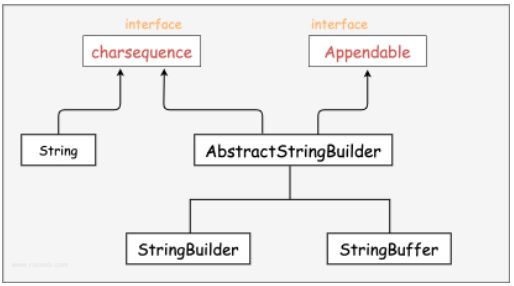
Java中字符串相关的类
目录
String类
StringBuffer类
StringBuilder类
String类
String类:代表字符串。Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的实例实现。
String是一个final类,代表不可变的字符序列。
字符串是常量,用双引号引起来表示。它们的值在创建之后不能更改。
String对象的字符内容是存储在一个字符数组value[]中的。
public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
......
}
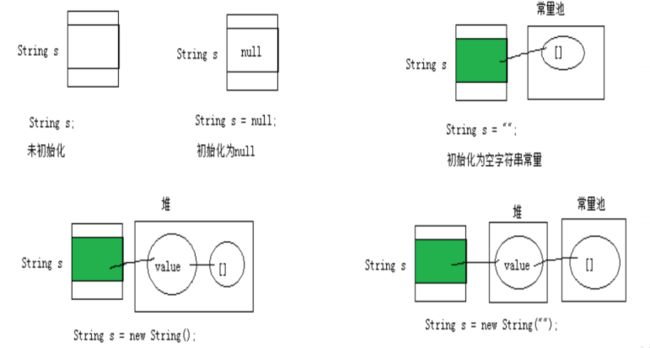
String 对象的创建
String str = "hello";
//本质上this.value = new char[0];
String s1 = new String();
//this.value = original.value;
String s2 = new String(String original);
//this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
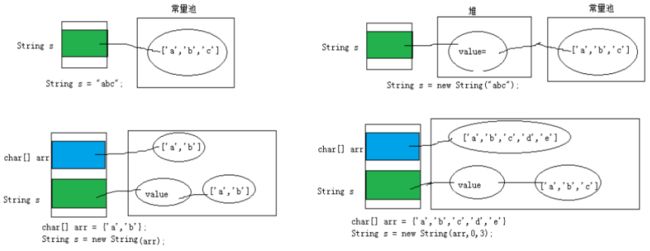
String s3 = new String(char[] a);
String s4 = new String(char[] a,int startIndex,int count);String str1 = “abc”;与String str2 = new String(“abc”);的区别?
字符串常量存储在字符串常量池,目的是共享;字符串非常量对象存储在堆中。
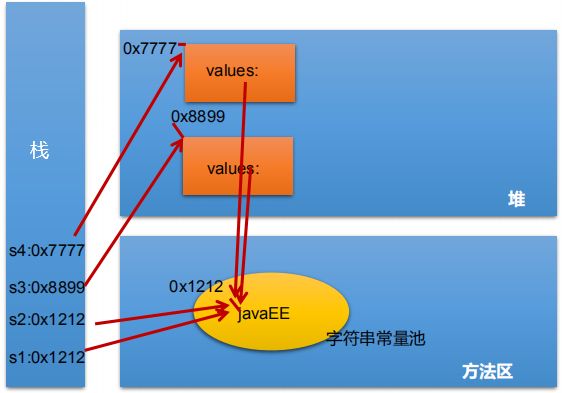
字符串对象的存储
String s1 = "javaEE";
String s2 = "javaEE";
String s3 = new String("javaEE");
String s4 = new String("javaEE");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//false
System.out.println(s1 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//falsePerson p1 = new Person("Tom",12);
Person p2 = new Person("Tom",12);
System.out.println(p1.name == p2.name);//true
字符串的特性
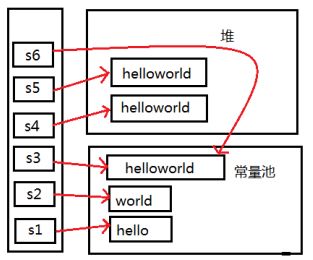
常量与常量的拼接结果在常量池,且常量池中不会存在相同内容的常量。只要其中有一个是变量,结果就在堆中。如果拼接的结果调用intern()方法,返回值就在常量池中。
String s1 = "hello" ;
String s2 = "world" ;
String s3 = "hel1o" + "world";
String s4 = s1 + "world";
String s5 = s1 + s2;
String s6 = (s1 + s2).intern();
System.out.print1n(s3==s4); //false
System.out.print1n(s3==s5); //false
System.out.print1n(s4==s5); //false
System.out.println(s3==s6); //true
String的使用陷阱
String s1 = "a"; 说明:在字符串常量池中创建了一个字面量为"a"的字符串。
s1 = s1 + "b"; 说明:实际上原来的“a”字符串对象已经丢弃了,现在在堆空间中产生了一个字符串s1+"b"(也就是"ab")。如果多次执行这些改变串内容的操作,会导致大量副本字符串对象存留在内存中,降低效率。如果这样的操作放到循环中,会极大影响程序的性能。
String s2 = "ab";说明:直接在字符串常量池中创建一个字面量为"ab"的字符串。
String s3 = "a" + "b";说明:s3指向字符串常量池中已经创建的"ab"的字符串。
String s4 = s1.intern();说明:堆空间的s1对象在调用intern()之后,会将常量池中已经存在的"ab"字符串赋值给s4。
String的常用方法
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | char charAt(int index) 返回指定索引处的 char 值。 |
| 2 | int compareTo(Object o) 把这个字符串和另一个对象比较。 |
| 3 | int compareTo(String anotherString) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串。 |
| 4 | int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写。 |
| 5 | String concat(String str) 将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。 |
| 6 | boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) 当且仅当字符串与指定的StringBuffer有相同顺序的字符时候返回真。 |
| 7 | static String copyValueOf(char[] data) 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 String。 |
| 8 | static String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count) 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 String。 |
| 9 | boolean endsWith(String suffix) 测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。 |
| 10 | boolean equals(Object anObject) 将此字符串与指定的对象比较。 |
| 11 | boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) 将此 String 与另一个 String 比较,不考虑大小写。 |
| 12 | byte[] getBytes() 使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。 |
| 13 | byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) 使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。 |
