内网自建yum源和apt源(含各信创系统)
现在Linux下面软件基本是通过yum/apt等从软件仓库在线安装,大的Linux发行版都有自己的软件仓库。如CentOS/RedHat使用yum方式仓库,ubuntu使用apt方式仓库。
很多政企单位内部网络是和互联网不连接的,或者是访问互联网速度受限,这样安装Linux软件不是很方便。可以自己建立yum或者apt源,方便软件安装。
本文先介绍建设笔者架设内网软件仓库的方式,然后逐步详细介绍所涉及的配置、工具和用法。
一、内网软件仓库实例
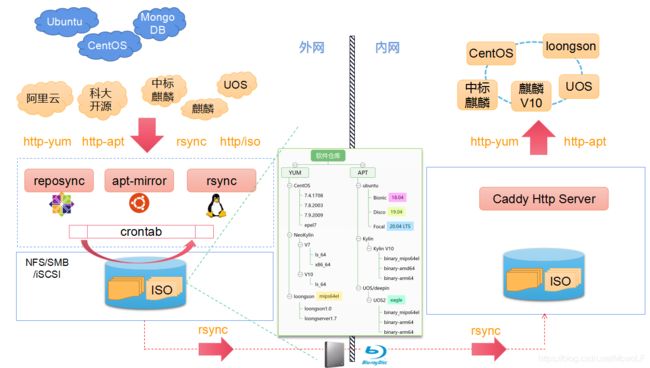
1. 整体架构
整个自建内网软件仓库架构如下图:
数据的流向是:(一)从互联网的软件源(及其镜像)->(二)内部外网区镜像(crontab定期更新) ->(三)通过网关或者移动介质传送到内部内网软件仓库服务器(HTTP)->(四)内部设备将软件源指向内网软件仓库服务器。
(一)获取软件源数据:一般可以使用4种方式:
- 对于ISO镜像文件,直接在官网上或者镜像站中下载,作为软件源使用的建议everything版本,实际上对于大多数企事业单位,使用ISO软件源已经足够。
- 对于yum方式的CentOS/loongson/NeoKylin(中标麒麟),可以通过reposync方式进行同步。配置文件 /etc/yum.repo.d/*.repo),本地路径为reposync指定;
- 对于apt方式的ubuntu/Kylin(麒麟/银河麒麟)/UOS通过apt-mirror工具同步。配置文件/etc/apt/mirror.list,本地路径也在mirror.list配置文件中指定;
- 对于支持rsync协议的软件源,如科大开源镜像站,可以在任何Linux系统上使用rsync命令进行同步,适合更新较为频繁的软件。
(二)外网区镜像,因为不同的软件源获取方式一般在不同服务器上,可以通过NFS/SMB或者iSCSI等方式存放在共享目录下,还可以通过软链接形成一个统一的目录树。通过crontab定期执行reposync、apt-mirror或rsync进行仓库更新。
(三)外网区数据到内网区有多种方式,如移动介质、网关传输甚至单向导入装置。对于更新要求高的场景,可能需要进行两次rsync操作,才能将数据同步到内网的软件仓库服务器。
(四)内网软件仓库服务器通过HTTP方式提供软件源URL,其它主机使用软件仓库指向对应的URL即可,对于YUM方式,指向repodata的父目录,对于APT方式,指向dists的父目录。可以使用Apache/Nginx等Http服务器,推荐使用Caddy Http服务器。
2. 同步命令及目录结构示例
注意下载前后检查一下硬盘空间:
df -hT #分区大小及所占用和剩余的空间
du -hs #某个目录所占用的空间 (一)centos7
CentOS/RedHat光盘中自带的我们一般称之为rhel源,是redhat公司在发布之前经过仔细测试兼容性的软件库,epel源大小比rhel多的多,收集有各种最新的、冷门的及未经仔细测试的包,有些情况下直接用epel源的东西比自己编译要方便的多, 一般的centos/redhat标准光盘也就4G左右的大小,epel7的大小约为27GB。
centos7源(下面例子中CentOS设备是7.7.1908版本)、epel源及同步.repo文件如下。
[base]
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
[extras]
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
[epel]
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7/$basearch
#baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7Server/$basearch同步命令及目录结构:
yum repolist #查看当前源清单
reposync -n --repoid=base --repoid=epel --repoid=extras --repoid=updates -p /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/centos/7.7.1908 #同步repoid指定的几个源
createrepo -v base #生成repolist文件
--------------------------------------------------------
/mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/centos/7.7.1908
├── base
│ ├── Packages
│ └── repodata
├── epel
│ ├── Packages
│ └── repodata
├── extras
│ ├── Packages
│ └── repodata
└── updates
├── Packages
└── repodata
(二) loongson系统、中标麒麟系统
loongson系统、中标麒麟系统系统源及同步.repo文件
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# cat fedora.repo
[fedora]
name= loongson 1.0-2003
baseurl=http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix/1.0/os/
[loongson-server1.7]
name= loongson-server 1.7-2007
baseurl=http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix-server/1.7/os/mips64el
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# cat neokylin.repo
[neokylin]
name= NeoKylin 7.0(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/releases/7.0/ls_64/
[neokylin10]
name= NeoKylin server V10(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/everything/v10/ls_64/中标麒麟同步及目录结构:
reposync -n --repoid=neokylin10 -p /mnt/remotenfs/neokylinV10
createrepo -v /mnt/remotenfs/neokylinV10/neokylin10/
neokylinV10/
└── neokylin10
├── repodata
└── RPMSloongnix同步及目录结构:
reposync -n --repoid=fedora -p /data/remotenfs/loongnix1.0/
createrepo -v /mnt/remotenfs/loongnix1.0/
/data/usbhd/loongson/
└── loongnix
├── fedora
└── repodata(三) ubuntu/Kylin/UOS
用一个ubuntu服务器作为ubuntu/Kylin和UOS的同步下载服务端(运行apt-mirror同步命令),其/etc/apt/mirror.list配置如下:
root@utunbu20:~# cat /etc/apt/mirror.list
set base_path /mnt/remotenfs/apt-mirror
set defaultarch amd64
set nthreads 20
#使用Ali yun的utuntu apt源
