prophet模块学习总结-20221228
prophet模块的基本介绍及相关用法说明。
文章目录
-
-
-
- 1.基本介绍
-
- Prophet包的特点
- 2.Prophet 模型介绍
-
-
- 2.1 长期趋势模型
- 2.2 The Seasonality Function(季节函数)
- 2.3 The Holiday/Event Function(节日函数)
-
- 3.使用示例
-
- 3.1 快速开始
- 3.2 调节参数
- 4.异常值处理
- 5.交叉验证和超参数选择
- 参考链接
-
-
1.基本介绍
Prophet是 Facebook 2017 年的工作——高质量且简单易用的时间预测模型。
适用于大规模的时序预测模型。它不仅解决了时序预测的建模问题,还解决了模型的可解释性问题。
Prophet是基于可分解(趋势+季节+节假日)模型的开源库。它让我们可以用简单直观的参数进行高精度的时间序列预测,并且支持自定义季节和节假日的影响。
Prophet包的特点
- 提供了直观易调的参数
- 大规模的时序预测模型,可解释性强。
- 灵活性强,易于分解,且在必要时也可以容纳新的成分;
- 拟合速度快,允许用户进行交互式探索;
- 测量值不需要有规则的间隔,也不需要对缺失值进行处理
- 提供了R包和python包,两种语言环境都可以使用
2.Prophet 模型介绍
用于分析和预测周期性数据时,一种强大而简单的方法是加法模型(additive model)。
这个想法很简单:将时间序列表示为每日、每周、每季度和每年度等不同时间维度的组合模式,并加以整体趋势。
加法模型可以向我们展示数据的模式/趋势,并根据这些观察结果进行预测。
(图见:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FaxBq_6ax6rzu7s-8_wpRw)
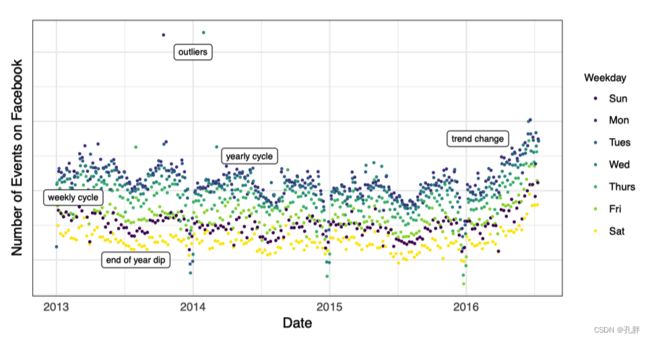
这是 Facebook 的真实数据集,每一天都有一个点,点的颜色按照星期进行编码,以展示一个星期的周期性。
从这张图中我们可以看到:这个时间序列具有周期性 (weekly、yearly)、趋势变化性 (Trend)、异常点 (outliers) 和节假日效应 (holiday)。
其中:
- g(t)是长时间段的变化趋势;
- s(t)表示短期或者季节性的变化规律;
- h(t)表示不规律的假期影响;
- e(t)误差项表示模型针对特定企业或个人的任何特殊变化;
- y(t)为预测值。
这类规范类似于广义可加模型 (Generalized additive model,GAM),这是一种非线性的回归模型。
我们可以使用时间序列分解将其分解为趋势、季节性、节假日:
下图显示了一个时间序列的加法模型,它分解为整体趋势、年度趋势和每周趋势。

2.1 长期趋势模型
- logistic growth model(饱和增长:逻辑斯谛增长模型)
如果预测数据是已达饱和的非线性数据(非线性增长且已达到饱和点,仅根据季节性发生很小的变化),那么建议使用 logistic growth模型
c是趋势变化点,可以进行人工调节。
- Flat(平滑模型)
最近,你可以选择flat模式。该模式的长期趋势随着时间的推移没有什么变化,主要调节季节性变化。
2.2 The Seasonality Function(季节函数)
季节函数是随着时间的傅里叶变化。
If you are unfamiliar with Fourier Series, an easy way to think about it is the sum of many successive sines and cosines. Each sine and cosine term is multiplied by some coefficient. This sum can approximate nearly any curve or in the case of Facebook Prophet, the seasonality (cyclical pattern) in our data. All together it looks like this:(不想翻译了,介绍傅里叶的)

If the above is difficult to decipher, I recommend this simple breakdown of the Fourier Series or this video on the intuition behind the Fourier series.
