Android系统架构(二)—Android系统启动过程
前言
作为一个Android应用层的开发者,我们平常开发Android应用程序可能对Android系统了解的并不深入。虽然Android系统底层细节并不需要应用层开发者十分了解,但能够知道Android系统的基本架构也是必要。
这里就分析一下Android系统的启动流程来了解一下Android系统的启动过程。
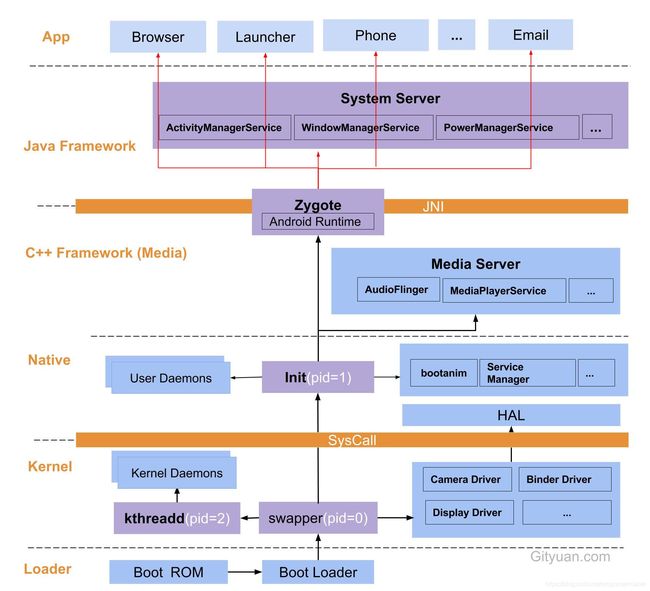
上图是Android系统启动过程的一个概览。从图中可以看到,Android系统的启动过程涉及到了Android系统的各层架构。我们可以看紫色标出的部分,从Boot Loader开始,到swapper -> init -> Zygote -> System Server。这就是Android系统启动后要做的事情。
Android系统的启动流程
我们知道Android系统是基于Linux内核的系统。与之类似,Android系统的启动过程前几步是:
启动电源以及系统启动:当按下电源键开机后,引导芯片代码从ROM(只读内存)里开始执行,然后加载引导程序到RAM(运行内存)中。
引导程序BootLoader:引导程序BootLoader是在Android操作系统开始运行前的一个小程序,它的主要作用是把系统OS拉起来并运行,并为内核的启动做准备。(它不是Android操作系统的一部分。引导程序是OEM厂商或者运营商加锁和限制的地方)
Linux内核启动:当内核启动时,设置缓存、被保护存储器、计划列表、加载驱动。在内核完成系统设置后,它首先在系统文件中寻找init.rc文件,并启动init进程。
init进程启动:init进程是第一个进程。它的任务是初始化系统环境,负责挂载目录,运行init。rc脚本。
init进程的启动
接下来就从init进程的进程启动开始说起。
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//......
bool is_first_stage = (getenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE") == nullptr);
if (is_first_stage) {
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// Clear the umask. 清除umask,作用就是设置文件属性为0777,即可读、可写、可执行
umask(0);
// 获取在initramdisk中放在一起的基本文件系统设置,在/然后我们将让rc文件找出其余部分
//创建挂载启动所需要的文件目录
mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);
mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC));
chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440);
gid_t groups[] = { AID_READPROC };
setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups);
mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL);
mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11));
if constexpr (WORLD_WRITABLE_KMSG) {
mknod("/dev/kmsg_debug", S_IFCHR | 0622, makedev(1, 11));
}
mknod("/dev/random", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 8));
mknod("/dev/urandom", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 9));
//......
//初始化Kennel的Log,以便可以从外界获取Kernel的日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
//......
}
// 初始化第二阶段
InitKernelLogging(argv);
//......
//对属性服务进行初始化
property_init();
//......
//创建epoll句柄.epoll是Linux中I/O多路复用的机制
epoll_fd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
if (epoll_fd == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "epoll_create1 failed";
}
//用于设置子进程信号处理函数,如果紫禁城异常退出,init进程会调用该函数中设定的信号处理函数来进行处理
sigchld_handler_init();
//导入默认的环境变量
property_load_boot_defaults();
export_oem_lock_status();
//启动属性服务
start_property_service();
set_usb_controller();
//在LoadBootScripts方法中解析了init.rc文件
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);
//......