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal main restricted universe multiverse
#麒麟OS apt源
deb-mips64el http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL 10.1 main restricted universe multiverse
#UOS2 apt源
deb-mips64el http://uos-packages.deepin.com/uos eagle main同步及目录结构:
root@utunbu20:/# tree -L 5 mnt/rdxhd/apt-mirror/
apt-mirror/
├── mirror
│ ├── archive.kylinos.cn
│ │ └── kylin
│ │ └── KYLIN-ALL
│ │ ├── dists
│ │ └── pool
│ ├── mirrors.aliyun.com
│ │ └── ubuntu
│ │ ├── dists
│ │ │ ├── bionic
│ │ │ ├── bionic-backports
│ │ │ ├── bionic-proposed
│ │ │ ├── bionic-security
│ │ │ ├── bionic-updates
│ │ │ ├── focal
│ │ │ ├── focal-backports
│ │ │ ├── focal-proposed
│ │ │ ├── focal-security
│ │ │ └── focal-updates
│ │ └── pool
│ │ ├── main
│ │ ├── multiverse
│ │ ├── restricted
│ │ └── universe
│ └── uos-packages.deepin.com
│ └── uos
│ └── pool
│ └── main
├── skel
│ ├── archive.kylinos.cn
│ │ └── kylin
│ │ └── KYLIN-ALL
│ │ └── dists
│ ├── mirrors.aliyun.com
│ │ └── ubuntu
│ │ └── dists
│ │ ├── bionic
│ │ ├── bionic-backports
│ │ ├── bionic-proposed
│ │ ├── bionic-security
│ │ ├── bionic-updates
│ │ ├── focal
│ │ ├── focal-backports
│ │ ├── focal-proposed
│ │ ├── focal-security
│ │ └── focal-updates
│ └── uos-packages.deepin.com
│ └── uos
│ └── dists
│ └── eagle
└── var
├── ALL
├── archive-log.0
......二、Linux软件管理
1. yum & apt软件管理工具
管理Linux服务器的运维或开发人员经常需要安装软件,最常用方式应该是通过Linux系统提供的包管理工具来在线安装,yum是redhat或centos系统管理软件包的工具,apt是debian或ubuntu系统管理软件包的工具,这些工具使用之前需要配置好yum源或apt源。
#yum/apt源的路径,一般至少支持三种协议:http、ftp、file,其中file表示本地文件。
软件包基本使用参考相关文档,本博客的《国产信创Linux桌面系统比较:软件包格式及软件管理、桌面环境及桌面应用》介绍了相关内容。
Linux执行某个linux命令时出现 command not found,想查找提供该命令的软件包(例如rsync命令)。
在yum/Centos下
yum whatprovides */rsync
#或者
yum provides */rsync在apt/ubuntu下
sudo apt-get install -y apt-file
apt-file update
#查询命令
root@local~ # apt-file search bin/rsync
#接正则表达式查询search -x(--regexp)
root@local~ # apt-file search -x 'bin/rs$'2. yum配置文件
CentOS/Fedora/loongson等使用yum方式安装软件,以最常用的CentOS服务器为例,CentOS的软件仓库yum配置文件是/etc/yum.repos.d/xxx.repo,如下:
[root@localhost]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os&infra=$infra
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates&infra=$infra
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
......[root@localhost rdxhd]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/neokylin.repo
[kylin7]
name= NeoKylin server 7.0(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/everything/7.0/ls_64
enabled=1
[neokylin10]
name= NeoKylin server V10(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/everything/v10/ls_64/
enabled=1
[neokylin7desk]
name= NeoKylin destktop 7.2(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/desktop/everything/7.2/ls_64/os/
enabled=1查看系统中使用的软件仓库:yum repolist
[root@localhost nfsshare]# yum repolist
源标识 源名称 状态
!base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base - mirrors.aliyun.com 10,072
!epel/x86_64 Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - x86_64 13,489
!extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras - mirrors.aliyun.com 448
!neokylin10 NeoKylin server V10(MIPS) 10,665
!neokylin7 NeoKylin server 7.0(MIPS) 10,603
!neokylin7desk NeoKylin destktop 7.2(MIPS) 11,650
!updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates - mirrors.aliyun.com 配置文件中涉及两个变量:$releasever和$basearch,分别代表版本和CPU架构
CentOS主流是7系列(CentOS8已经宣布不再发展,不建议使用),常见的版本有7.4.1708、7.5.1804、7.6.1810、7.7.1908、7.8.2003和7.9.2009,查看版本号命令如下。
yum install redhat-lsb #或者redhat-lsb-core