| 14 | void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 将字符从此字符串复制到目标字符数组。 |
| 15 | int hashCode() 返回此字符串的哈希码。 |
| 16 | int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。 |
| 17 | int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) 返回在此字符串中第一次出现指定字符处的索引,从指定的索引开始搜索。 |
| 18 | int indexOf(String str) 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。 |
| 19 | int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始。 |
| 20 | String intern() 返回字符串对象的规范化表示形式。 |
| 21 | int lastIndexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引。 |
| 22 | int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索。 |
| 23 | int lastIndexOf(String str) 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引。 |
| 24 | int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索。 |
| 25 | int length() 返回此字符串的长度。 |
| 26 | boolean matches(String regex) 告知此字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。 |
| 27 | boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) 测试两个字符串区域是否相等。 |
| 28 | boolean regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) 测试两个字符串区域是否相等。 |
| 29 | String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) 返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。 |
| 30 | String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) 使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。 |
| 31 | String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) 使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串。 |
| 32 | String[] split(String regex) 根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。 |
| 33 | String[] split(String regex, int limit) 根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串。 |
| 34 | boolean startsWith(String prefix) 测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始。 |
| 35 | boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) 测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始。 |
| 36 | CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 返回一个新的字符序列,它是此序列的一个子序列。 |
| 37 | String substring(int beginIndex) 返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。 |
| 38 | String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。 |
| 39 | char[] toCharArray() 将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组。 |
| 40 | String toLowerCase() 使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写。 |
| 41 | String toLowerCase(Locale locale) 使用给定 Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写。 |
| 42 | String toString() 返回此对象本身(它已经是一个字符串!)。 |
| 43 | String toUpperCase() 使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。 |
| 44 | String toUpperCase(Locale locale) 使用给定 Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。 |
| 45 | String trim() 返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白。 |
| 46 | static String valueOf(primitive data type x) 返回给定data type类型x参数的字符串表示形式。 |
| 47 | contains(CharSequence chars) 判断是否包含指定的字符系列。 |
| 48 | isEmpty() 判断字符串是否为空。 |
String的类型转换
基本数据类型、包装类 --> 字符串:
调用String类的public String valueOf(int n)可将int型转换为字符串。
相应的valueOf(byte b)、valueOf(long l)、valueOf(float f)、valueOf(double d)、valueOf(boolean b)可由参数的相应类型到字符串的转换。
字符串 --> 基本数据类型、包装类:
Integer包装类的public static int parseInt(String s):可将由“数字”字符组成的字符串转换为整型。
类似地,使用java.lang包中的Byte、Short、Long、Float、Double类调相应的类方法可以将由“数字”字符组成的字符串,转化为相应的基本数据类型。
字符数组 --> 字符串:
