Mysql高级语句
实验准备:
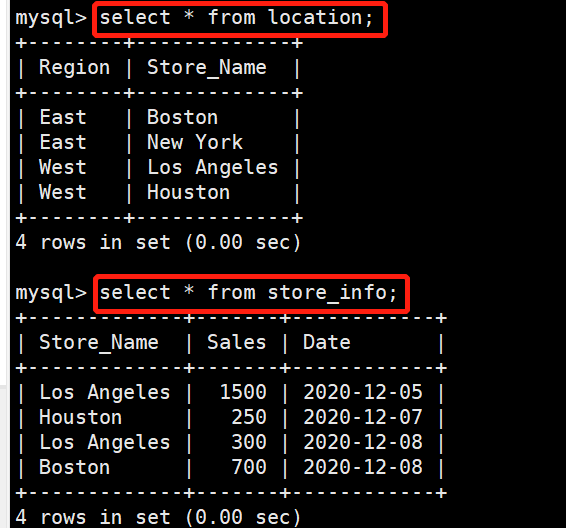
第一张表:
create table location (Region char(20),Store_Name char(20));
insert into location values('East','Boston');
insert into location values('East','New York');
insert into location values('West','Los Angeles');
insert into location values('West','Houston');
第二张表:
create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10));
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','1500','2020-12-05');
insert into store_info values('Houston','250','2020-12-07');
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','300','2020-12-08');
insert into store_info values('Boston','700','2020-12-08');高级查询
select
---- SELECT ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名";
eg:
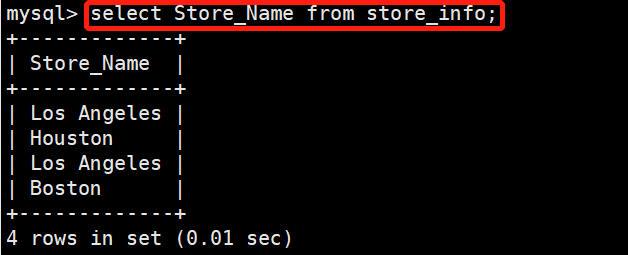
在store_info表中查找store_name的记录
select Store_Name from store_info;
+-------------+
| Store_Name |
+-------------+
| Los Angeles |
| Houston |
| Los Angeles |
| Boston |
+-------------+
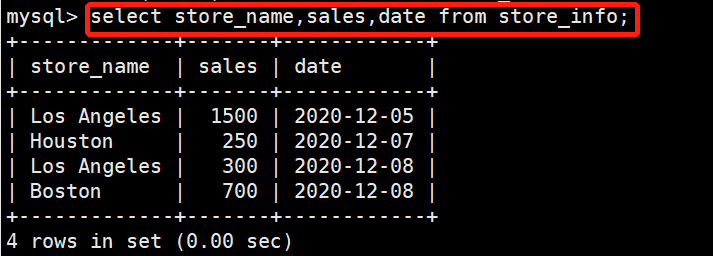
在store_info表中查找store_name,sales,date的记录(字段顺序无所谓)
select store_name,sales,date from store_info;
+-------------+-------+------------+
| store_name | sales | date |
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Los Angeles | 1500 | 2020-12-05 |
| Houston | 250 | 2020-12-07 |
| Los Angeles | 300 | 2020-12-08 |
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
+-------------+-------+------------+
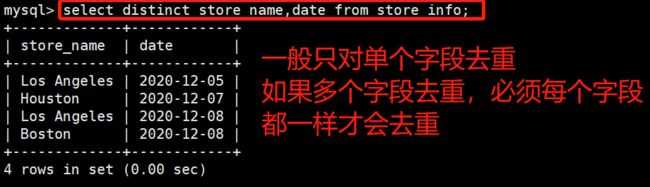
DISTINCT
---- DISTINCT ----不显示重复的数据记录
语法:SELECT DISTINCT "字段" FROM "表名";
eg:
select distinct store_name from store_info;
+-------------+
| store_name |
+-------------+
| Los Angeles |
| Houston |
| Boston |
+-------------+
select distinct store_name,date from store_info;
+-------------+------------+
| store_name | date |
+-------------+------------+
| Los Angeles | 2020-12-05 |