lsb_release -a #或者rpm -qi centos-release
[root@localhost nfsshare]# lsb_release -a
LSB Version: :core-4.1-amd64:core-4.1-noarch:cxx-4.1-amd64:cxx-4.1-noarch:desktop-4.1-amd64:desktop-4.1-noarch:languages-4.1-amd64:languages-4.1-noarch:printing-4.1-amd64:printing-4.1-noarch
Distributor ID: CentOS
Description: CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core)
Release: 7.7.1908
Codename: CoreLinux中使用命令arch可以初步查看出当前系统所识别出来的机器CPU类型,,如 "arm","mips64","x86_64"等;
[root@localhost home]# arch
x86_64对于本Linux机器,baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/,翻译后的完整路径便是baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/os/x86_64/
【注】对于后面下载镜像的Linux设备,因为会下载不同版本的发行版,直接手动设置
3. apt配置文件(/etc/apt/sources.list)
debian/ubuntu/UOS等使用apt软件安装方式,/etc/apt/sources.list 是包管理工具 apt 软件仓库配置文件,其条目如下所示的形式:
类型 镜像url 版本代号 软件包分类
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse类型 (Archive type):deb类型为二进制预编译软件包,deb-src:软件包的源代码。
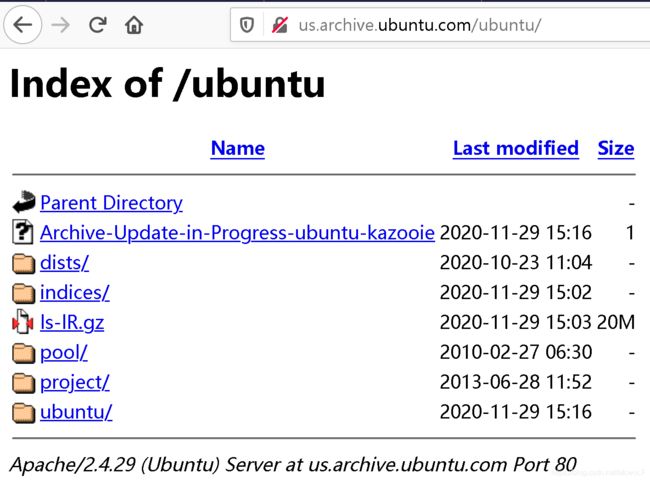
镜像url:每一个源目录下都应该至少包含dists和pool两个目录,以阿里镜像为例,浏览器打开http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/:
Index of /ubuntu/
../
dists/ 23-Oct-2020 11:04 -
indices/ 06-Dec-2020 05:48 -
pool/ 27-Feb-2010 06:30 -
project/ 28-Jun-2013 11:52 -
ubuntu/ 06-Dec-2020 06:02 -
ls-lR.gz 06-Dec-2020 01:06 20800510
- /dists/ 目录包含"发行版"(distributions), 此处是 Debian /Ubuntu发布版本(releases)和已发布版本(pre-releases)的软件包, 按codename(版本代号)分目录,下面再是按main/restricted/multiverse/universe分类。
- /pool/ 目录为软件包的物理地址. 软件包按照源码包名称分类存放。pool 目录下按属性再分类("main", "contrib" 和 "non-free"),分类下面再按源码包名称的首字母归档. 可以执行命令 apt-cache showsrc mypackagename, 查看 'Directory:' 行获知每个软件包的存放位置. 例如: apache 软件包存放在 pool/main/a/apache/ 目录中.另外, 由于lib*软件包数量巨大, 它们以特殊的方式归档: 例如, libpaper 软件包存放在 pool/main/libp/libpaper/.
- /tools/:用于创建启动盘, 磁盘分区, 压缩/解压文件, 启动 Linux 的 DOS 下的小工具。
- /doc/:基本的 Debian 文档, 如 FAQ, 错误报告系统指导等..
- /indices/:维护人员文件和重载文件.
- /project/:大部分为开发人员的资源, 如:project/experimental/,本目录包含了处于开发中的软件包和工具, 它们均处于 alpha 测试阶段. 用户不应使用这些软件.
版本代号(lsb_release -a可以查看当前版本codename,apt install lsb-release安装)如下:详细的清单参考《Ubuntu各版本代号简介》,比较常用的是18.04.5LTS Bionic、16.04Xenial和20.04.1LTS Focal。
- 14.04,Trusty Tahr (可靠的塔尔羊)
- 16.04,Xenial Xerus (好客的非洲地松鼠)
- 18.04,Bionic Beaver(仿生海狸)
- 18.10,Cosmic Cuttlefish (宇宙般大小的乌贼)
- 19.04,Disco Dingo
- 19.10,Eoan Ermine
- 20.04 LTS,Focal Fossa
软件包分类:main/restricted/multiverse/universe是ubuntu对软件的分类:
- main:官方支持的自由软件。
- restricted:官方支持的非完全自由的软件。
- universe:社区维护的自由软件。
- multiverse:非自由软件。
【注】ubuntu ARM镜像的地址是
4. yum下添加epel源
官方网址为:https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/EPEL/zh-cn,centos7 epel源一般都是预装了。
yum install epel-release#安装完成之后,会在/etc/yum.repo.d/ 目录下生成两个yum源的repo文件:
- epel.repo #正式版,所有的软件都是稳定可以信赖的
- epel-testing.repo #测试版,使用时需要慎重
epel默认使用的是国外的源(Fedora 官网提供),可以将源更改成国内的源如阿里云(http://mirrors.aliyun.com/help/epel),如下操作:
#备份(如有配置其他epel源)
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.bak
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo.bak
#下载新repo 到/etc/yum.repos.d/,下面为epel(RHEL 7)
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
#cat /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
[epel]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7/$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
......yum安装软件时,默认优先使用epel的源,如果想要优先使用CentOS的源,安装优先级插件:yum-plugin-priorities:
yum install yum-plugin-prioritiespriority=number,数字越小优先级越高
#在[epel]里的最后一行添加priority=10
#在[base]里的最后一行添加priority=1
5. 下一代YUM工具DNF与nexus 软件仓库管理工具
DNF(YUM v4)
在 CentOS8 中使用了基于DNF技术(YUM v4)的 YUM 工具,从fedora22开始, 就用 dnf代替yum了,dnf的用法根yum的用法基本兼容, 只是用dnf代替yum就可以了.
