三、线程间通信
3.1 线程间通信模型
线程间通信的模型有两种:共享内存和消息传递,以下方式都是基本这两种模型来实现的。我们来基本一道面试常见的题目来分析。
是事实上,线程间通信时通过维护volatile写-读语义和锁的写-读语义实现的。
由于Java的CAS同时具有volatile读和volatile写的内存语义,因此Java线程之间的通信现 在有了下面4种方式。
1)A线程写volatile变量,随后B线程读这个volatile变量。
2)A线程写volatile变量,随后B线程用CAS更新这个volatile变量。
3)A线程用CAS更新一个volatile变量,随后B线程用CAS更新这个volatile变量。
4)A线程用CAS更新一个volatile变量,随后B线程读这个volatile变量。
对于更深一步的概念可以学习《Java并发编程的艺术》
3.2 线程间通信案例:
场景:两个线程,一个线程对当前数值加 1,另一个线程对当前数值减 1,要求用线程间通信
3.2.1 Synchronized关键字方案
/**
* @author LWJ
* @date 2023/6/17
*/
// 1创建资源类,在资源类创建属性和操作方法。
class Share{
private int number = 0;
// 2在资源类操作方法
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//判断
if(number != 0){
this.wait();
}
//干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//判断
if(number != 1){
this.wait();
}
//干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadCommunicationExample1 {
// 3创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.incr();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.decr();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-B").start();
}
}
两个线程时,并没有问题,那我再加两个线程呢?
3.2.2 虚假唤醒
/**
* @author LWJ
* @date 2023/6/17
*/
// 1创建资源类,在资源类创建属性和操作方法。
class Share{
private int number = 0;
// 2在资源类操作方法
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//判断
if(number != 0){
this.wait();
}
//干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//判断
if(number != 1){
this.wait();
}
//干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadCommunicationExample1 {
// 3创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.incr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.decr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.incr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-C").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.decr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-D").start();
}
}
卧槽?出问题了,输出
D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\bin\java.exe "-javaagent:D:\CoderTools\IntelliJ IDEA 2022.3.3\lib\idea_rt.jar=60149:D:\CoderTools\IntelliJ IDEA 2022.3.3\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\charsets.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\deploy.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\javaws.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\jce.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\jfr.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\jsse.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\plugin.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\resources.jar;D:\CodingEnvironment\JDK1.8\jre\lib\rt.jar;D:\CodeWorkpace\idea-workspace\juc-study\out\production\juc-study ThreadCommunicationExample1
thread-A===number : 1
thread-B===number : 0
thread-A===number : 1
thread-B===number : 0
thread-A===number : 1
thread-B===number : 0
thread-A===number : 1
thread-B===number : 0
thread-C===number : 1
thread-A===number : 2
thread-C===number : 3
thread-B===number : 2
thread-D===number : 1
thread-D===number : 0
thread-C===number : 1
thread-A===number : 2
thread-C===number : 3
thread-D===number : 2
thread-B===number : 1
thread-B===number : 0
thread-D===number : -1
thread-C===number : 0
thread-C===number : 1
thread-A===number : 2
thread-C===number : 3
thread-D===number : 2
thread-B===number : 1
thread-B===number : 0
thread-D===number : -1
thread-C===number : 0
thread-C===number : 1
thread-A===number : 2
thread-C===number : 3
thread-D===number : 2
thread-B===number : 1
thread-D===number : 0
thread-A===number : 1
thread-D===number : 0
thread-A===number : 1
thread-D===number : 0
Process finished with exit code 0
这尼玛咋错了?其实这就是虚假唤醒问题
由于wait()的特新是“在哪里睡,在那里醒”,导致如果使用if判断,当”醒了“后,后续的操作会继续进行。导致出错。
解决办法是:使用while即使行了,还会继续判断是否向下执行。
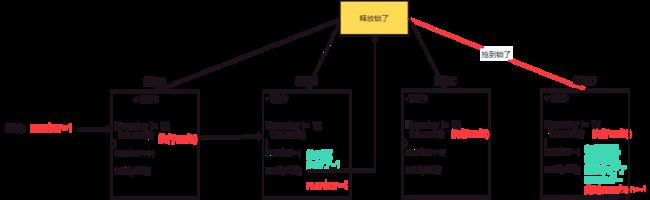
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author LWJ
* @date 2023/6/18
*/
// 1创建资源类,在资源类创建属性和操作方法。
class Share2{
private int number = 0;
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 2在资源类操作方法
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//判断
while(number != 0){
this.wait();
}
//干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//判断
while (number != 1){
this.wait();
}
//干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadCommunicationExample2 {
// 3创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.incr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.decr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.incr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-C").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share.decr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-D").start();