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
// 轮训等待事件产生
int epoll_timeout_ms = -1;
if (do_shutdown && !shutting_down) {
do_shutdown = false;
if (HandlePowerctlMessage(shutdown_command)) {
shutting_down = true;
}
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
if (!shutting_down) {
auto next_process_restart_time = RestartProcesses();
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (next_process_restart_time) {
epoll_timeout_ms = std::chrono::ceil(
*next_process_restart_time - boot_clock::now())
.count();
if (epoll_timeout_ms < 0) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
}
// If there's more work to do, wake up again immediately.
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
epoll_event ev;
int nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(epoll_wait(epoll_fd, &ev, 1, epoll_timeout_ms));
//循环 等待事件发生
if (nr == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_wait failed";
} else if (nr == 1) {
((void (*)()) ev.data.ptr)();
}
}
return 0;
}
init的main函数主要做了以下的事情:
创建和挂载启动所需的文件。
对属性进行初始化,并且启动属性服务。通过property_init方法初始化属性,通过start_property_service方法启动属性服务。
通过sigchld_handler_init方法设置子进程信号处理函数。主要作用是防止init的子进程成为僵尸进程。
解析init.rc文件
解析init.rc文件
init.rc是一个重要的配置文件,在init进程启动时会解析init.rc文件。rc文件主要包含Action、Service、Command、Options和import五种类型。接下来分析一个rc文件,init.zygote64.rc。这个文件是启动Zygote的脚本。除此之外还有init.zygote32.rc、init.zygote32_64.rc、init.zygote64_32.rc,每个文件对应不同版本的Zygote进程启动。
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
//表示进程名为Zygote
//执行的程序是app_process64
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
通过解析上面的rc文件,开始启动Zygote进程。
Zygote进程的启动
从启动Zygote进程的rc文件中可以看到执行的程序名是app_process64,也就是在/system/bin/app_process64这个路径下。在这里执行了app_main.cpp文件。
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
传到的参数argv为“-Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server”,也就是启动Zygote进程的参数
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
argc--;
argv++;
bool known_command = false;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
if (known_command == true) {
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
known_command = false;
continue;
}
for (int j = 0;
j < static_cast(sizeof(spaced_commands) / sizeof(spaced_commands[0]));
++j) {
if (strcmp(argv[i], spaced_commands[j]) == 0) {
known_command = true;
}
}
if (argv[i][0] != '-') {
break;
}
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0) {
++i; // Skip --.
break;
}
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
}
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
//解析参数
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
//判断当前是否在Zygote进程中运行
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;//对于64位系统nice_name为zygote64; 32位系统为zygote
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
//同样的,判断当前是否运行在SystemServer进程中
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
//是否在运行在应用程序进程中
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
Vector args;
if (!className.isEmpty()) {
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i);
}
} else {
// We're in zygote mode.
// 进入zygote模式,创建 /data/dalvik-cache路径
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
if (startSystemServer) {
//是否启动SystemServer进程
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
}
//设置进程名
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
}
if (zygote) {
// 启动AppRuntime
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
}
Zygote进程通过fork自身来创建子进程,这样Zygote进程以及它的子进程都会调用main方法。在main方法中可以看到其中区分了当前运行在哪个进程中。
如果运行在Zygote进程中就会调用AppRuntime的start方法,即runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
/*
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
* and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
* named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector& options, bool zygote)
{
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
//......
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
// 启动Java虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
// 为Java虚拟机注册JNI方法
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
// 找到className,其中className是参数calssName,为:com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
//将ClassName替换为com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
// 通过ClassName找到对应的类
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
//找到ZygoteInit的main方法
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
//通过JNI调用ZygoteInit的main方法
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
//......
}
上面的start方法中主要完成了Java虚拟机的启动、注册了JNI方法、通过ClassName找到ZygoteInit并且了调用ZygoteInit的main方法。从这里就进入了Java框架层。
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
//......
final Runnable caller;
try {
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
//......