YUM v4 与之前在 CentOS7 上使用的 YUM v3 相比,DNF包管理器克服了YUM包管理器的一些瓶颈,提升了包括用户体验,内存占用,依赖分析,运行速度等多方面的内容。
在 CentOS8 中把软件源分成了两部分:
- BaseOS 存储库 :以传统 RPM 包的形式提供底层核心 OS 内容
- AppStream 存储库 :提供用户空间中运行的所有应用程序,也就是诸多第三方的应用
centos 8默认提供的yum命令仅为dnf的软链接!
nexus 软件仓库管理工具
前面介绍的都是手工管理自建仓库,如果涉及到的软件仓库数量多而复杂,可能就需要专门的软件仓库管理工具。如Nexus、
Sonatype Nexus是非常强大的软件仓库管理工具,支持常见的Docker、Maven、npm、PyPI等仓库的管理,适合比较复杂的环境,尤其和maven等构建工具一起使用,当然作为私有yum服务器也很合适。
Nexus我们可以搭建本仓库,支持几种repository的类型:
- hosted,本地仓库,通常我们会部署自己的构件到这一类型的仓库。比如公司的第二方库。
- proxy,代理仓库,它们被用来代理远程的公共仓库,如maven中央仓库。
- group,仓库组,用来合并多个hosted/proxy仓库,当你的项目希望在多个repository使用资源时就不需要多次引用了,只需要引用一个group即可。
从上图可以看出,Nexus更适合开发环境,以及提高开发环境-》生产环境的一致性,尤其是开发在线服务的供应商。可以参考《如何优雅的打造 All-in One 仓库》等资料,本文不再涉及具体内容。
三、 使用国内源
国内有不少优秀的镜像源服务器,比如mirrors.aliyun.com(阿里云)、科大开源软件镜像站(https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/)、mirrors.163.com、清华大学开源软件镜像站等。以阿里云镜像为例。
1. ubuntu/apt
打开https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/网址,如下:
点击Ubuntu,进入【Ubuntu 镜像】,选择版本:utunbu版本名称,14.04 LTS(Trusty Tahr);16.04 LTS(Xenial Xerus);18.04 LTS(Bionic Beaver);19.04(Disco Dingo);debian如:debian7(wheezy)、debian6(squeeze)、debian8(jessie),根据自己使用的系统版本来源设置(使用lsb_release -a查看版本名称codename)。
图形界面配置:新手推荐使用图形界面配置: 系统设置 -> 软件和更新 ,选择下载服务器 -> "mirrors.aliyun.com"
手动更改:编辑/etc/apt/sources.list(注意备份原来的sources.list文件),从网页上复制配置内容,样例如下:
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse更新一下:
#更新软件列表
sudo apt-get update
#更新软件包(可选)
sudo apt-get upgrade2. CentOS/yum
centos的yum源设置类似,选择版本下载,比如这里下载的是CentOS-7.repo(首先备份/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo):
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
#或者
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
运行以下命令生成缓存:
[root@localhost ~]# yum clean all
[root@localhost ~]# yum makecache查看目前配置了的源清单:
yum repolist四、内网环境自建源
很多公司企业为了网络安全都建立了自己的内部网络,内部网络不与Internet相通,导致很多开源软件,系统rpm包,deb包安装都异常复杂,而且如果依赖关系复杂,通过手动上传rpm包或者deb包就更加麻烦,需要将公网上的包下载下来,并制作成自己内部网络的yum源和apt源。
1. 光盘(或iso镜像)源
挂载光盘或者iso文件:
# mkdir /media/centos7
# mount /dev/cdrom /media/centos7 --挂载光盘
# mount -o loop /opt/centos7-6.8-x86_64-dvd.iso /media/centos7 --或挂载 ISO文件(一)yum/CentOS:
注释掉或者重命名CentOS-Media.repo外的其它repo文件的后缀(例如rename repo repo.bak *repo 批量修改后缀)。修改CentOS-Media.repo文件:
[base]
name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux
baseurl=file:///media/centos7/
enabled=1 # 启用这个repo
gpgcheck=0 # 校验包的合法性,0标识不校验
gpgkey=file:///mnt/centos7/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release最后,执行 yum clean all (清除缓存)
yum clean all
#yum makecache --将服务器软件包信息缓存至本地,提高搜索安装效率(可选)
yum list --获取yum源安装的列表看一下我们制作的本地光盘yum源是否生效:#mount的路径,系统重启会失效,可以添加到rc.local中,实现开机自动挂载,如下:
echo “mount /dev/cdrom /iso” >> /etc/rc.local
# 或者iso自动挂载
echo "mount -o loop /opt/centos7-6.8-x86_64-dvd.iso /media/centos7" >> /etc/rc.local(二)apt/ubuntu:
对于ubuntu/apt,过程差不多,挂载后,配置的是/etc/apt/source.list文件。
注:utunbu版本名称,14.04 LTS(Trusty Tahr);16.04 LTS(Xenial Xerus);18.04 LTS(Bionic Beaver);19.04(Disco Dingo),详见《【Linux】Ubuntu各版本号和名称对照》。
#挂载镜像文件
sudo mount /mnt/ubuntu-18.04.5-server-amd64.iso /mnt/cdrom/
## 设置本地源,baseurl中file路径对应挂载的路径
# cat /etc/apt/source.list
deb file:///mnt/cdrom bionic main
# 或者apt-cdrom直接添加挂载点镜像文件到更新源
sudo apt-cdrom -m -d /mnt/cdrom add
#测试是否正确配置源
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgradeUbuntu的source.list文件的具体内容:《详解Ubuntu的source.list文件 》
注:光盘或者ISO挂载作为Local源,也可以再通过网络共享后作为本地网络源使用!