String 类的构造器:String(char[]) 和 String(char[],int offset,int length) 分别用字符数组中的全部字符和部分字符创建字符串对象。
字符串 --> 字符数组:
public char[] toCharArray():将字符串中的全部字符存放在一个字符数组中的方法。
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin):提供了将指定索引范围内的字符串存放到数组中的方法。
字节数组 --> 字符串:
String(byte[]):通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。
String(byte[],int offset,int length) :用指定的字节数组的一部分,即从数组起始位置offset开始取length个字节构造一个字符串对象。
字符串 --> 字节数组:
public byte[] getBytes() :使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) :使用指定的字符集将 此 String 编码到 byte 序列,并将结果存储到新的 byte 数组。
StringBuffer类
当对字符串进行修改的时候,需要使用 StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类。
和 String 类不同的是,StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类的对象能够被多次的修改,并且不产生新的未使用对象。
java.lang.StringBuffer代表可变的字符序列,JDK1.0中声明,可以对字符串内容进行增删,此时不会产生新的对象。所以如果需要对字符串进行修改推荐使用 StringBuffer。
作为参数传递时,方法内部可以改变值。
abstract class AbstractstringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence {
/**
* The value is used for character storage.
* value没有final声明,value可以不断扩容。
*/
char[] value;
/**
* The count is the number of characters used.
* count记录有效字符的个数。
*/
int count ;
......
}构造方法
StringBuffer类不同于String,其对象必须使用构造器生成。有三个构造器:
| StringBuffer() | 初始容量为16的字符串缓冲区 |
| StringBuffer(int size) | 构造指定容量的字符串缓冲区 |
| StringBuffer(String str) | 将内容初始化为指定字符串内容 |
常用方法
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public StringBuffer append(String s) 将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。 |
| 2 | public StringBuffer reverse() 将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。 |
| 3 | public delete(int start, int end) 移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
| 4 | public insert(int offset, int i) 将 int 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。 |
| 5 | insert(int offset, String str) 将 str 参数的字符串插入此序列中。 |
| 6 | replace(int start, int end, String str) 使用给定 String 中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
当append和insert时,如果原来value数组长度不够,可扩容。
如上这些方法支持方法链操作。方法链的原理:
StringBuilder类
StringBuilder 类在 Java 5 中被提出,它和 StringBuffer 之间的最大不同在于 StringBuilder 的方法不是线程安全的(不能同步访问)。
StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer 很类似,均代表可变的字符序列,而且提供相关功能的方法也一样。由于 StringBuilder 相较于 StringBuffer 有速度优势,所以多数情况下建议使用 StringBuilder 类。
StringBuffer 类的其他常用方法:
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | int capacity() 返回当前容量。 |
| 2 | char charAt(int index) 返回此序列中指定索引处的 char 值。 |
| 3 | void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) 确保容量至少等于指定的最小值。 |
| 4 | void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 将字符从此序列复制到目标字符数组 dst。 |
| 5 | int indexOf(String str) 返回第一次出现的指定子字符串在该字符串中的索引。 |
| 6 | int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 从指定的索引处开始,返回第一次出现的指定子字符串在该字符串中的索引。 |
| 7 | int lastIndexOf(String str) 返回最右边出现的指定子字符串在此字符串中的索引。 |
| 8 | int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) 返回 String 对象中子字符串最后出现的位置。 |
| 9 | int length() 返回长度(字符数)。 |
| 10 | void setCharAt(int index, char ch) 将给定索引处的字符设置为 ch。 |
| 11 | void setLength(int newLength) 设置字符序列的长度。 |
| 12 | CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end) 返回一个新的字符序列,该字符序列是此序列的子序列。 |
| 13 | String substring(int start) 返回一个新的 String,它包含此字符序列当前所包含的字符子序列。 |
| 14 | String substring(int start, int end) 返回一个新的 String,它包含此序列当前所包含的字符子序列。 |
| 15 | String toString() 返回此序列中数据的字符串表示形式。 |