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
//根据参数设置标志
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
//创建一个Server端的Socket
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
//预加载资源
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
//是否启动SysTemServer进程
if (startSystemServer) {
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
//等待AMS请求,AMS请求就是创建应用程序的请求,AMS即ActivityManagerService
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
ZygoteInit的main方法主要做了4件事:
创建一个Server端的Socket;
预加载资源;
启动SystemServer进程;
等待AMS请求创建新的应用程序;
创建Socket
void registerServerSocket(String socketName) {
if (mServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
//拼接Socket名称,ANDROID_SOCKET_ + ""
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName;
try {
//获取Socket的环境变量
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
//将环境变量转换为文件描述符的参数
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
//创建文件描述符
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
//创建爱你服务端Socket
mServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}
预加载资源
static void preload() {
//预加载位于/system/etc/preloaded-classes文件中的类
preloadClasses();
//预加载资源,包含drawable和color资源
preloadResources();
//预加载OpenGL
preloadOpenGL();
//通过System.loadLibrary()方法,
//预加载"android","compiler_rt","jnigraphics"这3个共享库
preloadSharedLibraries();
//预加载 文本连接符资源
preloadTextResources();
//仅用于zygote进程,用于内存共享的进程
WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInZygote();
}
启动SystemServer
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
//......
//创建args数组,保存启动参数
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
//创建SystemServer进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
//关闭socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
//处理启动SystemServer进程的其他事情
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
//......
return null;
}
监听AMS请求
Runnable runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
ArrayList fds = new ArrayList();
ArrayList peers = new ArrayList();
//将Socket的文件描述符加入到列表中
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
//在死循环中等待AMS请求
while (true) {
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
//将fds的储存信息转移到pollFds中
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
如果i==0说明与服务端已经建立连接
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (i == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
try {
ZygoteConnection connection = peers.get(i);
final Runnable command = connection.processOneCommand(this);
if (mIsForkChild) {
if (command == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("command == null");
}
return command;
} else {
if (connection.isClosedByPeer()) {
connection.closeSocket();
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//.....
}
}
}
}
}
}
SystemServer进程的启动
上面学习了Zygote进程的启动过程,这里讲学习一下SystemServer的启动过程。从上面的代码可以看出在Zygote进程启动后,后fork出一个SystemServer进程。SystemServer进程主要是用于创建系统服务,比如AMS(活动服务)、WMS(窗口服务)、PMS(Power服务)等。
在ZygoteInit类中通过fork的方式启动了SystemServer进程。在forkSystemServer方法创建了SystemServer进程,除此之外还需要完成SystemServer进程启动的其他工作。
/**
* Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
*/
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs) {
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
//......
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
//创建ClassLoader
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
//传递其他参数到SystemServer
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
}
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
//......
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
//启动Binder线程池,SystemServer通过Binder与其他进程通信
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
//进入SystemServer的main方法
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
通过RuntimeInit类来进入SystemServer的main方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run() {
try {
//......
//创建一个消息Looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Create the system service manager.
//创建系统服务管理。
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setRuntimeRestarted(mRuntimeRestart);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get();
} finally {
traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
//启动引导服务
startBootstrapServices();
//启动核心服务
startCoreServices();
//启动其他服务
startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
从上面的分析可以看到,SystemServer进程启动后主要完成了:
启动Binder线程池,用来与其他进程通信;
创建SystemServiceManager,用来管理系统服务;
启动各种系统服务;
Launcher启动过程
经过上面进程的启动后,Android系统基本处于就绪状态。最后一步是启动一个应用程序来显示已安装的应用程序,即Launcher(Android系统的桌面)。
在SystemServer进程启动的过程中会启动PackageManagerService,然后PackageManagerService会将系统中的应用程序安装完成。接下来通过ActivityManagerService将Launcher启动。入口就是ActivityManagerService的systemReady方法。
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, BootTimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
...
startHomeActivityLocked(currentUserId, "systemReady");
...
}
总结
通过上面的学习,将Android系统启动的主要过程描述一遍。由于整个Android系统的启动流程非常复杂,同时涉及到了非常多的底层代码,阅读起来会感觉到吃力。所以在最后要简要的总结一下Android系统的启动流程加强整个过程的理解。
启动电源以及系统启动,当按下电源键后,引导芯片代码从ROM中开始执行。加载引导程序BootLoader到RAM中。
通过引导程序BootLoader将系统OS拉起来并运行。
Linux内核启动,设置缓存、计划列表、加载驱动。当内核完成系统设置时,解析init.rc文件,然后启动init进程。
init进程启动主要初始化和启动属性服务,然后启动Zygote进程。
Zygote进程创建Java虚拟机,创建服务端的Socket进程通信,然后启动SystemServer进程。
SystemServer进程启动Binder线程池、创建SystemServiceManager,并且启动各种系统服务。
Launcher应用程序启动。
可以看出,在Android系统的启动过程中主要涉及到了3个重要的进程,这3个进程向Android应用程序提供了必要的服务。最后启动了Launcher应用程序,将系统桌面呈现给了用户。