2. http内部网络源
yum/apt源支持file、http/ftp等方式,以CentOS EveryThing为例,可以用smb/nfs方式共享后,在内部yum服务器上挂载,即file模式。但更方便的方法是在内网上搭建一个HTTP服务器作为yum源,将上面的CentOS EveryThing用HTTP发布。比如使用HTTP服务器apache/Nginx,这里推荐CaddyHTTP服务器,Caddy是轻量级的HTTP 服务器,而且具有全自动的HTTPS支持,一行命令就开启HTTP服务,更适合作为Yum服务器。参考《简单易用的caddy http服务器 》。
例如,在/home/linuxrepo下作为所有软件仓库,并建立多个版本的yum源,如centos1908,ubuntu,KylinV10(MIPS),KylinV10(ARM)等,可以将软件库复制到这里,也可以挂载光盘,如下以CentOS1708版本为例。
mkdir /home/linuxrepo/centos1908
mount -o loop /home/linuxrepo/CentOS-7-x86_64-Everything-1708.iso /home/linuxrepo/centos1908进入/home/linuxrepo,在下面运行caddy服务:
cd /home/linuxrepo/
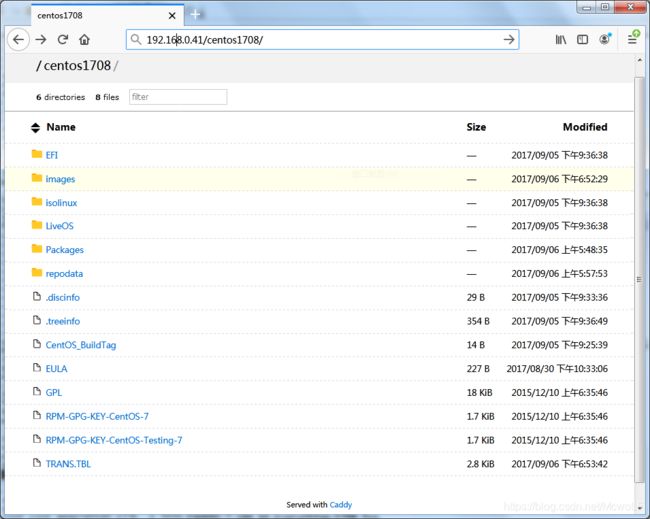
caddy file-server --browse浏览器访问测试一下:
一切OK后,YUM仓库已经建立。
需要使用仓库的Linux上,以Centos为例,创建repo配置文件指向这台yum源服务器,如下:
$cat CentOS-local.repo
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Local
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os&infra=$infra
baseurl=http://192.168.0.41/centos1908/
failovermethod=priority
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
gpgkey=http://192.168.0.41/centos1908/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7可以将多个版本的ISO文件(如中标麒麟、银河麒麟V10、UOS、CentOS等)分别挂载在目录下,可以建成一个基本的小型内网YUM/APT仓库。
3. 通过rsync同步源
epel等源可以使用rsync工具去internet上同步,上游 yum 源必须要支持 rsync 协议。以中科大开源镜像为例,其官方指导文档是http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/help/rsync-guide.html
中科大开源镜像站允许下游站点使用 rsync 协议同步站点上的内容。"因可能消耗大量服务器资源,我们非常不推荐下游镜像站点或个人用户使用 HTTP / HTTPS / FTP 协议从站点大规模同步数据。 我们可能采取技术措施对使用非 rsync 协议进行大量内容同步的用户进行限流或封禁。"
目前,科大镜像站所有仓库的同步都必须添加 /repo/ 的前缀来进行访问。 如ubuntu 仓库的实际路径为 rsync://rsync.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/repo/ubuntu/ ,而非 rsync://rsync.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu 。
我们强烈推荐用户在实际进行 rsync 同步之前先使用 rsync 工具列出目录内容以实际观察目录结构。 例如,用户可以使用如下命令列出 ubuntu 仓库根目录的具体内容: rsync rsync://rsync.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/repo/ubuntu/ 。
[root@localhost opt]# rsync rsync://rsync.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/repo/ubuntu/
_______________________________________________________________
| University of Science and Technology of China |
| Open Source Mirror (mirrors.ustc.edu.cn) |
|===============================================================|
| |
| We mirror a great many OSS projects & Linux distros. |
| |
| Currently we don't limit speed. To prevent overload, Each IP |
| is only allowed to start upto 2 concurrent rsync connections. |
| |
| This site also provides http/https access. |
| |
| Supported by USTC Network Information Center |
| and USTC Linux User Group (http://lug.ustc.edu.cn/). |
| |
| Sync Status: https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/status/ |
| News: https://servers.ustclug.org/ |
| Contact: [email protected] |
| |
|_______________________________________________________________|
drwxr-xr-x 216 2020/12/08 08:53:59 .
