OpenAI - tiktoken ⏳ | fast BPE tokeniser
文章目录
-
- 关于 ⏳ tiktoken
-
- 性能表现
- 安装
- tiktoken 如何计算 token
- Encodings
- Tokenizer libraries 对不同编程语言的支持
- How strings are typically tokenized
- 使用
-
- 编解码
- 比较 encodings
- 计算chat API调用的tokens
- 拓展 tiktoken
关于 ⏳ tiktoken
tiktoken is a fast BPE tokeniser for use with OpenAI’s models.
初看这个名字,以为是跟 tiktok 相关,没想到是 openai 下面的,这取名还真是有趣呢。
- github https://github.com/openai/tiktoken
- openai-cookbook / examples / How_to_count_tokens_with_tiktoken.ipynb
https://github.com/openai/openai-cookbook/blob/main/examples/How_to_count_tokens_with_tiktoken.ipynb
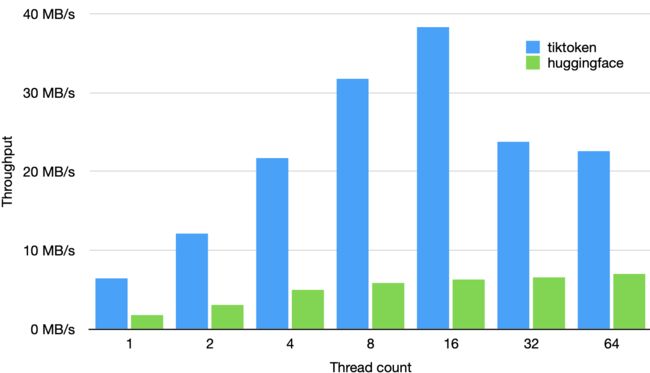
性能表现
tiktoken 比其他开源 tokeniser 快 3-6 倍
基于 1GB 文本进行测试,使用 GPT-2 tokeniser,使用 GPT2TokenizerFast from tokenizers==0.13.2, transformers==4.24.0 and tiktoken==0.2.0。
安装
pip install tiktoken
tiktoken 如何计算 token
给定一个文本字符:"tiktoken is great!",和一个 encoding,比如 "cl100k_base"。
一个 tokenizer 可以讲文本字符串分割成一系列 tokens,如: ["t", "ik", "token", " is", " great", "!"]
GPT 模型使用这种类型的 token。
知道文本字符串中有多少令牌,可以告诉你(a)字符串是否太长,文本模型无法处理,以及(b)OpenAI API调用的成本(因为使用是按令牌定价的)。
Encodings
编码指定如何将文本转换为标记。不同的模型使用不同的编码。
OpenAI models 使用 tiktoken 支持下面三种编码:
| Encoding name | OpenAI models |
|---|---|
cl100k_base |
gpt-4, gpt-3.5-turbo, text-embedding-ada-002 |
p50k_base |
Codex models, text-davinci-002, text-davinci-003 |
r50k_base (or gpt2) |
GPT-3 models like davinci |
您可以获取一个模型的编码 ,使用 tiktoken.encoding_for_model() 如下:
encoding = tiktoken.encoding_for_model('gpt-3.5-turbo')
注意,p50k_base 与 r50k_base 基本类似,对于非代码应用程序,它们通常会给出相同的令牌。
Tokenizer libraries 对不同编程语言的支持
对于 cl100k_base 和 p50k_base encodings:
- Python: tiktoken
- .NET / C#: SharpToken
对于 r50k_base (gpt2) encodings, tokenizers are available in many languages.
- Python: tiktoken (or alternatively GPT2TokenizerFast)
- JavaScript: gpt-3-encoder
- .NET / C#: GPT Tokenizer
- Java: gpt2-tokenizer-java
- PHP: GPT-3-Encoder-PHP
(OpenAI不对第三方库进行背书或保证。)
How strings are typically tokenized
In English, tokens commonly range in length from one character to one word (e.g., "t" or " great"), though in some languages tokens can be shorter than one character or longer than one word. Spaces are usually grouped with the starts of words (e.g., " is" instead of "is " or " "+"is"). You can quickly check how a string is tokenized at the OpenAI Tokenizer.
