Hook攻防之InlineHook
什么是InlineHook
Inline Hook,又称为超级Hook,是一种强大而又灵活的Hook技术。
Inline Hook的主要思想就是直接修改目标函数的代码,通常是在目标函数的开头插入一个跳转指令(jmp)。这个跳转指令会将程序的执行流跳转到我们自定义的函数中。
在我们的自定义函数中,我们可以执行任意的代码,然后再跳回目标函数的剩余部分。这样,我们就可以在不改变目标函数原有逻辑的基础上,添加自己的功能
一个简单的Hook实例
首先用C语言创建一个简单的加法程序
include<Windows.h>
include<cstdio>
int ADD(int a,int b) {
return a + b;
}
int main() {
int a, b;
scanf("%d,%d",&a, &b);
printf("结果是:%d", ADD(a, b));
}
将程序拖入OD中,并且找到Add函数的call的地址并在此处下个断点
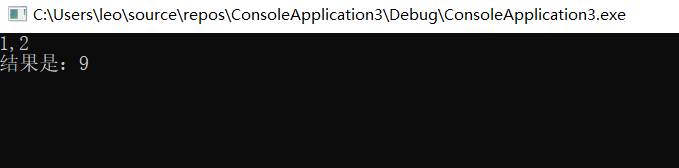
OD运行程序输入数据,这里我们输入1,2
F7进入Add函数的call,通过右下角的堆栈窗口可以查看上述输入的实参(1,2),也就是说,如果将这个堆栈里的参数值给修改了,那么就可以修改函数的返回值
首先在函数头部地址添加一个JMP汇编指令,跳转的地址是任意的,只要这个地址周围没有指令,这里以跳转到401045为例
红色部分的汇编指令就是我们自行创建的,以此来实现修改堆栈中的函数参数值
这里也要注意平衡堆栈,原先的call是有push ebp和mov ebp,esp指令的,由于添加了jmp指令导致它们被覆盖,所以这里要添上
最后的jmp指令再跳转回到401003
最后程序运行结果为9,这是因为我们把参数从原先的1和2, 修改成了4和5
代码实现思路
这里我们会介绍两种实现 Inline Hook 的方法:
- 使用
jmp指令:这种方法通过插入一条jmp指令到目标函数的开始,使得函数在调用时直接跳转到我们自定义的函数。这里需要计算jmp后面的地址,因为jmp指令的目标地址是相对于下一条指令的位置计算的。计算公式为:jmp后面的地址 = 目的地址 - 源地址 - 5。其中,5 是jmp指令的字节数。 - 使用
mov eax, address和jmp eax指令:这种方法首先把自定义函数的地址加载到eax寄存器,然后使用jmp eax跳转到该地址。这样,当目标函数被调用时,它会直接跳转到我们自定义的函数。
这两种方法各有优劣。使用 jmp 指令的方法简洁直观,但对源地址和目的地址的位置有一定的限制,如果目标和源地址之间的距离过大,可能导致 jmp 指令无法正确跳转。而使用 mov eax, address 和 jmp eax 的方法则没有这个问题,但需要更多的指令,可能会覆盖掉目标函数的更多代码
代码实现
1.借助eax间接jmp
include <windows.h>
include <stdio.h>
include <iostream>
include <tchar.h>
BYTE NewCode[7] = { 0xB8, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0xFF ,0xE0 }; // 新代码,用于Hook
BYTE OldCode[7] = { 0 }; // 旧代码,用于保存被Hook函数的原始字节
FARPROC MessageBoxAddress; // MessageBox函数的地址
// 自定义的MessageBoxA函数
int WINAPI MyMessageBoxA(HWND hWnd, LPCTSTR lpText, LPCTSTR lpCaption, UINT uType)
{
printf("MessageBoxA 已经被Hook\n"); // 打印信息
// 在调用原始函数之前,恢复原始代码
WriteProcessMemory(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, (void*)MessageBoxAddress, (void*)OldCode, 7, NULL);
// 调用原始的MessageBoxA函数
int ret = MessageBoxA(NULL, "Hello World", "Title", MB_OK);
// 在调用原始函数之后,再次将Hook代码写入
WriteProcessMemory(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, (void*)MessageBoxAddress, (void*)NewCode, 7, NULL);
return ret;
}
void InlineHook()
{
HMODULE hModule_User32 = LoadLibrary("user32.dll"); //加载user32.dll模块
MessageBoxAddress = GetProcAddress(hModule_User32, "MessageBoxA"); //获取MessageBoxA函数的地址
printf("MessageBoxA Addr is %x\n", MessageBoxAddress);
printf("MyMessageBoxA Addr is %x\n", MyMessageBoxA);
// 读取MessageBoxA函数的前7个字节,并保存在OldCode数组中
