHUTDOWN状态转换为TIDYING状态。
- 当线程池处于STOP状态时,如果线程池中无工作线程,则线程池会由STOP状态转换为TIDYING状态。
- 当线程池处于TIDYING状态时,调用线程池的terminated()方法,线程会由TIDYING状态转换为TERMINATED状态。
线程池的创建
通过Executors类创建线程池
Executors类是JDK中提供的一个创建线程池的工具类,提供了多个创建线程池的方法,常用的创建线程池的方法如下:
Executors.newCachedThreadPool方法
当调用Executors.newCachedThreadPool方法创建线程池时,表示创建一个可缓存的线程池,如果线程池中的线程数超过了运行任务的需要,则可以灵活地回收空闲线程池。如果在向线程池提交新任务时,线程池中无空闲线程,则新创建线程来执行任务。
Executors.newFixedThreadPool方法
当调用Executors.newFixedThreadPool方法创建线程池时,表示创建一个固定长度的线程池,也就是线程池中的工作线程的数量是固定的,能够有效的控制线程池的最大并发数。当向线程池中提交任务时,如果线程池中有空闲线程,则执行任务。如果线程池中无空闲线程,则将任务放入阻塞队列中,待线程池中出现空线程池,再执行阻塞队列中的任务。
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool方法
当调用Executors.newScheduledThreadPool方法创建线程池时,表示创建一个可以周期性执行任务的线程池,能够定时,周期性的执行任务。
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutors方法
当调用Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor方法创建线程池时,表示创建只有一个工作线程的线程池,即线程池中只有一个线程执行任务,能够保证提交到线程池中的所有任务按照先进先出的顺序,或者按照某个优先级的顺序来执行。当向线程池中提交任务时,如果线程池种无空闲线程,则会将任务保存到阻塞队列中。
Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor方法
当调用Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor方法创建线程池时,表示只创建一个工作线程的线程池,并且线程支持定时,周期性执行任务。
Executors.newWorkStealingPool方法
当调用Executors.newWorkStealingPool方法创建线程池时,表示创建一个具有并行级别的线程池。此方法时JDK1.8新增的方法,能够为线程池设置并行级别,具有比通过Executors类中的其他方法创建的线程池更高的并发度和性能。
通过ThreadPoolExecutor类创建线程池
查看ThreadPoolExecutor类的源码,其构造方法如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
threadFactory, defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
通过源码可知,ThreadPoolExecutor类创建线程池时最终调用的构造方法如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
参数解析
- corePoolSize:表示线程中的核心线程数
- maximumPoolSize:表示线程池中的最大线程数
- keepAliveTime:表示线程池中的线程空闲时,能够保持的最长时间。换句话说,就是线程池中的线程数量超过corePoolSize时,如果没有新任务被提交,核心线程外的线程就不会立即销毁,而是需要等待keepAliveTime时间后才会终止。
- unit :表示keepAliveTime的时间单位。
- workQueue :表示线程池中的阻塞队列,同于存储等待执行的任务。
- threadFactory:表示用来创建线程的线程工厂。在创建线程池时,会提供一个默认的线程工厂,默认的线程工厂创建的线程会具有相同的优先级,并且是设置了线程名称的非守护线程。
- handler:表示线程池拒绝处理任务时的策略。如果线程池中的workQueue阻塞队列满了,同时,线程池中的线程数已达到maximumPoolSize,并且没有空闲的线程,此时继续有任务提交到线程池,就需要采用某种策略来拒绝任务的执行。
其中,corePoolSize,maximumPoolSize和workQueue三个参数的关系如下:
- 当线程池中运行的线程数小于corePoolSize时,如果向线程池中提交任务,那么即使线程池中存在空闲线程也会直接创建新线程来执行任务。
- 如果线程池中运行的线程数大于corePoolSize,并且小于maximumPoolSize,那么只有当workQueue队列已满时,才会创建新的线程来执行新提交的任务。
- 当调用ThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法时,如果传递的corePoolSize和maximumPoolSize参数相同,那么创建的线程池的大小是固定的。此时,如果向线程池中提交任务,并且workQueue队列未满,就会将新提交的任务保存到workQueue队列中,等待空闲的线程,从workQueue队列中获取任务并执行。