可以对β进行调节,值越大,季节效应越明显;值越小,季节效应越不明显。
2.3 The Holiday/Event Function(节日函数)
节日函数允许根据一年中的重大节日或者事件来调节预估值。
Prophet 允许用户设置过去和未来的假日或者事件,并且设置节假日影响的时间长短。
于是,
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ALLiRI8a-1672222719567)(evernotecid://4A2C0413-3745-487E-BADD-865195851786/appyinxiangcom/25370018/ENResource/p9223)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/407baf3b9e814ac195e037095d18b7f4.jpg)
z(t)为因节日而引起的变化函数,k值越大,节假日对模型的影响越大;值越小,节假日对模型的影响越小。
3.使用示例
3.1 快速开始
import pandas as pd
# read data from NY times
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nytimes/covid-19-data/master/us.csv")
# engineer new cases
df['new_cases'] = df.cases - df.cases.shift().fillna(0)
# create pandas time series
df.date = pd.to_datetime(df.date)
df.set_index('date',inplace=True)
df['rolling_weekly_avg'] =df.new_cases.rolling(window=7).mean().fillna(0)
# create timeseries readable by fbprophet
ts = pd.DataFrame({'ds':df.index,'y':df.new_cases}) # 时间:新增病例#ts['cap'] = 30000 # unused in linear growth
#ts['floor'] = 0 # unused in linear growth
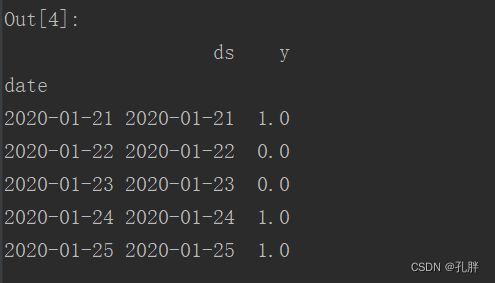
ts.head()
from fbprophet import Prophet
# instantiate the model and fit the timeseries
prophet = Prophet()
prophet.fit(ts)
# create a future data frame
future = prophet.make_future_dataframe(periods=25)
forecast = prophet.predict(future)
# display the most critical output columns from the forecast
forecast[['ds','yhat','yhat_lower','yhat_upper']].head()
# plot
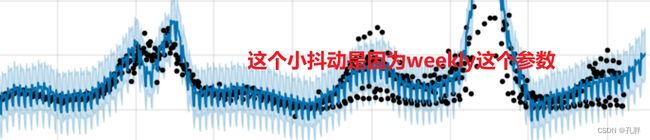
fig = prophet.plot(forecast)
同样,可以添加辅助线来查看发现的趋势变化点。
from fbprophet.plot import add_changepoints_to_plot
a = add_changepoints_to_plot(fig.gca(),prophet,forecast)
fig
这个结果比较合理,但仍然有微调的空间。
3.2 调节参数
可以看到,在来年确诊人数下降,但模型仍呈上升趋势。
常用参数介绍
| 参数名 | 中文名 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| changepoint_range | 突变点的选取范围 | 默认为0.8,即在前80%的数据内确定突变点,过高容易导致过拟合 |
| n_changepoints | 突变点个数 | 设置突变点个数,若设置30个,则相当于要在突变点的选取范围内平均划分30个突变点 |
| changepoint_prior_scale | ||
| seasonality_prior_scale | ||
| holidays_prior_scale | ||
| seasonality_mode |
from fbprophet import Prophet
# instantiate the model and fit the timeseries
prophet = Prophet(weekly_seasonality=False, changepoint_range=1,changepoint_prior_scale=0.75)
prophet.fit(ts)
这里可以看参数注释: https://www.sktime.org/en/v0.6.0/api_reference/modules/auto_generated/sktime.forecasting.fbprophet.Prophet.html
4.异常值处理
The best way to handle outliers is to remove them - Prophet has no problem with missing data. If you set their values to NA in the history but leave the dates in future, then Prophet will give you a prediction for their values.
