LeetCode——两数相加
目录
一、两数相加
1、题目
2、题目解读
3、代码
二、反转链表
1、题目
2、题目解读
3、代码
三、两数相加 II
1、题目
2、题目解读
3、代码
反转链表再进行计算
借助栈
一、两数相加
1、题目
2. 两数相加 - 力扣(Leetcode)
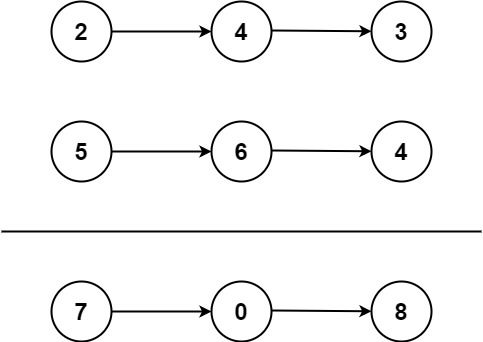
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] 输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围
[1, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
2、题目解读
因为题目所给链表节点的范围是[1,100],所以我们无法通过将两个链表转换成两个数再进行计算,然后重新转换成链表,数太大了。
题目说:它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
因此我们就直接进行计算两个链表的值,然后对10进行取模,再进行进位操作。
如下操作:
sum = x + y + carry
carry = sum / 10
sum = sum % 10还需要注意的是如果最后sum不为0还需要进位,也就是再添加一个节点。
运行条件:链表从头遍历到尾,逐位相加 (1)需要保存进位 (2)需要保存结果
结束时:
- 两个链表只要有一个非空就需要往后进行
- 如果链表遍历结束,进位不为0,需要把进位项添加在链表后面
3、代码
java:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public static ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = pre;
int carry = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum);
cur = cur.next;
if(l1 != null)
l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null)
l2 = l2.next;
}
if(carry == 1) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return pre.next;
}
}
Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 创建一个结点值为 None 的头结点, dummy 和 p 指向头结点, dummy 用来最后返回, p 用来遍历
dummy = p = ListNode(None)
s = 0 # 初始化进位 s 为 0
while l1 or l2 or s:
# 如果 l1 或 l2 存在, 则取l1的值 + l2的值 + s(s初始为0, 如果下面有进位1, 下次加上)
s += (l1.val if l1 else 0) + (l2.val if l2 else 0)
p.next = ListNode(s % 10) # p.next 指向新链表, 用来创建一个新的链表
p = p.next # p 向后遍历
s //= 10 # 有进位情况则取模, eg. s = 18, 18 // 10 = 1
l1 = l1.next if l1 else None # 如果l1存在, 则向后遍历, 否则为 None
l2 = l2.next if l2 else None # 如果l2存在, 则向后遍历, 否则为 None
return dummy.next # 返回 dummy 的下一个节点, 因为 dummy 指向的是空的头结点, 下一个节点才是新建链表的后序节点
二、反转链表
1、题目
206. 反转链表 - 力扣(Leetcode)
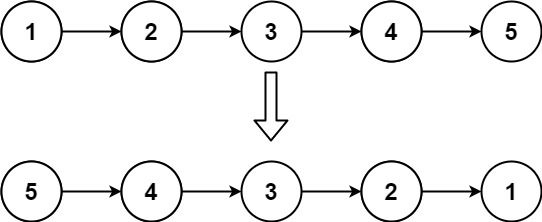
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
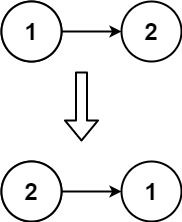
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
2、题目解读
链表简单反转
3、代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
pre = None
cur = head
while cur:
temp = cur.next # 先把原来cur.next位置存起来
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre
三、两数相加 II
1、题目
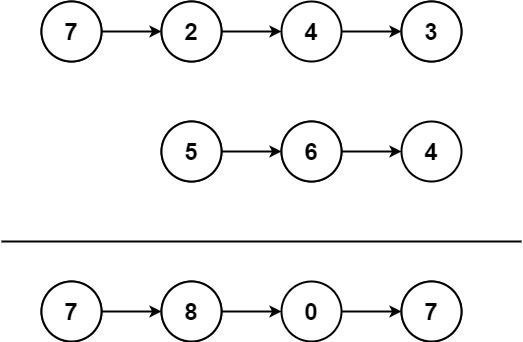
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例1:
输入:l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,8,0,7]
示例2:
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[8,0,7]
示例3:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 链表的长度范围为
[1, 100] 0 <= node.val <= 9- 输入数据保证链表代表的数字无前导 0
2、题目解读
这题拆解开来就是上面两题,先进行链表反转,然后继续两数相加。
或者通过栈来完成链表上面数的保存,然后进行计算。
3、代码
反转链表再进行计算
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pre1=null;
ListNode cur1=l1;
while (cur1!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur1.next;
cur1.next=pre1;
pre1=cur1;
cur1=tmp;
}
ListNode pre2=null;
ListNode cur2=l2;
while (cur2!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur2.next;
cur2.next=pre2;
pre2=cur2;
cur2=tmp;
}
l1=pre1;
l2=pre2;
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = pre;
int carry = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum);
cur = cur.next;
if(l1 != null)
l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null)
l2 = l2.next;
}
if(carry == 1) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
cur=pre.next;
pre=null;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}借助栈
使用栈区进行存储数字,然后再相加计算。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode head = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry > 0) {
int sum = carry;
sum += stack1.isEmpty()? 0: stack1.pop();
sum += stack2.isEmpty()? 0: stack2.pop();
ListNode node = new ListNode(sum % 10);
node.next = head;
head = node;
carry = sum / 10;
}
return head;
}
}