- 如果线程池中运行的线程数大于maximumPoolSize,并且此时workQueue队列已满,则会触发指定的拒绝策略来拒绝任务的执行。
通过ForkJoinPool类创建线程池
从jdk1.8开始,java在Executors类中增加了work-stealing线程池的方法,源码如下:
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism) {
return new ForkJoinPool
(parallelism,
ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,
null, true);
}
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool() {
return new ForkJoinPool
(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),
ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,
null, true);
}
从源码中可以看出,在调用Executors.newWorkStealingPool方法创建线程时,本质上调用的是ForkJoinPool类的构造方法,从代码结构上来看,ForkJoinPool类继承自AbstractExecutorService抽象类。ForkJoinPool类的构造方法如下:
public ForkJoinPool() {
this(Math.min(MAX_CAP, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()),
defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory, null, false);
}
public ForkJoinPool(int parallelism) {
this(parallelism, defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory, null, false);
}
public ForkJoinPool(int parallelism,
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory,
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler,
boolean asyncMode) {
this(checkParallelism(parallelism),
checkFactory(factory),
handler,
asyncMode ? FIFO_QUEUE : LIFO_QUEUE,
"ForkJoinPool-" + nextPoolId() + "-worker-");
checkPermission();
}
private ForkJoinPool(int parallelism,
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory,
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler,
int mode,
String workerNamePrefix) {
this.workerNamePrefix = workerNamePrefix;
this.factory = factory;
this.ueh = handler;
this.config = (parallelism & SMASK) | mode;
long np = (long)(-parallelism); // offset ctl counts
this.ctl = ((np << AC_SHIFT) & AC_MASK) | ((np << TC_SHIFT) & TC_MASK);
}
通过ForkJoinPool类的源码可知,在调用ForkJoinPool类的构造方法时,最终调用的是如下私有方法。
private ForkJoinPool(int parallelism,
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory,
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler,
int mode,
String workerNamePrefix) {
this.workerNamePrefix = workerNamePrefix;
this.factory = factory;
this.ueh = handler;
this.config = (parallelism & SMASK) | mode;
long np = (long)(-parallelism); // offset ctl counts
this.ctl = ((np << AC_SHIFT) & AC_MASK) | ((np << TC_SHIFT) & TC_MASK);
}
参数说明
- parallelism:表示线程的并发级别
- factory:表示创建线程池的工厂类对象
- handler:表示当前线程池中的线程抛出未捕获的异常时,会统一交由UncaughtExceptionHandler 类的对象来处理。
- mode:mode的取值为FIFO_QUEUE和LIFO_QUEUE
- workerNamePrefix:表示线程池中执行任务的线程的前缀。
