程序替换原理
文章目录
- 一、程序替换
一、程序替换
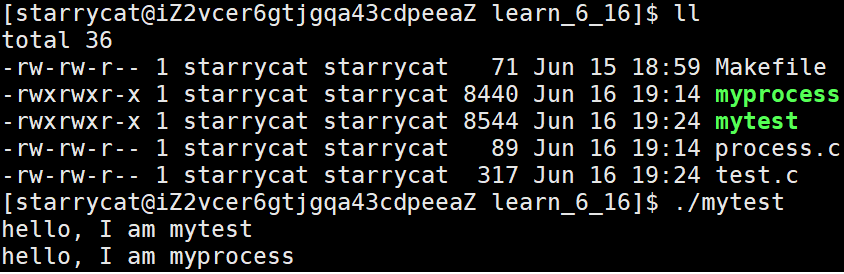
程序替换用于将当前进程的用户空间的代码和数据全部替换为新程序的代码和数据,程序替换不会创建新进程,而是用当前进程执行新程序的代码,fork 创建子进程后,子进程默认执行的是父进程的代码,通过程序替换便可让子进程执行新程序
exec 系列的函数,头文件 unistd.h
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ..., char *const envp[]);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
返回值:调用成功,则直接执行新程序,没有返回值,出错返回 -1,exec 系列的函数只有出错才会返回
参数:
- path:替换的可执行程序的路径
- file:替换的可执行程序的文件名,操作系统会自动在环境变量 PATH 中查找可执行程序
- arg 和 可变参数 … :替换的可执行程序的命令行参数,可变参数中的最后一个参数必须为 NULL
- argv 数组:命令行参数组成的数组,最后一个元素必须为 NULL
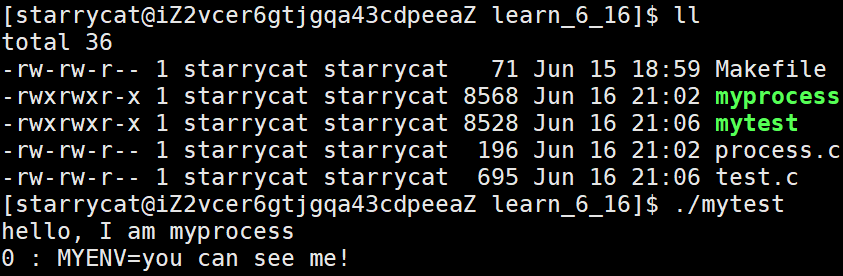
- envp 数组: 环境变量组成的数组,最后一个元素必须为 NULL
//process.c -> myprocess
#include exec 系列的函数可以参考如下方法记忆:
- l 表示命令行参数以 list 列表形式传递
- v 表示命令行参数以 vector 数组形式传递
- p 表示操作系统自动在环境变量 PATH 中查找
- e 表示用户自己维护环境变量
// test.c -> mytest
#include // test.c -> mytest
#include //process.c -> myprocess
#include exec 系列的库函数底层都是调用系统调用 execve
int execve(const char *filename, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);