1.链表的实现:不带哨兵
一、链表linked list
1.定义
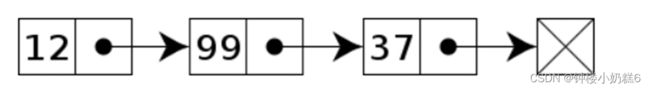
链表是数据元素的线性集合,其每个元素都指向下一个元素,元素存储上并不连续,链表逻辑连续。
2.分类
①单向链表:每个元素只知道其下一个元素是谁
②双向链表: 每个元素知道其上一个元素和下一个元素
③循环链表
3.哨兵节点
不存储数据,用作头尾,用来简化边界判断
4.链表性能
①随机访问(读取)
根据index查找,时间复杂O(n)。
根据索引查找元素的时候,要从头节点挨个查找
②插入或删除
起始位置:O(1)
结束位置:已知尾节点是O(1),不知道尾结点是O(n)
中间位置:根据index查找时间+O(1)
二、单向链表,不带哨兵
1.代码实现
①定义节点
public class SinglyLinkedList{
/**
* 节点类
* 数据域和地址域
*/
private static class Node {
int value;// 值
Node next;// 指向下一个节点,因为节点的类型是Node
public Node() {
}
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node head; //头指针
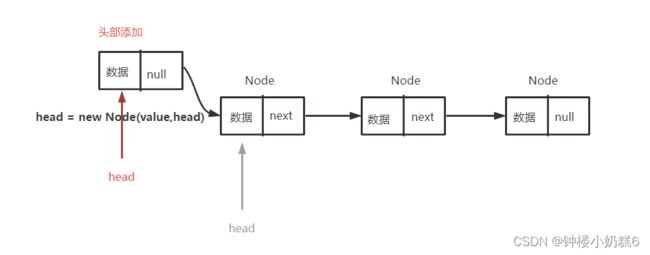
}②头部添加:每次是往表头依次添加,把新节点指向此时的head。然后让head再指向新节点。
如果head是null,就是head = new Node(value,null)
public void addFirst(int value) {
// 1.链表为空时,head是null 相当于head = new Node(value,null)
// 2.链表不为空时,new Node(value,head) 然后把新节点当为头结点head = new Node(value,head)
// 3.优化如下
head = new Node(value, head);
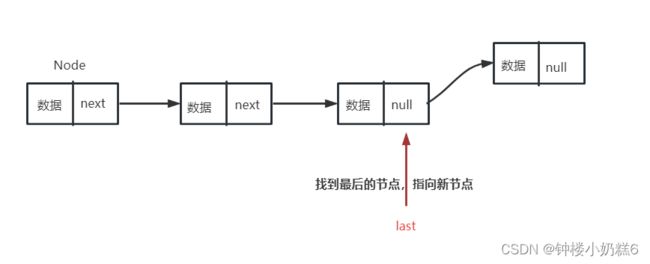
}②尾部添加:先找到最后一个节点的地址 while(p.next != null),如果链表为空,返回null
public Node findLast() {
// 判断是否为空
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 链表不为空
Node p = head;
while (p.next != null) {
p = p.next;
}
return p;
}返回的是最后一个节点地址last.next=new Node(value, null);如果返回的是null,那么就表头添加。
public void addLast(int value) {
Node last = findLast();
if (last == null) {
addFirst(value);
return;
}
// 找到尾巴节点
last.next = new Node(value, null);
}
③遍历节点1:定义一个辅助节点p指向头结点,条件是while(p!=null),一直到链表为空
/**
* 2.遍历节点1
*/
public void loop1() {
Node p = head;
while (p != null) {
System.out.println(p.value);
p = p.next;
}
}
/**
* 遍历节点2
*/
public void loop2() {
for (Node p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {
System.out.println(p.value);
}
}也可以用增强for循环,重写iterator()
public class SinglyLinkedList implements Iterable {
....
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Iterator() {
Node p = head;
// 是否有下一个元素
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return p != null;
}
// 返回当前元素,指向下一个元素
@Override
public Integer next() {
int value = p.value;
p = p.next;
return value;
}
};
}
} 测试用这个
Iterator iterator = singlyLinkedList.iterator();
for (Integer integer:singlyLinkedList){
System.out.println(integer);
} ④根据索引查找get(i) 0,1,2,3...,先查找这个索引的节点。没有找到返回null,找到的话返回当前节点
public Node findNode(int index) {
Node p = head;
int i = 0;
while (p != null) {
// 找到了
if (index == i) {
return p;
}
i++;
p = p.next;//指向下一个节点
}
// 没找到
return null;
}如果为null,说明此时不合法
public int get(int index){
Node node = findNode(index);
if (node == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
String.format("inndex[%d]不合法%n",index)
);
}
return node.value;
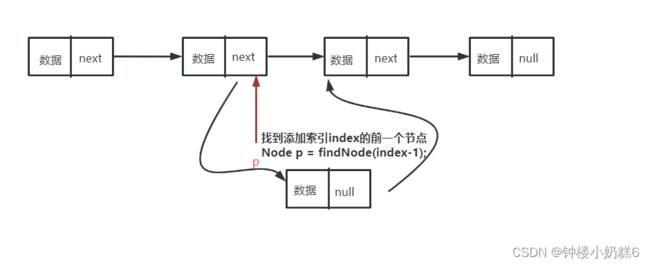
}⑤插入到索引位置,先定义辅助节点p指向索引的前一个地址,先让新节点的地址指向p的地址,再让p节点指向新节点的地址。如果p为空,插入失败。如果索引为0,那么调用头部添加的方法
/**
* 4.insert(int index)
* 根据索引插入,插在索引的位置,所以找索引前面的节点
*/
public void insert(int index,int value){
if (index == 0){
// 插入头位置
addFirst(value);
System.out.println("插入成功");
return;
}
Node p = findNode(index-1); // 找到索引的前一个节点
if (p == null){
// 链表为空,或者索引超出了范围
System.out.println("插入失败");
return;
}
// 找到索引的前一个节点
Node newNode = new Node(value,p.next);
p.next = newNode;
System.out.println("插入成功");
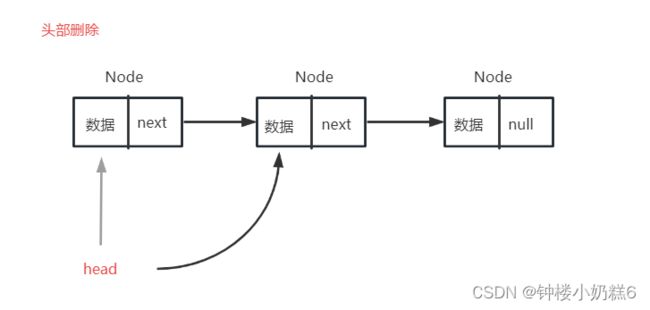
}⑥:按照索引删除节点,先实现删除头结点,让head指向head.next
public void removeFirst(){
if (head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空,删除失败");
return;
}
head = head.next; //
}// 删除节点
/**
* 删除节点:按照索引
*/
public void removeIndex(int index){
if (index == 0){
// 删除头结点
removeFirst();
return;
}
Node prev= findNode(index - 1);
// 如果为空
if (prev == null){
// 链表为空或者超过了索引范围
System.out.println("删除失败");
return;
}
// 此时node是删除索引的前一个节点
Node removed = prev.next;
if (removed == null ){
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
prev.next=removed.next;// 索引的前一个节点,指向索引的后一个节点
System.out.println("删除成功");
}