在英语中,tokens的长度通常从一个字符到一个单词(例如,t 或 great ),尽管在一些语言中,tokens 可以短于一个字符或长于一个单词。
空格通常以单词的开头分组(例如, is 而不是 is 或 + is。
您可以在[OpenAI Tokenizer]快速检查字符串是如何tokenize的。
OpenAI Tokenizer : https://beta.openai.com/tokenizer
使用
编解码
import tiktoken
# 使用名字加载 encoding
# 第一次运行时,可能需要连接互联网来下载;下一次不需要联网
encoding = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base")
# 对于给定的模型名,自动加载正确的 encoding
encoding = tiktoken.encoding_for_model("gpt-3.5-turbo")
# 将文本转化为 tokens 列表
encoding.encode("tiktoken is great!")
# [83, 1609, 5963, 374, 2294, 0]
# 计算 encode 返回列表的长度
def num_tokens_from_string(string: str, encoding_name: str) -> int:
"""Returns the number of tokens in a text string."""
encoding = tiktoken.get_encoding(encoding_name)
num_tokens = len(encoding.encode(string))
return num_tokens
num_tokens_from_string("tiktoken is great!", "cl100k_base") # 6
# 将 tokens 转化为 文本
encoding.decode([83, 1609, 5963, 374, 2294, 0])
# 'tiktoken is great!'
警告:尽管 .decode() 可以应用于单个令牌,但要注意,对于不在utf-8边界上的令牌,它可能会有损耗。
对于单个 tokens,.decode_single_token_bytes() 方法安全地将单个整数令牌转换为它所代表的字节。
[encoding.decode_single_token_bytes(token) for token in [83, 1609, 5963, 374, 2294, 0]]
# [b't', b'ik', b'token', b' is', b' great', b'!']
(字符串前面的 b 表示字符串是字节字符串。)
比较 encodings
不同的编码在拆分单词、组空格和处理非英语字符的方式上各不相同。使用上面的方法,我们可以比较几个示例字符串的不同编码。
def compare_encodings(example_string: str) -> None:
"""Prints a comparison of three string encodings."""
# print the example string
print(f'\nExample string: "{example_string}"')
# for each encoding, print the # of tokens, the token integers, and the token bytes
for encoding_name in ["gpt2", "p50k_base", "cl100k_base"]:
encoding = tiktoken.get_encoding(encoding_name)
token_integers = encoding.encode(example_string)
num_tokens = len(token_integers)
token_bytes = [encoding.decode_single_token_bytes(token) for token in token_integers]
print()
print(f"{encoding_name}: {num_tokens} tokens")
print(f"token integers: {token_integers}")
print(f"token bytes: {token_bytes}")
compare_encodings("antidisestablishmentarianism")
Example string: "antidisestablishmentarianism"
gpt2: 5 tokens
token integers: [415, 29207, 44390, 3699, 1042]
token bytes: [b'ant', b'idis', b'establishment', b'arian', b'ism']
p50k_base: 5 tokens
token integers: [415, 29207, 44390, 3699, 1042]
token bytes: [b'ant', b'idis', b'establishment', b'arian', b'ism']
cl100k_base: 6 tokens
token integers: [519, 85342, 34500, 479, 8997, 2191]
token bytes: [b'ant', b'idis', b'establish', b'ment', b'arian', b'ism']
compare_encodings("2 + 2 = 4")
Example string: "2 + 2 = 4"
gpt2: 5 tokens
token integers: [17, 1343, 362, 796, 604]
token bytes: [b'2', b' +', b' 2', b' =', b' 4']
p50k_base: 5 tokens
token integers: [17, 1343, 362, 796, 604]
token bytes: [b'2', b' +', b' 2', b' =', b' 4']
cl100k_base: 7 tokens
token integers: [17, 489, 220, 17, 284, 220, 19]
token bytes: [b'2', b' +', b' ', b'2', b' =', b' ', b'4']
compare_encodings("お誕生日おめでとう")