| Houston | 2020-12-07 |
| Los Angeles | 2020-12-08 |
| Boston | 2020-12-08 |
+-------------+------------+
 WHERE
WHERE
---- WHERE ----有条件查询
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "条件";
eg:
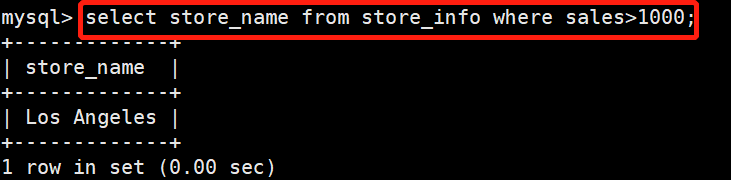
查找sales大于1000的store_name
select store_name from store_info where sales>1000;
+-------------+
| store_name |
+-------------+
| Los Angeles |
+-------------+
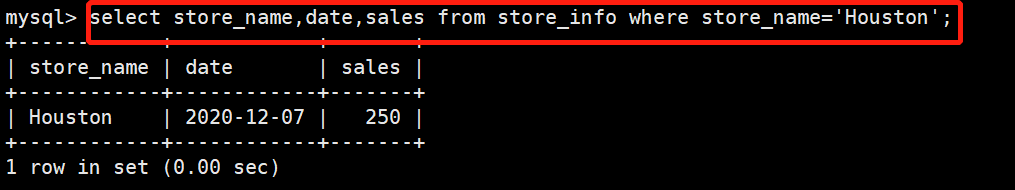
查找store_name为“Houston”的记录
select store_name,date,sales from store_info where store_name='Houston';
+------------+------------+-------+
| store_name | date | sales |
+------------+------------+-------+
| Houston | 2020-12-07 | 250 |
+------------+------------+-------+AND OR
---- AND OR ----且 或
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "条件1" {[AND|OR] "条件2"}+ ;
eg:
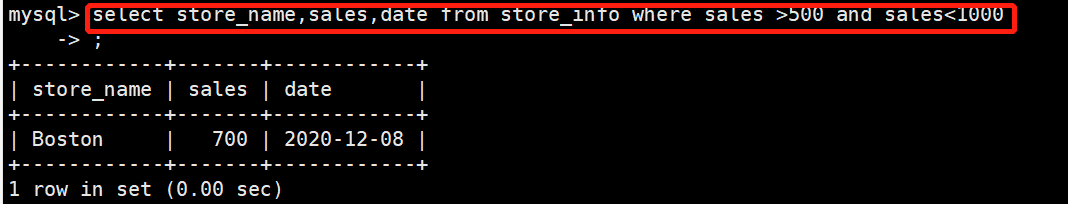
查找sales大于500且sales小于1000的store_name,sales,date
select store_name,sales,date from store_info where sales >500 and sales<1000;
+------------+-------+------------+
| store_name | sales | date |
+------------+-------+------------+
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
+------------+-------+------------+
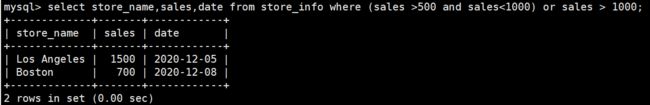
查找sales大于500且sales小于1000,或者sales大于1000的store_name,sales,date(注意把括号里的当成一个整体,并且优先执行)
select store_name,sales,date from store_info where (sales >500 and sales<1000) or sales > 1000;
+-------------+-------+------------+
| store_name | sales | date |
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Los Angeles | 1500 | 2020-12-05 |
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
+-------------+-------+------------+
IN
---- IN ----显示已知的值的数据记录
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" IN ('值1', '值2', ...);
eg:
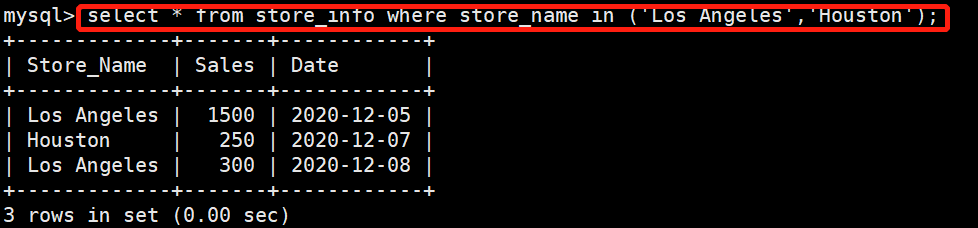
在store_info表中查找store_name为Los Angeles或者Houston的字段