通过ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类创建线程池
在Executors类中,提供了创建定时任务类线程池的方法,如下:
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory));
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(
int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}
通过上述源码可以看出,在通过Executors类创建定时任务类的线程池时,本质上调用了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法,在ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类中,提供的构造方法如下:
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler);
}
而ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类继承了ThreadPoolExecutor类,本质上ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法还是调用了ThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法。只不过在ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法中,当调用了ThreadPoolExecutor类的构造方法时,传递的队列为DelayedWorkQueue。
线程池执行任务的核心流程
执行任务的流程
ThreadPoolExecutor是java线程池中最核心的类之一,它能够保证线程按照正常的业务逻辑执行任务,并通过原子方式更新线程池每个阶段的状态。
ThreadPoolExecutor类中存在一个workers工作线程集合,用户可以向线程池中添加需要执行的任务,workers集合中的工作线程可以直接执行任务,或者从队列中获取任务后执行。
ThreadPoolExecutor类中提供了线程池从创建dao执行任务,再到消亡的整个流程方法。
线程池任务的核心流程可以简化为如下图所示:
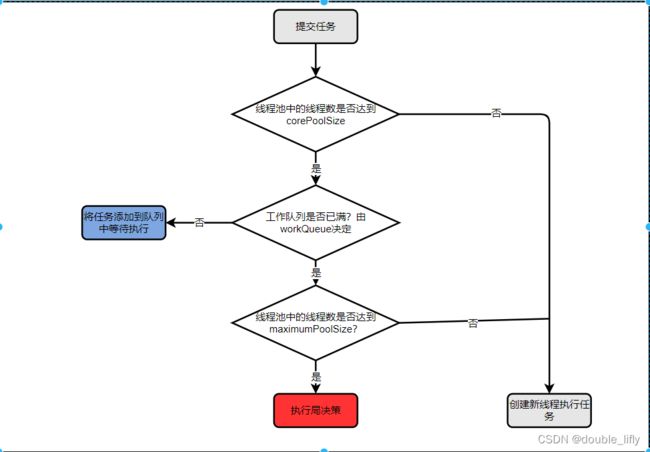
由上图可以看出,当向线程池提交任务时,线程池执行任务的流程如下:
- 判断线程池中的线程数是否达到corePoolSize,如果线程池中的线程数未达到corePoolSize,则直接创建新线程执行任务。否则,进入步骤2.
- 判断线程池中的工作队列是否已满,如果线程池中的工作队列已满,则将任务添加到队列中等待执行。否则,进入步骤3.
- 判断线程池中的线程数是否达到maximumPoolSize,如果线程中的线程数未达到maximumPoolSize,则直接创建新线程执行任务。否则,进入步骤4.
- 执行拒绝策略
拒绝策略
如果线程池中的workQueue阻塞队列已满,同时,线程池中的线程数已达到maximumPoolSize,并且没有空闲的线程,此时继续有任务提交到线程池,就需要采取某种策略来拒绝任务的执行。
在ThreadPoolExecutor类的execute()方法中,会有适当的时候调用reject(command)方法来执行拒绝策略。在ThreadPoolExecutor类中,reject(command)方法的实现如下:
final void reject(Runnable command) {
handler.rejectedExecution(command, this);
}
在reject(command)方法中调用了handler的rejectedExecution()方法。
public interface RejectedExecutionHandler {
void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor);
}
可以看到RejectedExecutionHandler是一个接口,其中定义了一个rejectedExecution()方法。在jdk中,默认有4个类实现了RejectedExectionHandler接口,分别为AbortPolicy,CallerRunsPolicy,DiscardOldestPolicy和DiscardPolicy。这4个类也正是线程池中默认提供的4中拒绝策略的实现类。
至于reject(command)方法具体汇之星哪个类的拒绝策略,是根据创建线程池时传递的参数决定的。如果没有传递拒绝策略的参数,则默认执行AbortPolicy类的拒绝策略;否则会执行传递的类的拒绝策略。
在创建线程池时,除了能够传递jdk默认提供的拒绝策略,还可以传递自定义的拒绝策略。如果想使用自定义的拒绝策略,则只需要实现RejectExecutionHandler接口,并重写rejectExecution(Runnable,ThreadPoolExecutor)方法。
线程池的关闭方式
shutdown()方法
调用shutdown()方法关闭线程池时,线程池不能接受新提交的任务,但是不会中断正在执行任务的线程,同时能够处理阻塞队列中已经保存的任务。待线程池中的任务全部执行完毕,线程池才会关闭。
shutdownNow()方法
在调用shutdownNow()方法关闭线程时,线程池不能接受新提交的任务,也不能继续处理阻塞队列中的任务,同时,还会中断正在执行的线程,使得正在执行的任务被中断,线程池立即关闭并抛出异常。