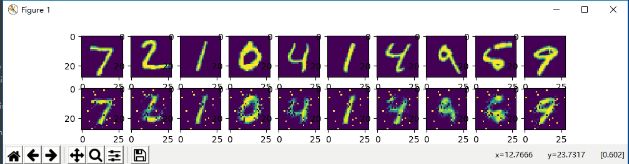
自编码器(minist)
自编码器(minist数据集)
(摘自《深度学习》)
简要介绍
自编码器是一种最经典的无监督网络,它是实现无监督数据特征提取的一种方法。无监督模型的泛化能力更强。
在无监督学习中,希望模型可以提取数据内部的规律特征,其中一大特征是稀疏性(sparsity).稀疏性存在的最大意义是降维,数据具有稀疏性,那么模型需要提取的特征的数量就远比输入神经元数量要小。数据的稀疏性导致了模型的稀疏性。
自编码器主要包括encoder和decoder。其中,encoder和decoder也可以分别采用CNN,LSTM等(如:https://blog.csdn.net/niuniuyuh/article/details/59108795和https://blog.csdn.net/stockholm0215/article/details/84954264)。自编码器主要用于降维和去噪。
对于自编码器来说,最直观的损失函数便是衡量输入与输出之间的均方误差(MSE).
L1正则化可以约束模型学习稀疏性特征。另外一种经常用来作为规范项的指标,叫做相对熵(KL Divergence,KLD),相对熵又称为KL散度,是一种衡量两个分布之间差异的方法。
无论是使用Sigmoid函数还是ReLU函数,损失函数中都包括了均方误差项来实现对输入数据的重构。至于稀疏性约束,相对熵和Sigmoid函数配合使用,而L1正则化和ReLU配合使用。
代码
基于tensorflow的实现
(摘自网上的代码,并做稍作修改)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.io as sio
import os
# 导入MNIST数据
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("E:/MNIST_data/", one_hot=False)
learning_rate = 0.01
training_epochs = 10
batch_size = 256
display_step = 1
examples_to_show = 10
n_input = 784
# tf Graph input (only pictures)
X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_input])
# 用字典的方式存储各隐藏层的参数
n_hidden_1 = 256 # 第一编码层神经元个数
n_hidden_2 = 128 # 第二编码层神经元个数
# 权重和偏置的变化在编码层和解码层顺序是相逆的
# 权重参数矩阵维度是每层的 输入*输出,偏置参数维度取决于输出层的单元数
weights = {
'encoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_hidden_1])),
'encoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2])),
'decoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2, n_hidden_1])),
'decoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_input])),
}
biases = {
'encoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])),
'encoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])),
'decoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])),
'decoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input])),
}
# 每一层结构都是 xW + b
# 构建编码器
def encoder(x):
layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['encoder_h1']),
biases['encoder_b1']))
layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['encoder_h2']),
biases['encoder_b2']))
return layer_2
# 构建解码器
def decoder(x):
layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['decoder_h1']),
biases['decoder_b1']))
layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['decoder_h2']),
biases['decoder_b2']))
return layer_2
# 构建模型
encoder_op = encoder(X)
decoder_op = decoder(encoder_op)
# 预测
y_pred = decoder_op
y_true = X
# 定义代价函数和优化器
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(y_true - y_pred, 2)) # 最小二乘法
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from
# 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 首先计算总批数,保证每次循环训练集中的每个样本都参与训练,不同于批量训练
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size) # 总批数
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # max(x) = 1, min(x) = 0
# Run optimization op (backprop) and cost op (to get loss value)
_, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs})
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch + 1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(c))
print("Optimization Finished!")
encoder_=sess.run(encoder_op,feed_dict={X:mnist.train.images})
sio.savemat('features_all.mat',{'encoder_':encoder_})
encode_decode = sess.run(
y_pred, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[:examples_to_show]})
f, a = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(10, 2))
for i in range(examples_to_show):
a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i], (28, 28)))
a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(encode_decode[i], (28, 28)))
plt.show()
基于keras的实现
(摘自网上的代码,并做稍作修改)
from keras.layers import Input, Dense
from keras.models import Model
from keras.datasets import mnist
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
x_train = x_train.reshape((len(x_train), np.prod(x_train.shape[1:])))
x_test = x_test.reshape((len(x_test), np.prod(x_test.shape[1:])))
print(x_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape)
encoding_dim = 32
input_img = Input(shape=(784,))
encoded = Dense(encoding_dim, activation='relu')(input_img)
decoded = Dense(784, activation='sigmoid')(encoded)
autoencoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=decoded)
encoder = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=encoded)
encoded_input = Input(shape=(encoding_dim,))
decoder_layer = autoencoder.layers[-1]
decoder = Model(inputs=encoded_input, outputs=decoder_layer(encoded_input))
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adadelta', loss='binary_crossentropy')
autoencoder.fit(x_train, x_train, epochs=50, batch_size=256,
shuffle=True, validation_data=(x_test, x_test))
encoded_imgs = encoder.predict(x_test)
decoded_imgs = decoder.predict(encoded_imgs)
n = 10 # how many digits we will display
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1 + n)
plt.imshow(decoded_imgs[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()