select * from store_info where store_name in ('Los Angeles','Houston');
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Store_Name | Sales | Date |
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Los Angeles | 1500 | 2020-12-05 |
| Houston | 250 | 2020-12-07 |
| Los Angeles | 300 | 2020-12-08 |
+-------------+-------+------------+
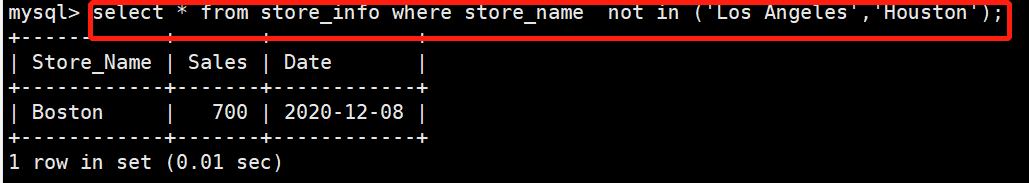
在store_info表中查找store_name不为Los Angeles或者Houston的字段
select * from store_info where store_name not in ('Los Angeles','Houston');
+------------+-------+------------+
| Store_Name | Sales | Date |
+------------+-------+------------+
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
+------------+-------+------------+
BETWEEN
---- BETWEEN ----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" BETWEEN '值1' AND '值2';
eg:
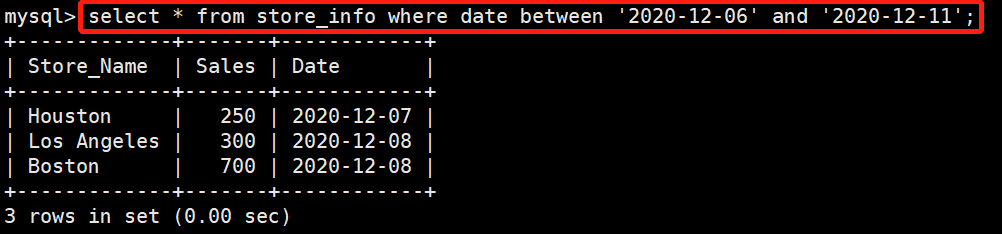
在store_info表中查找时间在2020-12-06到2020-12-11的数据
select * from store_info where date between '2020-12-06' and '2020-12-11';通配符与like
---- 通配符 ----通常通配符都是跟 LIKE 一起使用的
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符
_ :下划线表示单个字符
'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。
'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。
'%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。
'%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。
'_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。
---- LIKE ----匹配一个模式来找出我们要的数据记录
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" LIKE {模式};
eg:
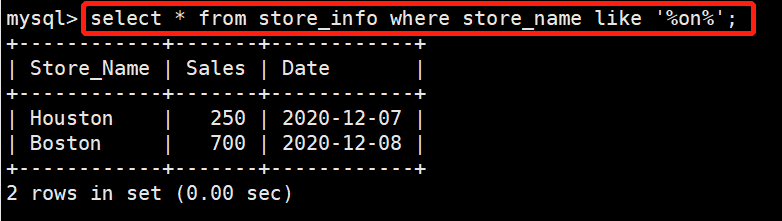
在store_info表中查找所有包含‘on’的数据
select * from store_info where store_name like '%on%';ORDER BY
---- ORDER BY ----按关键字排序
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" [WHERE "条件"] ORDER BY "字段" [ASC, DESC];
#ASC 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。
#DESC 是按降序方式进行排序。
eg:
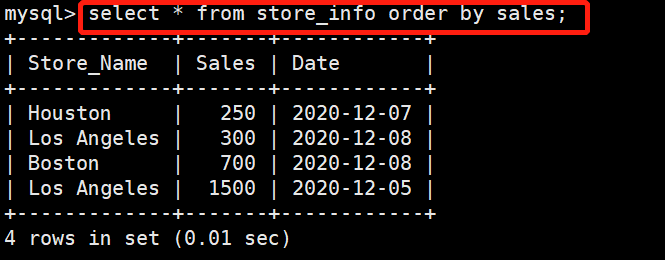
如果不指定排序方式,默认对sales字段进行升序排列