-rw-r--r-- 20,844,531 2020/12/08 02:23:10 ls-lR.gz
lrwxrwxrwx 1 2010/11/24 19:01:53 ubuntu
drwxr-xr-x 88 2020/03/07 05:41:20 .trace
drwxr-xr-x 1,432 2020/10/23 19:04:49 dists
drwxr-xr-x 152,760 2020/12/08 02:22:25 indices
drwxr-xr-x 160 2010/02/27 14:30:27 pool
drwxr-xr-x 168 2013/06/28 19:52:35 project以下载Centos7.9 2009为例,同步命令如下:
#rsync rsync://rsync.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/repo/centos/7.9.2009/os/x86_64/
rsync -vzP -rtDl --delete rsync://rsync.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/repo/centos/7.9.2009/os/x86_64/ /mnt/usbhd/centos2009/rsync下载的centos7.9目录和光盘目录结构一致,客户端的URL指向repodata目录所在主目录即可。
4. reposync工具同步yum镜像源
同步镜像源最方便是使用reposync工具(yum-utils工具包中),通过reposync 工具完整的下载rpm包,然后再用createrepo工具建立自己的repodata目录,从而将Internet上的yum源克隆到本地。
(1)是将CentOS官方源和EPEL源都指向国内镜像(前面讲解过如何指向Aliyun镜像),然后查看当前系统中的yum仓库(自动解析/etc/yum.repos.d/下面的所有repo文件)。
[root@localhost]yum install yum-utils #reposync命令在yum-utils工具包中
[root@localhost]mkdir -p /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/centos/1709 #创建下载目录
[root@localhost]yum repolist #使用yum repolist获取repoid
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
源标识 源名称 状态
base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base - mirrors.aliyun.com 10,072
epel/x86_64 Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - x86_64 13,486
extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras - mirrors.aliyun.com 448
updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates - mirrors.aliyun.com 775
repolist: 24,781
- repoid有4个分别为base、epel、extras、updates
- 在.repo文件中[serverid]就是repoid
- serverid用于区别各个不同的repository,必须有一个独一无二的名称,若重复后面的会覆盖前面
(2)执行同步:
同步存储库时可以指定一个repoid,也可以指定多个repoid,会自动创建以repoid命令的目录
#-n --newest-only 仅下载per-repo的最新软件包;
#-p 输出的目录
reposync -n --repoid=base --repoid=epel --repoid=extras --repoid=updates -p /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/centos/1709reposync命令执行会在-p指定的目录下生成以repoid为名的文件夹,里面放着一层或者多层目录包含的rpm文件,没有repodata文件夹。需要在克隆完毕之后手动使用createrepo命令创建repo,生成repodata文件夹。
#yum install createrepo
cd /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/centos/1709
createrepo -v base/
......可以建立定时同步,每周一的3点同步:
crontab -e
0 3 * * 1 /usr/bin/reposync -np /data/centos/1908实际上,还需要重新刷新repo文件, createrepo --update base/
客户端的URL指向repodata文件夹,如下
[customrepo]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch
baseurl=http://192.168.0.41/centos1908/
failovermethod=priority
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0最终的目录结构如下
[root@localhost rdxhd]# tree -L 3 /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/
/mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/
├── centos
│ ├── centos7.7.1908
│ │ ├── base
│ │ ├── extras
│ │ └── updates
│ ├── centos7.9.2009
│ │ ├── CentOS_BuildTag
│ │ ├── EFI
│ │ ├── EULA
│ │ ├── GPL
│ │ ├── images
│ │ ├── isolinux
│ │ ├── LiveOS
│ │ ├── Packages
│ │ └── repodata
│ └── epel7
│ ├── Packages
│ └── repodata
├── loongson
│ ├── loongnix-server1.7-2007
│ │ ├── loongserver1.7-2007
│ │ └── repodata
│ └── loongson-1.0
│ ├── loongnix
│ └── repodata
├── neokylin
│ ├── neokylin-desktop-7.2MIPS
│ │ └── 7.2
│ ├── neokylin-server-v10MIPS
│ │ └── neokylin10
│ └── neokylin-server-v7MIPS
│ └── kylin7
└── nfs4
└── nfs4.0-server-X64
├── Packages
└── repodata5. apt-mirror同步apt源
和yum下reposync对应的,apt工具是apt-mirro。
安装apt-mirror:
apt-get install apt-mirror【注】apt-mirror实际上是perl脚本,可以在CentOS/loongson等系统上使用,https://github.com/apt-mirror/apt-mirror/blob/master/apt-mirror下载apt-mirror和mirror.list文件,然后将apt-mirror复制到/usr/bin,将mirror.list复制到/etc/apt/,其它使用情况同ubuntu系统。下面的操作实际上都是在loongson 3A4000的电脑上完成。
修改apt-mirror配置文件【 /etc/apt/mirror.list】,并配置主版本,常见的是18.04.5LTS Bionic、16.04Xenial和20.04.1LTS Focal,注意都是要小写字母!