if (ReadProcessMemory(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, MessageBoxAddress, OldCode, 7, NULL) == 0)
{
printf("ReadProcessMemory error\n");
return;
}
printf("OldCode is %x%x%x%x%x%x%x\n", OldCode[0], OldCode[1], OldCode[2], OldCode[3], OldCode[4], OldCode[5], OldCode[6]);
DWORD JmpAddress = (DWORD)MyMessageBoxA - (DWORD)MessageBoxAddress - 5; // 获取自定义的MessageBoxA函数的地址
memcpy(&NewCode[1], &JmpAddress, 4); // 将地址写入到NewCode的第二个字节开始的位置
DWORD dwOldProtect = 0; // 用于保存原始页保护
printf("NewBytes is %x%x%x%x%x\n", NewCode[0], NewCode[1], NewCode[2], NewCode[3], NewCode[4], NewCode[5], NewCode[6]);
// 使用VirtualProtect函数改变MessageBoxA函数所在页的保护属性,使其可读可写可执行。
VirtualProtect(MessageBoxAddress, 7, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE,&dwOldProtect);
// 使用WriteProcessMemory函数将我们的Hook代码写入到MessageBoxA函数的开头。
WriteProcessMemory(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, MessageBoxAddress, NewCode, 7,NULL);
// 使用VirtualProtect函数恢复MessageBoxA函数所在页的保护属性。
VirtualProtect(MessageBoxAddress, 7, dwOldProtect, &dwOldProtect);
}
void main()
{
InlineHook();
MessageBoxA(NULL, "Hello World", "Title", MB_OK);
}
该代码首先将自定义函数MyMessageBoxA的地址加载到eax寄存器,然后通过jmp eax指令跳转到MyMessageBoxA。OldCode用于保存原始的MessageBoxA函数的前7个字节
然后通过WriteProcessMemory函数恢复原始的MessageBoxA函数的前7个字节,接着调用原始的MessageBoxA函数,最后再次通过WriteProcessMemory函数将NewCode写回到MessageBoxA函数的开头,以确保下次调用MessageBoxA时仍然会被Hook
在InlineHook函数中,程序首先获取MessageBoxA函数的地址,然后读取该地址的前7个字节并保存在OldCode数组中,接着计算出MyMessageBoxA函数的地址与MessageBoxA函数的地址之间的偏移量并保存在NewCode数组的第二个字节开始的位置,然后通过VirtualProtect函数修改MessageBoxA函数所在页的保护属性使其可读可写可执行,最后通过WriteProcessMemory函数将NewCode写入到MessageBoxA函数的开头
2.直接jmp
include <windows.h>
include <stdio.h>
include <iostream>
BYTE JmpOriginal[5] = { 0xE9, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // 用于跳转到MyMessageBoxA的指令,0xE9代表JMP指令
BYTE OldCode[5] = { 0 }; // 存储原始MessageBoxA的前5个字节
FARPROC MessageBoxAddress; // MessageBoxA的函数地址
void* Trampoline; // 桥接函数地址
// 自定义的MessageBoxA函数
int WINAPI MyMessageBoxA(HWND hWnd, LPCTSTR lpText, LPCTSTR lpCaption, UINT uType)
{
printf("MessageBoxA 已经被Hook\n"); // 打印被Hook的信息
// 使用桥接函数调用原始的MessageBoxA,这里需要类型转换
int ret = ((int (WINAPI*)(HWND, LPCTSTR, LPCTSTR, UINT))Trampoline)(hWnd, lpText, lpCaption, uType);
return ret;
}
void InlineHook()
{
HMODULE hModule_User32 = LoadLibraryA("user32.dll"); // 加载user32.dll模块
MessageBoxAddress = GetProcAddress(hModule_User32, "MessageBoxA"); // 获取MessageBoxA的函数地址
DWORD JmpAddress = (DWORD)MyMessageBoxA - (DWORD)MessageBoxAddress - 5; // 计算跳转到MyMessageBoxA的地址