select * from store_info order by sales;
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Store_Name | Sales | Date |
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Houston | 250 | 2020-12-07 |
| Los Angeles | 300 | 2020-12-08 |
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
| Los Angeles | 1500 | 2020-12-05 |
+-------------+-------+------------+
对sales字段进行降序排列
select * from store_info order by sales desc;
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Store_Name | Sales | Date |
+-------------+-------+------------+
| Los Angeles | 1500 | 2020-12-05 |
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
| Los Angeles | 300 | 2020-12-08 |
| Houston | 250 | 2020-12-07 |
+-------------+-------+------------+
 函数
函数
数学函数
| 数学函数 | 含义 |
| abs(x) | 返回 x 的绝对值 |
| rand() | 返回 0 到 1 的随机数 |
| mod(x,y) | 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数 |
| power(x,y) | 返回 x 的 y 次方 |
| round(x) | 返回离 x 最近的整数 |
| round(x,y) | 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值 |
| sqrt(x) | 返回 x 的平方根 |
| truncate(x,y) | 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值 |
| ceil(x) | 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
| floor(x) | 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
| greatest(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值 |
| least(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小 |
eg:
select abs(-1),rand(),mod(5,3),power(2,3),round(1.89);
abs(-1)绝对值
rand()生成 0 到 1 的随机数
mod(5,3) 5除以3的余数
power(2,3)2的3次方
round(1.89)1.89四舍五入后的结果
+---------+--------------------+----------+------------+-------------+
| abs(-1) | rand() | mod(5,3) | power(2,3) | round(1.89) |
+---------+--------------------+----------+------------+-------------+
| 1 | 0.4283285573388716 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
+---------+--------------------+----------+------------+-------------+