############# config ##################
set base_path /mnt/rdxhd/apt-mirror
#
# 镜像文件下载地址
# set mirror_path $base_path/mirror
# 临时索引下载文件目录,也就是存放软件仓库的dists目录下的文件(默认即可)
# set skel_path $base_path/skel
# 配置日志(默认即可)
# set var_path $base_path/var
# clean脚本位置
# set cleanscript $var_path/clean.sh
# 架构配置,i386/amd64,默认的话会下载跟本机相同的架构的源
set defaultarch amd64
# set postmirror_script $var_path/postmirror.sh
# set run_postmirror 0
# 下载线程数
set nthreads 20
set _tilde 0
#
############# end config ##############
#使用Ali yun的apt源
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
#麒麟操作系统的mips64和arm64版本
deb-mips64el http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL 10.1 main restricted universe multiverse
deb-arm64 http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL 10.1 main restricted universe multiverse
#uos操作系统的mips64和arm64版本
deb-mips64el http://uos-packages.deepin.com/uos eagle main
deb-arm64 http://uos-packages.deepin.com/uos eagle main
#clean http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu
#clean http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL
#clean http://uos-packages.deepin.com/uos执行:
apt-mirror然后等待长时间(镜像差不多100G左右),同步的镜像文件目录树如下图,例如ubuntu下载路径为/mnt/rdxhd/apt-mirror/mirror/mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/。
[root@localhost rdxhd]# tree -L 4 /mnt/rdxhd/apt-mirror/mirror/
/mnt/rdxhd/apt-mirror/mirror/
├── archive.kylinos.cn
│ └── kylin
│ └── KYLIN-ALL
│ ├── dists
│ └── pool
├── mirrors.aliyun.com
│ └── ubuntu
│ ├── dists
│ │ ├── bionic
│ │ ├── bionic-backports
│ │ ├── bionic-proposed
│ │ ├── bionic-security
│ │ ├── bionic-updates
│ │ ├── focal
│ │ ├── focal-backports
│ │ ├── focal-proposed
│ │ ├── focal-security
│ │ └── focal-updates
│ └── pool
│ ├── main
│ ├── multiverse
│ ├── restricted
│ └── universe
└── uos-packages.deepin.com
└── uos
├── dists
│ └── eagle
└── pool
└── main注1:当apt-mirror 被意外中断时,只需要重新运行即可,apt-mirror支持断点续存;另外,意外关闭,需要apt-mirror/var目录下面删除 apt-mirror.lock文件【 sudo rm apt-mirror.lock 】,之后执行apt-mirror重新启动
注2: apt-mirror同步后在本地的$var_path/下生成一个clean.sh的脚本,列出了遗留在本地的旧版本和无用的软件包。当某些软件包在服务器端进行了升级或者不再需要时,可以在mirror.list文件中或者手动运行clean http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu脚本来删除。
客户端配置
1、在/etc/apt/sources.list配置如下:
deb ssh://root@[host]/var/www/repo/ubuntu focal main
deb http://[host]:[port]/ubuntu/focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://[host]:[port]/ubuntu/focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://[host]:[port]/ubuntu/focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://[host]:[port]/ubuntu/focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://[host]:[port]/ubuntu/focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse2、更新apt-get源
sudo apt-get update #这步很重要
sudo apt-get upgrade6. 其它第三方yum/apt源
很多流行的开源软件有自己的yum/apt源,如MongoDB、docker等。
(1)yum源,在客户端添加相应的yum源然后执行yum install。
如下是mongoDB的公网yum源:
[mongodb-org-4.0]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/4.0/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc下面是docker官网给出的yum源添加方法
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo其repo文件实际是这样的
[docker-ce-stable]
name=Docker CE Stable - $basearch
baseurl=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/$basearch/stable
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/gpg和前面一样,可以克隆yum软件源到本地,然后把客户端的.repo文件中URL写成本地。
mkdir redhat7 #cd到caddy开启的目录下执行
reposync -n --repoid=mongodb-org-4.0-redhat7 -p ./redhat7/
reposync -n --repoid=docker-ce-stable -p ./redhat7/(2)apt源
除了yum源外,MongoDB和Docker也都提供自己的Internat的apt源,克隆到本地在mirror.list文件中加入
#docker
deb https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable
#mongodb
deb https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse同步完之后,就会在mirror目录下看到如mirror/repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu,目录下会有dist文件夹,dist目录在哪,客户端的URL地址就应该填哪里。
五、信创系统常见软件源
1. Loongnix系统Yum源
loongxin系统现在有:Loongnix-server-1.7.2003 服务器系统和Loongnix-1.0.2003 系统,在社区网站上可以下载liveCD和完整 ISO 文件http://www.loongnix.org/。
loongxin系统的软件仓库URL是:http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/
Loongnix-1.0 Yum源地址
rpm: http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix/1.0/os/
debug: http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix/1.0/debug/
srpm: http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix/1.0/SRPMS/
配置社区Yum源
cd /etc/yum.repos.d //Loongnix Fedora21系统
wget http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix/1.0/fedora.repo
yum makecache
loongnix系统中,repo文件片段如下:
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]cat fedora.repo
[fedora]
name=Fedora $releasever - $basearch
failovermethod=priority
baseurl=http://ftp.loongnix.org/os/loongnix/1.0/os/
#metalink=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=fedora-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=1
metadata_expire=7d
......