Example string: "お誕生日おめでとう"
gpt2: 14 tokens
token integers: [2515, 232, 45739, 243, 37955, 33768, 98, 2515, 232, 1792, 223, 30640, 30201, 29557]
token bytes: [b'\xe3\x81', b'\x8a', b'\xe8\xaa', b'\x95', b'\xe7\x94\x9f', b'\xe6\x97', b'\xa5', b'\xe3\x81', b'\x8a', b'\xe3\x82', b'\x81', b'\xe3\x81\xa7', b'\xe3\x81\xa8', b'\xe3\x81\x86']
p50k_base: 14 tokens
token integers: [2515, 232, 45739, 243, 37955, 33768, 98, 2515, 232, 1792, 223, 30640, 30201, 29557]
token bytes: [b'\xe3\x81', b'\x8a', b'\xe8\xaa', b'\x95', b'\xe7\x94\x9f', b'\xe6\x97', b'\xa5', b'\xe3\x81', b'\x8a', b'\xe3\x82', b'\x81', b'\xe3\x81\xa7', b'\xe3\x81\xa8', b'\xe3\x81\x86']
cl100k_base: 9 tokens
token integers: [33334, 45918, 243, 21990, 9080, 33334, 62004, 16556, 78699]
token bytes: [b'\xe3\x81\x8a', b'\xe8\xaa', b'\x95', b'\xe7\x94\x9f', b'\xe6\x97\xa5', b'\xe3\x81\x8a', b'\xe3\x82\x81', b'\xe3\x81\xa7', b'\xe3\x81\xa8\xe3\x81\x86']
计算chat API调用的tokens
ChatGPT models like gpt-3.5-turbo and gpt-4 use tokens in the same way as older completions models, but because of their message-based formatting, it’s more difficult to count how many tokens will be used by a conversation.
Below is an example function for counting tokens for messages passed to gpt-3.5-turbo-0301 or gpt-4-0314.
Note that the exact way that tokens are counted from messages may change from model to model. Consider the counts from the function below an estimate, not a timeless guarantee.
像 gpt-3.5-turbo 和 gpt-4 这样的ChatGPT模型使用tokens 的方式与旧的完成模型相同,但由于它们基于消息的格式,很难计算会话将使用多少tokens。
下面是一个示例函数,用于对传递到 gpt-3.5-turbo-0301 或 gpt-4-0314 的消息的tokens进行计数。
请注意,从消息中计算tokens的确切方式可能会因模型而异。将函数中的计数视为一个估计值,而不是一个永恒的保证。
def num_tokens_from_messages(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0301"):
"""Returns the number of tokens used by a list of messages."""
try:
encoding = tiktoken.encoding_for_model(model)
except KeyError:
print("Warning: model not found. Using cl100k_base encoding.")
encoding = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base")
if model == "gpt-3.5-turbo":
print("Warning: gpt-3.5-turbo may change over time. Returning num tokens assuming gpt-3.5-turbo-0301.")
return num_tokens_from_messages(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0301")
elif model == "gpt-4":
print("Warning: gpt-4 may change over time. Returning num tokens assuming gpt-4-0314.")
return num_tokens_from_messages(messages, model="gpt-4-0314")
elif model == "gpt-3.5-turbo-0301":
tokens_per_message = 4 # every message follows <|start|>{role/name}\n{content}<|end|>\n
tokens_per_name = -1 # if there's a name, the role is omitted
elif model == "gpt-4-0314":
tokens_per_message = 3
tokens_per_name = 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"""num_tokens_from_messages() is not implemented for model {model}. See https://github.com/openai/openai-python/blob/main/chatml.md for information on how messages are converted to tokens.""")