select round(1.8937,3),truncate(1.235,2),ceil(5.2),floor(2.1),least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1);
round(1.8937,3)四舍五入并保留三位小数
truncate(1.235,2)给1.235直接截断成2位小数
ceil(5.2)返回大于5.2的最小整数
floor(2.1)返回小于2.1的最大整数
least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1)返回这组数中最小的值
+-----------------+-------------------+-----------+------------+-----------------------+
| round(1.8937,3) | truncate(1.235,2) | ceil(5.2) | floor(2.1) | least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1) |
+-----------------+-------------------+-----------+------------+-----------------------+
| 1.894 | 1.23 | 6 | 2 | 1.89 |
+-----------------+-------------------+-----------+------------+-----------------------+
聚合函数
| 聚合函数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| avg() | 返回指定列的平均值 |
| count() | 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数 |
| min() | 返回指定列的最小值 |
| max() | 返回指定列的最大值 |
| sum(x) | 返回指定列的所有值之和 |
eg:
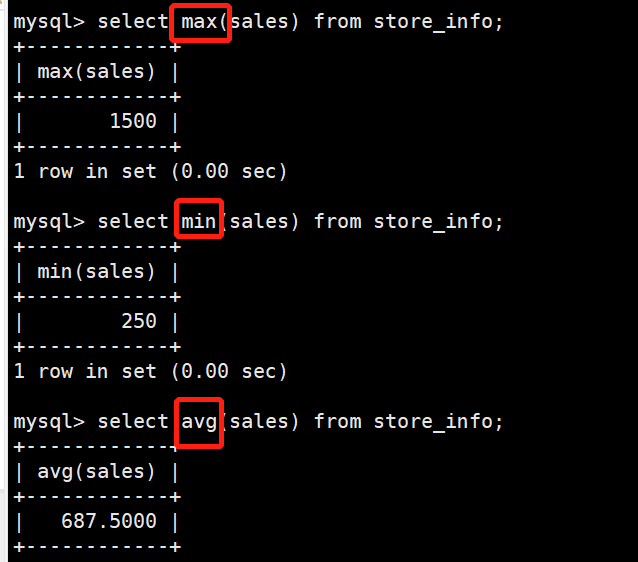
找到最大的sales
mysql> select max(sales) from store_info;
+------------+
| max(sales) |
+------------+
| 1500 |
+------------+
找到最小的sales
mysql> select min(sales) from store_info;
+------------+
| min(sales) |
+------------+
| 250 |
+------------+
求sales的平均值
mysql> select avg(sales) from store_info;
+------------+
| avg(sales) |
+------------+
| 687.5000 |
+------------+
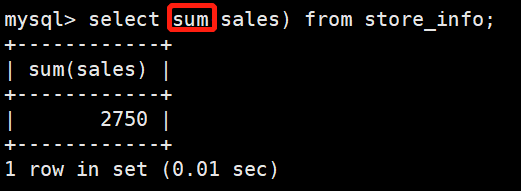
求sales的和
mysql> select sum(sales) from store_info;
+------------+
| sum(sales) |
+------------+
| 2750 |
+------------+
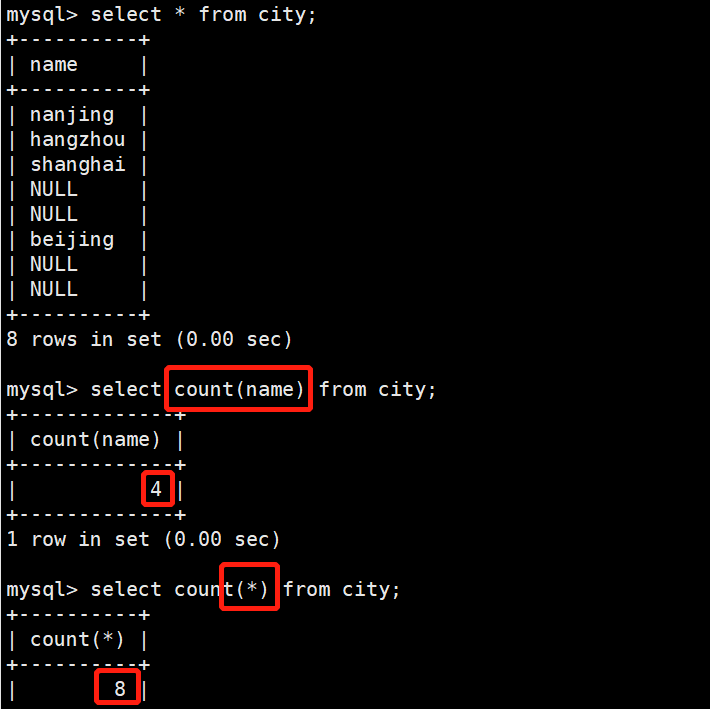
新建一个city表,用来演示count()函数
create table city (name char(20));
insert into city values('nanjing');
insert into city values('hangzhou');
insert into city values('shanghai');
insert into city values();
insert into city values();
insert into city values('beijing');