memcpy(&JmpOriginal[1], &JmpAddress, 4); // 将跳转地址复制到JmpOriginal的第二个字节
ReadProcessMemory(GetCurrentProcess(), MessageBoxAddress, OldCode, 5, NULL); // 读取并保存MessageBoxA的前5个字节
// 分配10个字节的内存空间作为桥接函数
Trampoline = VirtualAlloc(NULL, 10, MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
memcpy(Trampoline, OldCode, 5); // 复制MessageBoxA的前5个字节到桥接函数
// 计算并写入桥接函数的跳回地址
DWORD jmpBackAddr = (DWORD)MessageBoxAddress + 5 - (DWORD)Trampoline - 5;
memcpy((void*)((DWORD)Trampoline + 5), &JmpOriginal[0], 5);
memcpy((void*)((DWORD)Trampoline + 6), &jmpBackAddr, 4);
DWORD dwOldProtect;
// 修改MessageBoxA的前5个字节的页属性,使其可读可写可执行
VirtualProtect(MessageBoxAddress, 5, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE, &dwOldProtect);
// 替换MessageBoxA的前5个字节为跳转到MyMessageBoxA的指令
WriteProcessMemory(GetCurrentProcess(), MessageBoxAddress, &JmpOriginal[0], 5, NULL);
// 恢复MessageBoxA的前5个字节的原始页属性
VirtualProtect(MessageBoxAddress, 5, dwOldProtect, &dwOldProtect);
}
void main()
{
InlineHook(); // 实施Inline Hook
MessageBoxA(NULL, "Hello World", "Title", MB_OK); // 调用MessageBoxA函数
}
与上述代码不同的是, 这里需计算跳转到我们自定义的MyMessageBoxA函数的跳转指令。除此之外,我们还在虚拟内存分配了一块区域用来存放被覆盖的原始代码,并在其后面添加一个跳转指令,使其能够返回被Hook的函数,这样做的好处是可以避免每次调用hook函数时都需要恢复和再次修改被Hook的函数代码
3.使用detours库
在windows 10操作系统中由于ASLR(地址随机化)的缘故,手工实现InLine比较麻烦,这里使用微软的一个轻量级的开源库Detours,
Detours 是一个由 Microsoft Research 开发的库,用于钩取和修改 Windows API 调用和其他函数调用。你可以从其 GitHub 仓库下载它:https://github.com/microsoft/Detours
这里我使用vcpkg来按照Detours库,运行如下命令,至于如何安装和使用vcpkg可以看这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/xf555er/article/details/130465197
vcpkg install detours
以下是具体的实现代码:
include<Windows.h>
include<stdio.h>
include <detours/detours.h>
// 声明一个函数指针OldMessageBoxA,指向MessageBoxA函数
static int (WINAPI* OldMesssageBoxA)
(
HWND hWnd,
LPCSTR lpText,
LPCSTR lpCaption,
UINT uType
) = MessageBoxA;
// 自定义函数MyFunction0,当MessageBoxA被调用时,会跳转到这个函数
int WINAPI MyFunction0(HWND hWnd, LPCSTR lpText, LPCSTR lpCaption, UINT uType)
{
// 在这个函数中,调用原来的MessageBoxA函数,显示特定的信息
return OldMesssageBoxA(NULL, "Hook Success!", "Warming", MB_OKCANCEL);
}
int main() {
// 开始一次新的Detour操作
DetourTransactionBegin();
// 告诉Detour这个线程将被影响
DetourUpdateThread(GetCurrentThread());
// 将OldMessageBoxA函数指针替换为MyFunction0,也就是说当MessageBoxA被调用时,跳转到MyFunction0
DetourAttach(&(PVOID&)OldMesssageBoxA, MyFunction0);
// 如果需要移除Hook,可以调用DetourDetach
// DetourDetach(&(PVOID&)OldMesssageBoxA, MyFunction0);
// 提交Detour操作
DetourTransactionCommit();