num_tokens = 0
for message in messages:
num_tokens += tokens_per_message
for key, value in message.items():
num_tokens += len(encoding.encode(value))
if key == "name":
num_tokens += tokens_per_name
num_tokens += 3 # every reply is primed with <|start|>assistant<|message|>
return num_tokens
# let's verify the function above matches the OpenAI API response
import openai
example_messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful, pattern-following assistant that translates corporate jargon into plain English.",
},
{
"role": "system",
"name": "example_user",
"content": "New synergies will help drive top-line growth.",
},
{
"role": "system",
"name": "example_assistant",
"content": "Things working well together will increase revenue.",
},
{
"role": "system",
"name": "example_user",
"content": "Let's circle back when we have more bandwidth to touch base on opportunities for increased leverage.",
},
{
"role": "system",
"name": "example_assistant",
"content": "Let's talk later when we're less busy about how to do better.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "This late pivot means we don't have time to boil the ocean for the client deliverable.",
},
]
for model in ["gpt-3.5-turbo-0301", "gpt-4-0314"]:
print(model)
# example token count from the function defined above
print(f"{num_tokens_from_messages(example_messages, model)} prompt tokens counted by num_tokens_from_messages().")
# example token count from the OpenAI API
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model=model,
messages=example_messages,
temperature=0,
max_tokens=1 # we're only counting input tokens here, so let's not waste tokens on the output
)
print(f'{response["usage"]["prompt_tokens"]} prompt tokens counted by the OpenAI API.')
print()
gpt-3.5-turbo-0301
127 prompt tokens counted by num_tokens_from_messages().
127 prompt tokens counted by the OpenAI API.
gpt-4-0314
129 prompt tokens counted by num_tokens_from_messages().
129 prompt tokens counted by the OpenAI API.
拓展 tiktoken
您可能希望扩展 tiktoken 以支持新的编码。有两种方法可以做到这一点。
按照您想要的方式创建Encoding对象,然后简单地传递它。
方式一:
cl100k_base = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base")
# In production, load the arguments directly instead of accessing private attributes
# See openai_public.py for examples of arguments for specific encodings
enc = tiktoken.Encoding(
# If you're changing the set of special tokens, make sure to use a different name
# It should be clear from the name what behaviour to expect.
name="cl100k_im",
pat_str=cl100k_base._pat_str,
mergeable_ranks=cl100k_base._mergeable_ranks,
special_tokens={
**cl100k_base._special_tokens,
"<|im_start|>": 100264,
"<|im_end|>": 100265,
}
)
方式二:
使用 tiktoken_ext 插件机制 向tiktoken注册Encoding对象。
只有当您需要 tiktoken.get_encoding 来查找您的编码时,这才有用,否则更适合上面方式1。
要做到这一点,您需要在 tiktoken_ext 下创建一个命名空间包。
这样布局你的项目,确保省略 tiktoken_ext/__init__.py文件:
my_tiktoken_extension
├── tiktoken_ext
│ └── my_encodings.py
└── setup.py
my_encodings.py 应该是一个包含名为 ENCODING_CONSTRUCTORS 的变量的模块。
这是一个从编码名称到函数的字典,该函数不接受参数,并返回可以传递给 tiktoken.encoding 的参数来构造该编码。
例如,请参阅 tiktoken_ext/openai_public.py。有关详细信息,请参阅 tiktoken/registry.py 。
你的setup.py 应该是这样的:
from setuptools import setup, find_namespace_packages
setup(
name="my_tiktoken_extension",
packages=find_namespace_packages(include=['tiktoken_ext*']),
install_requires=["tiktoken"],
...
)
然后简单地执行 pip install ./my_tiktoken_extension,您应该能够使用自定义编码!请确保不要使用可编辑安装。
2023-03-31(五)