insert into city values();
insert into city values();
select count(name) from city; #count(name)仅记录值不为NULL的
+-------------+
| count(name) |
+-------------+
| 4 |
+-------------+
select count(*) from city; #count(*)会将NULL值记录进去
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 8 |
+----------+
字符串函数
| 字符串函数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| trim() | 返回去除指定格式的值 |
| concat(x,y) | 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 |
| substr(x,y) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同 |
| substr(x,y,z) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串 |
| length(x) | 返回字符串 x 的长度 |
| replace(x,y,z) | 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y |
| upper(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
| lower(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
| left(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 |
| right(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 |
| repeat(x,y) | 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 |
| space(x) | 返回 x 个空格 |
| strcmp(x,y) | 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 |
| reverse(x) | 将字符串 x 反转 |
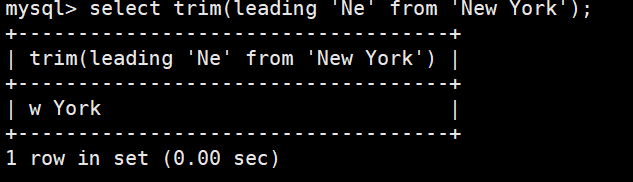
返回去除指定格式的值
SELECT TRIM ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] FROM ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 LEADING (起头), TRAILING (结尾), BOTH (起头及结尾)。
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
select trim(leading 'Ne' from 'New York');将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串
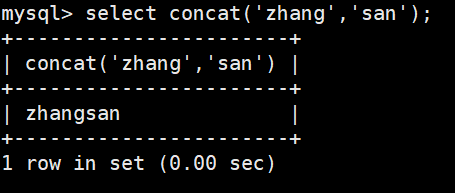
#将zhang和san拼接起来
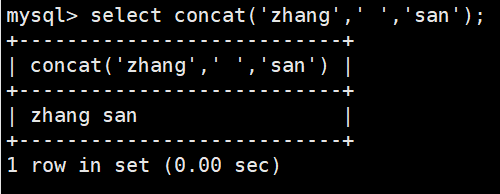
select concat('zhang','san');#在zhangsan中间加个空格,就是添加一个空格字符串
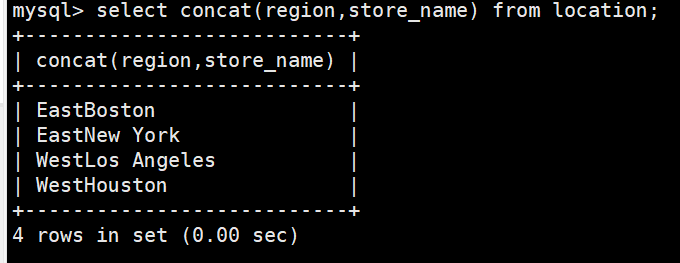
select concat('zhang',' ','san');对location表中的两个字段进行合并,注意不要加引号
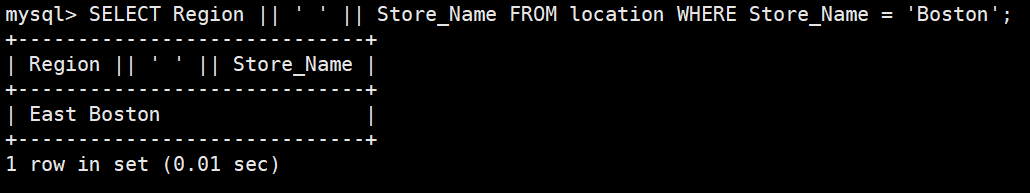
