Python的Gym库中的Box类
一文李青 理清Gym中的Box类
在OpenAI公司的gym库中,任何一个拥有连续状态的强化学习游戏环境都会用到Box数据类型,Box是一个类。
Box的部分官方代码如下:
import numpy as np
import warnings
from .space import Space
from gym import logger
class Box(Space):
"""
A (possibly unbounded) box in R^n. Specifically, a Box represents the
Cartesian product of n closed intervals. Each interval has the form of one
of [a, b], (-oo, b], [a, oo), or (-oo, oo).
There are two common use cases:
* Identical bound for each dimension::
>>> Box(low=-1.0, high=2.0, shape=(3, 4), dtype=np.float32)
Box(3, 4)
* Independent bound for each dimension::
>>> Box(low=np.array([-1.0, -2.0]), high=np.array([2.0, 4.0]), dtype=np.float32)
Box(2,)
"""
上面的代码来自gym的box.py文件。并且官方有对这个box类的注释,翻译过来如下:

那么究竟什么是box数据类型呢?
做一个实验你就懂了,如下:
box数据类型有两种常用方式。
第一种用法(对数据sample)
from gym import spaces
a=spaces.Box(low=-1,high=2,shape=(3,4))
print("\r",a.sample(),end=" ")
运行后会输出结果:

sample函数是box类自带的采样函数,可以对数据进行随机的采样(采样符合正太分布,数据的上限与下限自己定义)
所以,第一种box函数的作用是:
输出一个与shape参数指定大小的矩阵,矩阵的数值正态分布采样生成,并且这个3*4的矩阵的数值的上限为high参数,下限为low参数。
第一种用法(不对数据sample)
from gym import spaces
a=spaces.Box(low=-1,high=2,shape=(3,4))
print("\r",a,end=" ")
第二种用法(对数据sample)
import numpy as np
from gym import spaces
a=spaces.Box(low=np.array([-1, -2]), high=np.array([2.0, 4.0]), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(10):
print(a.sample())
运行后会输出结果:

我们循环打印了10次a的采样值,从第二种用法的输出结果我们可以判断出,第二种box函数的作用是:
输出一个1 * 2(一行两列)的ndarray类型(ndarray类型是numpy包里定义的数据类型)的数组,数组的数值正态分布采样生成,并且这个1*2的数组的数值的上限为high参数,下限为low参数。
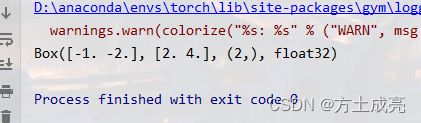
第二种用法(不对数据sample)
import numpy as np
from gym import spaces
a=spaces.Box(low=np.array([-1, -2]), high=np.array([2.0, 4.0]), dtype=np.float32)
print(a)
如果是自己编写的游戏环境,其实对于环境的状态(observation_space)是可以不对其进行Box数据类型处理的。