yum repolist查看软件源repoid:
[root@localhost]# yum repolist
源标识 源名称 状态
fedora Fedora 21 - mips64el 40,194
fedora-source Fedora 21 - Source 0
openstack-rocky Loongnix for Fedora 21 - Rocky 1,643
repolist: 41,837
同步下载龙芯系统软件源(使用一台龙芯Loongnix 1.0系统上操作,repoid=fedora),命令如下:
reposync -n --repoid=fedora -p /data/loongnix
cd /data/loongnix
createrepo -v fedora/2. 中标麒麟
中标麒麟属于Centos/Fedora类型,包格式rpm,软件管理工具yum。
中标麒麟软件源网站是:http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/
仓库主目录下面分了Server Desktop等,中标麒麟7.0服务器MIPS版中的标准repo文件片段如下:
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# cat neokylin.repo
[neokylin]
name= NeoKylin 7.0
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/releases/7.0/ls_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-neokylin-$basearchserver下有三个软件源:everything、release和update,如果在内网同步中标麒麟软件源,最好是everything版本,在下载服务器上(本例为Centos7)增加中标麒麟的repo源。
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# cat neokylin.repo
[neokylin7]
name= NeoKylin server 7.0(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/everything/7.0/ls_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-neokylin-$basearch
[neokylin10]
name= NeoKylin server V10(MIPS)
baseurl=http://download.cs2c.com.cn/neokylin/server/everything/v10/ls_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-neokylin-$basearchyum repolist一下
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum repolist
......
源标识 源名称 状态
base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base - mirrors.aliyun.com 10,072
epel/x86_64 Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - x86_64 13,486
extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras - mirrors.aliyun.com 448
neokylin10 NeoKylin server V10(MIPS) 10,665
neokylin7 NeoKylin server 7.0(MIPS) 10,603
updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates - mirrors.aliyun.com 775
repolist: 46,049
同步下载中标麒麟系统软件源(NeoKylin serverV10-MIPS),同步命令如下:
reposync -n --repoid=neokylin10 -p /data/neokylinV10
cd /data/neokylinV10
createrepo -v neokylin10/3. 麒麟/银河麒麟V10
麒麟/银河麒麟是属于Debain/Ubuntu体系,包格式是deb,软件管理工具是apt。
麒麟/银河麒麟软件源地址:http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL/
在系统的/etc/apt/sources.list文件中,根据不同版本URL如下(省略V10之前的版本)
.......
#10.0版本:
deb http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL 10.0 main restricted universe multiverse
#10.1版本:
deb http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL 10.1 main restricted universe multiverse例如访问:http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL/dists/10.1/main/,支持如下处理器架构
Index of /kylin/KYLIN-ALL/dists/10.1/main/
../
binary-amd64/ 02-Dec-2020 01:38 -
binary-arm64/ 02-Dec-2020 01:38 -
binary-armhf/ 02-Dec-2020 01:38 -
binary-i386/ 02-Dec-2020 01:38 -
binary-mips64el/ 02-Dec-2020 01:38 -
debian-installer/ 02-Dec-2020 01:36 -
debug/ 如果需要同步源在内部网络使用,apt-mirror工具的/etc/apt/mirror.list文件中相应部分是(这里下载的是MIPS64el处理器的10.1版):
deb-mips64el http://archive.kylinos.cn/kylin/KYLIN-ALL 10.1 main restricted universe multiverse注:下载机如果是x86-64位,默认下载64位的x86源,即deb-amd64,上面deb-mips64el指定了下载mips64le的源(目录是binary-mips64el)。
4. UOS/Deepin
uos/deepin也是属于Debain/Ubuntu体系。
UOS软件源的地址是:http://uos-packages.deepin.com/uos/,也有华为云等镜像
codename 是eagle
在uos 20/deepin V20中添加华为软件源:
在/etc/apt/sources.list.d/中创建一个名为deepin.list的文件,增加以下华为镜像的URL
[root@localhost]cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/deepin.list
deb [trusted=yes] https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/deepin stable main contrib non-free
#deb-src deb https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/deepin stable main然后,sudo apt-get update;sudo apt-get upgrade
如果需要同步源在内部网络使用,apt-mirror工具的/etc/apt/mirror.list文件中相应部分是:
deb-mips64el http://uos-packages.deepin.com/uos eagle main5. 中科方德NFS4.0(x86_64架构)
中科方德软件源URL是:http://update.os.nfschina.com/static。中科方德桌面版3.1使用的是apt/deb,服务器版4.0既有apt源(http://update.os.nfschina.com/static/nfs-4.0/),也有yum源(http://update.os.nfschina.com/static/NFS4.0/GenOS/RPMS/NFS4.0-20200323/),且只支持x86_64架构。
这里只考虑服务器版NFS4.0 yum软件库:
[nfs4.0-server-X64]
name= nfs server(AMD64)
baseurl=http://update.os.nfschina.com/static/NFS4.0/GenOS/RPMS/Releases/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0同步和下载类似中标麒麟:
reposync -n --repoid=nfs4.0-server-X64 -p /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/nfs4/
cd /mnt/rdxhd/yumdata/nfs4/
createrepo -v nfs4.0-server-X64/参考:
- 《自建企业内部yum源和apt源》
- 《ubuntu下的apt内网本地源的正确搭建》
- 《通过 rsync 搭建 CentOS 本地 yum 源服务器》,目录结构可以参考
- 《真实靠谱的基于reposync/createrepo命令YUM本地源搭建过程》
- 《reposync同步镜像源库到本地》
- 《Centos7通过reposync同步国内yum源-搭建局域网内网本地Yum源》
- 《搭建apt源》
- 《在centos中搭建基于nginx的apt源服务器,整合yum源和apt源在一台服务器》