select concat(region,store_name) from location;#如sql_mode开启了PIPES_AS_CONCAT,"||"视为字符串的连接操作符而非或运算符,和字符串的拼接函数Concat相类似,这和Oracle数据库使用方法一样的
SELECT Region || ' ' || Store_Name FROM location WHERE Store_Name = 'Boston';
获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串
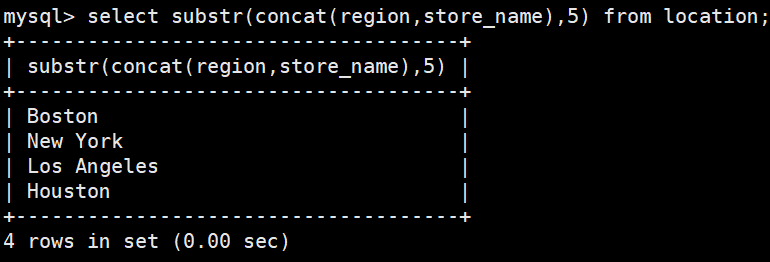
#将region和store_name先进行拼接,并获取从第五个字符开始字符串
select substr(concat(region,store_name),5) from location;#在store_name中从第五个字符开始,截取长度为6的字符串
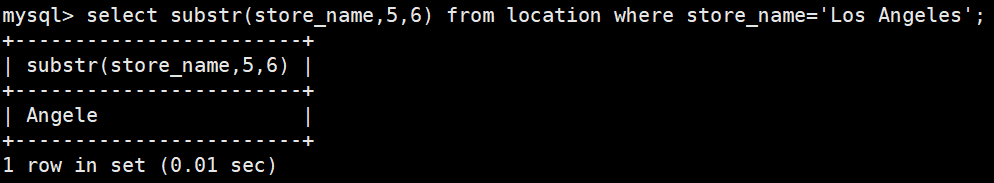
select substr(store_name,5,6) from location where store_name='Los Angeles';返回字符串 x 的长度
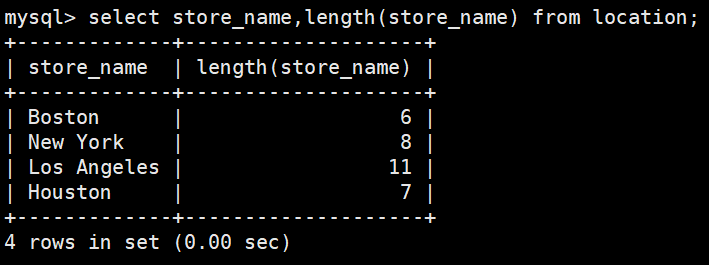
#返回store_name中,每个字段的的长度
select store_name,length(store_name) from location;将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y
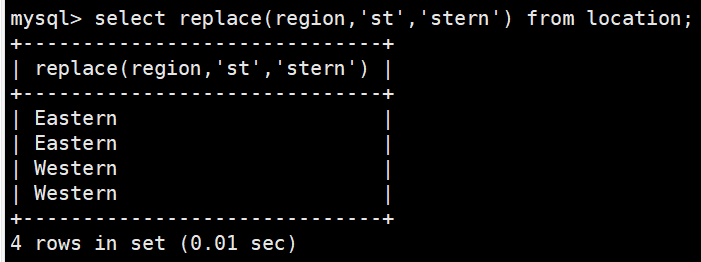
#将st替换成stern
select replace(region,'st','stern') from location;mysql进阶查询(2)
GROUP BY
对GROUP BY后面的字段的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
GROUP BY 有一个原则,凡是在 GROUP BY 后面出现的字段,必须在 SELECT 后面出现;
凡是在 SELECT 后面出现的、且未在聚合函数中出现的字段,必须出现在 GROUP BY 后面
语法:SELECT "字段1", SUM("字段2") FROM "表名" GROUP BY "字段1";
#降序
select store_name,sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name order by sum(sales) desc;
#不指定默认升序
select store_name,sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name order by sum(sales);HAVING
用来过滤由 GROUP BY 语句返回的记录集,通常与 GROUP BY 语句联合使用
HAVING 语句的存在弥补了 WHERE 关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。
语法:SELECT "字段1", SUM("字段2") FROM "表格名" GROUP BY "字段1" HAVING (函数条件);
#eg:
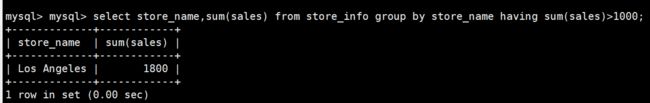
select store_name,sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales)>1000;
别名
字段別名 表格別名
语法:SELECT "表格別名"."字段1" [AS] "字段別名" FROM "表格名" [AS] "表格別名";
#对字段设置别名
select store_name,sum(sales) as total from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales)>1000;
#对表设置别名