最好的方式是移除空值。如果你的历史数据中存在缺失值,而在future数据中给出确实值的日期,那么prophet会给出确实值的预测值。
5.交叉验证和超参数选择
- 交叉验证
prophet可以对时间序列进行交叉验证以衡量历史数据上的预测误差。通过在历史数据中选择一系列cutoff点的方式来进行验证,从起始数据到不同的cutoff点的数据来拟合模型,返回包含真实值y和预测值yhat的dataframe。
# Python
from prophet.diagnostics import cross_validation
df_cv = cross_validation(m, initial='730 days', period='180 days', horizon = '365 days')
df_cv.head()
可以使用performance_metrics工具来计算预测效果(MSE,RMSE,MAE…)
# Python
from prophet.diagnostics import performance_metrics
df_p = performance_metrics(df_cv)
df_p.head()
交叉验证度量效果可以通过plot_cross_validation_metric函数进行查看。
# Python
from prophet.plot import plot_cross_validation_metric
fig = plot_cross_validation_metric(df_cv, metric='mape')
- 并行交叉验证
设置parallel参数实现 - 超参数调优
交叉验证用于超参数调优示例
# Python
import itertools
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
param_grid = {
'changepoint_prior_scale': [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 0.5],
'seasonality_prior_scale': [0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0],
}
# Generate all combinations of parameters
all_params = [dict(zip(param_grid.keys(), v)) for v in itertools.product(*param_grid.values())]
rmses = [] # Store the RMSEs for each params here
# Use cross validation to evaluate all parameters
for params in all_params:
m = Prophet(**params).fit(df) # Fit model with given params
df_cv = cross_validation(m, cutoffs=cutoffs, horizon='30 days', parallel="processes")
df_p = performance_metrics(df_cv, rolling_window=1)
rmses.append(df_p['rmse'].values[0])
# Find the best parameters
tuning_results = pd.DataFrame(all_params)
tuning_results['rmse'] = rmses
print(tuning_results)
# Python
best_params = all_params[np.argmin(rmses)]
print(best_params)
可以用来调节的参数:
- changepoint_prior_scale
- seasonality_prior_scale
- holidays_prior_scale
- seasonality_mode
也许可以调节的参数:
- changepoint_range
不可以用来调节的参数:
- growth
- changepoints
- n_changepoints
- yearly_seasonality
- weekly_seasonality
- daily_seasonality
- holidays
- mcmc_samples
- interval_width
- uncertainty_samples
- stan_backend
参考链接
官网链接:
https://facebook.github.io/prophet/docs/quick_start.html#python-api
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/time-series-analysis-using-facebook-prophet/?ref=gcse
https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-analysis-with-facebook-prophet-how-it-works-and-how-to-use-it-f15ecf2c0e3a
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/52330017
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ven_4JbWYFswIkGyhjTcww
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9B3KMzR_8PePv2XCq-iO2w
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FaxBq_6ax6rzu7s-8_wpRw
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/mFgqV6C8RDzL5KidC1U-jA
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/smjRKQ-JntGTwCDCUS61GQ
https://pythondata.com/forecasting-time-series-data-prophet-trend-changepoints/
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mSuopgyQ-1672222719563)(evernotecid://4A2C0413-3745-487E-BADD-865195851786/appyinxiangcom/25370018/ENResource/p9235)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/dee17ade6d384fd9af9724a6bec18c10.jpg)


![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4gr1CxkN-1672222719567)(evernotecid://4A2C0413-3745-487E-BADD-865195851786/appyinxiangcom/25370018/ENResource/p9232)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d0a76e81c2be4b3f9956b53fcf4d92b9.jpg)