}
}
3.2.3 Lock方案
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author LWJ
* @date 2023/6/18
*/
// 1创建资源类,在资源类创建属性和操作方法。
class Share2{
private int number = 0;
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
// 2在资源类操作方法
public void incr() throws InterruptedException {
try{
lock.lock();
//判断
while(number != 0){
condition.await();
}
//干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
condition.signalAll();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decr() throws InterruptedException {
try{
lock.lock();
//判断
while(number != 1){
condition.await();
}
//干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + "number : " + number);
//通知
condition.signalAll();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ThreadCommunicationExample2 {
// 3创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share2 share2 = new Share2();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share2.incr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share2.decr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share2.incr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-C").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
share2.decr();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-D").start();
}
}
3.2.4 Condition接口
- 所有已知实现类:
- AbstractQueuedLongSynchronizer.ConditionObject,
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject这应该时AQS,基础阶段先放下,高级篇时候学
- 介绍
Condition 将 Object 监视器方法(wait、notify 和 notifyAll)分解成截然不同的对象,以便通过将这些对象与任意 Lock 实现组合使用,为每个对象提供多个等待 set(wait-set)。其中,Lock 替代了 synchronized 方法和语句的使用,Condition 替代了 Object 监视器方法的使用。
Condition(也称为_条件队列_ 或_条件变量_)为线程提供了一个含义,以便在某个状态条件现在可能为 true 的另一个线程通知它之前,一直挂起该线程(即让其“等待”)。因为访问此共享状态信息发生在不同的线程中,所以它必须受保护,因此要将某种形式的锁与该条件相关联。wait提供一个条件的主要属性是:以原子方式 释放相关的锁,并挂起当前线程,就像 Object.wait 做的那样。
Condition 实例实质上被绑定到一个锁上。要为特定 Lock 实例获得 Condition 实例,请使用其 newCondition() 方法。
作为一个示例,假定有一个绑定的缓冲区,它支持 put 和 take 方法。如果试图在空的缓冲区上执行 take 操作,则在某一个项变得可用之前,线程将一直阻塞;如果试图在满的缓冲区上执行 put 操作,则在有空间变得可用之前,线程将一直阻塞。我们喜欢在单独的等待 set 中保存 put 线程和 take 线程,这样就可以在缓冲区中的项或空间变得可用时利用最佳规划,一次只通知一个线程。可以使用两个 Condition 实例来做到这一点。
- 方法摘要
| 方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
| void | await() |
| 造成当前线程在接到信号或被中断之前一直处于等待状态。 | |
| boolean | await(long time, TimeUnit unit) |
| 造成当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态。 | |
| long | awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) |
| 造成当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态。 | |
| void | awaitUninterruptibly() |
| 造成当前线程在接到信号之前一直处于等待状态。 | |
| boolean | awaitUntil(Date deadline) |
| 造成当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定最后期限之前一直处于等待状态。 | |
| void | signal() |
| 唤醒一个等待线程。 | |
| void | signalAll() |
| 唤醒所有等待线程。 |
Condition (Java Platform SE 6)
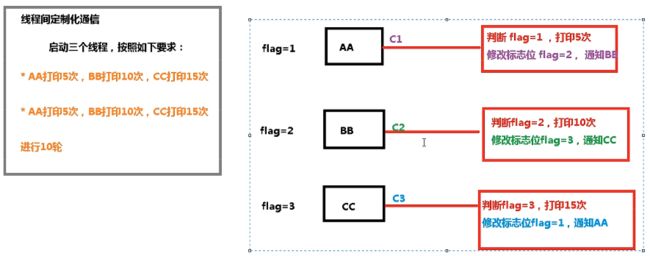
3.3 线程间定制化通信
3.3.1 线程按指定顺序打印案例
3.3.2 案例代码
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author LWJ
* @date 2023/6/18
*/
//创建资源类,创建其属性和操作方法
class ShareResource{
private int flag = 1; //1表示线程A 2表示线程B 3表示线程C
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition();
Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition();
Condition conditionC = lock.newCondition();
//定义操作
public void peint5(int loop) throws InterruptedException {
try{
lock.lock();
//判断
while(flag != 1){
conditionA.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "===" + i + "===" + "轮数" + loop);
}
//通知
flag = 2;
conditionB.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void peint10(int loop) throws InterruptedException {
try{
lock.lock();
//判断
while(flag != 2){
conditionB.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "===" + i + "===" + "轮数" + loop);
}
//通知
flag = 3;
conditionC.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void peint15(int loop) throws InterruptedException {
try{
lock.lock();
//判断
while(flag != 3){
conditionC.await();
}
//干活
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "===" + i + "===" + "轮数" + loop);
}
//通知
flag = 1;
conditionA.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ThreadCommunicationExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareResource shareResource = new ShareResource();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.peint5(i);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.peint10(i);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.peint15(i);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
},"thread-C").start();
}
}