select store_name,sum(sales) from store_info as a group by a.store_name;子查询
连接表格,在WHERE 子句或 HAVING 子句中插入另一个 SQL 语句
语法:SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格1" WHERE "字段2" [比较运算符] #外查询
(SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格2" WHERE "条件"); #内查询
#可以是符号的运算符,例如 =、>、<、>=、<= ;也可以是文字的运算符,例如 LIKE、IN、BETWEEN
#括号里的查询语句作为where语句的查询条件
SELECT SUM(Sales) FROM store_info WHERE store_name IN (SELECT Store_Name FROM location WHERE Region = 'West');EXISTS
用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果,类似布尔值是否为真
#如果有的话,系统就会执行外查询中的SQL语句。若是没有的话,那整个 SQL 语句就不会产生任何结果。
语法:SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格1" WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM "表格2" WHERE "条件");
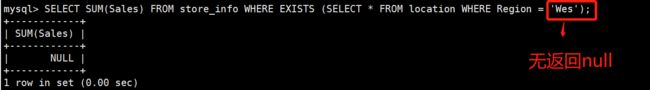
SELECT SUM(Sales) FROM store_info WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM location WHERE Region = 'West');连接查询
inner join(内连接):只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行
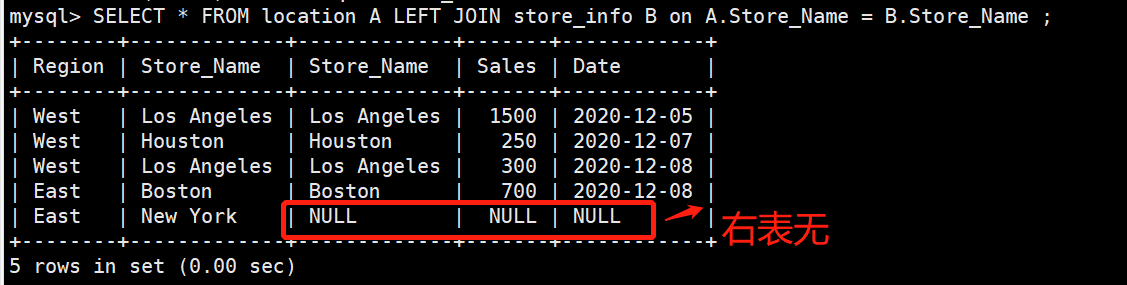
left join(左连接):返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录
right join(右连接):返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联结字段相等的记录
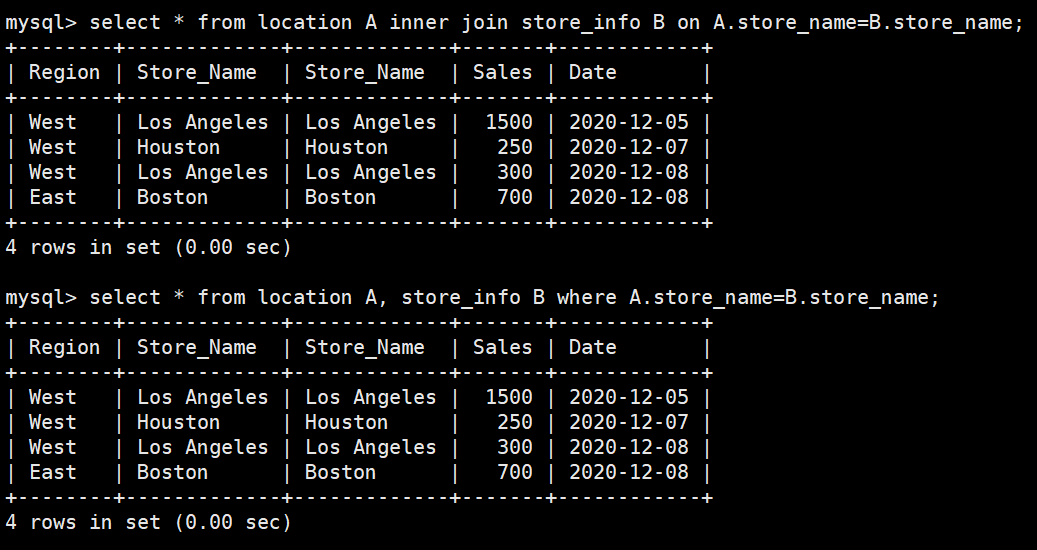
inner join(内连接)
#连接两个表中字段记录相等的数据记录
方法一:
select * from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name=B.store_name;
方法二:
select * from location A, store_info B where A.store_name=B.store_name;left join(左连接)
SELECT * FROM location A LEFT JOIN store_info B on A.Store_Name = B.Store_Name ;right join(右连接)
SELECT * FROM location A RIGHT JOIN store_info B on A.Store_Name = B.Store_Name ;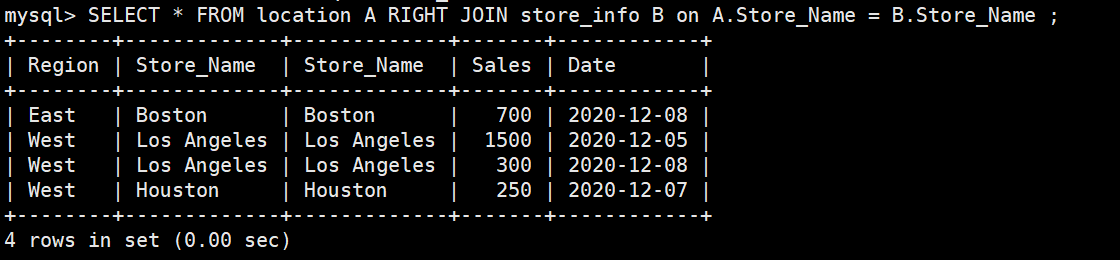 自我连接
自我连接
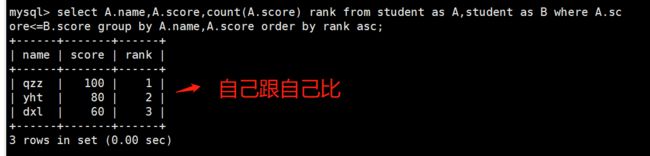
#分组汇总后统计 score 字段的值是比自己本身的值小的以及 score 字段 和 name 字段都相同的数量
select A.name,A.score,count(A.score) rank from student as A,student as B where A.score<=B.score group by A.name,A.score order by rank asc;