// 调用MessageBoxA,但实际上会跳转到MyFunction0
MessageBoxA(0, 0, 0, 0);
return 0;
}
定义一个函数指针 OldMessageBoxA,这个函数指针指向了MessageBoxA函数,同时定义了一个新的函数MyFunction0
DetourTransactionBegin来开始一个新的Detour操作,然后使用DetourUpdateThread来更新当前线程的状态,使得Detour操作能影响到当前线程
DetourAttach函数是Detour操作的核心,这个函数会将OldMessageBoxA的调用重定向到MyFunction0,也就是说,当其他代码尝试调用MessageBoxA时,实际上会调用MyFunction0
调用DetourTransactionCommit来提交Detour操作,使得之前的重定向生效。这时候,任何尝试调用MessageBoxA的代码,实际上都会调用MyFunction0
注意,如果想要取消Detour操作,只需要使用DetourDetach函数,将OldMessageBoxA和MyFunction0之间的重定向取消即可
编写Dll
代码实现
如下是通过detour库实现inlineHook的动态链接库代码:
include<Windows.h>
include<stdio.h>
include <detours/detours.h>
// 声明一个函数指针OldMessageBoxA,指向MessageBoxA函数
static int (WINAPI* OldMesssageBoxA)
(
HWND hWnd,
LPCSTR lpText,
LPCSTR lpCaption,
UINT uType
) = MessageBoxA;
// 自定义函数MyFunction0,当MessageBoxA被调用时,会跳转到这个函数
int WINAPI MyFunction0(HWND hWnd, LPCSTR lpText, LPCSTR lpCaption, UINT uType)
{
// 在这个函数中,调用原来的MessageBoxA函数,显示特定的信息
return OldMesssageBoxA(NULL, "Hook Success!", "Warming", MB_OKCANCEL);
}
DWORD WINAPI ThreadProc(LPVOID lpParameter)
{
// 开始一次新的Detour操作
DetourTransactionBegin();
// 告诉Detour这个线程将被影响
DetourUpdateThread(GetCurrentThread());
// 将OldMessageBoxA函数指针替换为MyFunction0,也就是说当MessageBoxA被调用时,跳转到MyFunction0
DetourAttach(&(PVOID&)OldMesssageBoxA, MyFunction0);
// 如果需要移除Hook,可以调用DetourDetach
// DetourDetach(&(PVOID&)OldMesssageBoxA, MyFunction0);
// 提交Detour操作
DetourTransactionCommit();
// 调用MessageBoxA,但实际上会跳转到MyFunction0
//MessageBoxA(0, 0, 0, 0);
return 0;
};
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain(HMODULE hModule,
DWORD ul_reason_for_call,
LPVOID lpReserved
)
{
switch (ul_reason_for_call)
{
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: {
HANDLE hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, ThreadProc, (LPVOID)NULL, 0, NULL);
break;
}
case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:
case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:
case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:
break;
}
return TRUE;
}
如下是用来测试InlineHook_dll的可执行程序代码, 在没被Hook的情况下会弹框提示"HelloWorld", 被Hook后会弹框提示"Hook Success!"
include <Windows.h>
include <stdio.h>
int main() {
LoadLibraryA("InlineHook_dll.dll");
getchar();
MessageBoxA(NULL, "HelloWorld", "窗口标题", NULL);
return 0;
}
运行测试
执行HookTest.exe, 按回车后出现弹框, 提示"Hook Success!"
参考文章
- https://idiotc4t.com/persistence/detous-inline-hook#inline-hook-jian-jie
GitHub项目地址
https://github.com/xf555er/InlineHook