注解实现自动装配
要使用注解须知:
1.导入约束 context约束
2.配置注解的支持
官方配置文件
自己的配置文件
@Autowired
注意:Autowire优先按类型,找不到就报错,找到多个则按名字
一般是放在属性上,也可以放在set上
自动装配
@Autowired会先根据类型进行注入,如果容器中有多个满足类型的实例,就会根据ID进行注入。并不是单纯只根据类型注入
这边设置可以为null,就可以不用在bean里面装配,老师是因为调用了shout()方法才导致的报错
package com.kuang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class People {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired(required = false)
private Cat cat;
private String name;
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"dog=" + dog +
", cat=" + cat +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
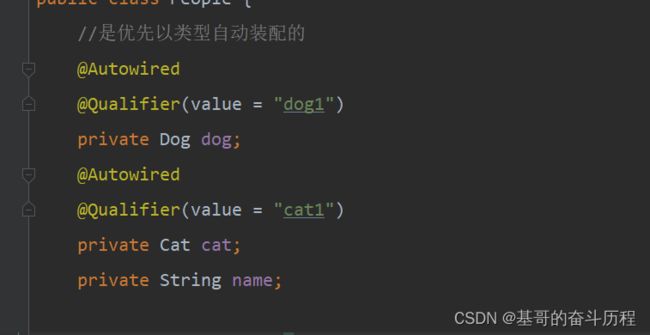
如果@Autowire自动装配的环境比较复杂,自动装配无法通过一个注解【@Autowired】完成的时候,我们可以使用@Qualifier(value="xxx") 与Bean对象的ID相同 才能注入 与去配合@Autowired的使用,指定一个唯一的bean对象注入!
@Resource注解
@Resource(name = "cat11")
private Cat cat;
private String name;
小结:
@Resource和@Autowired的区别:
- 都是用来自动装配的,都可以放在属性字段上
- @Autowired通过byType的方式实现,而且必须要求这个对象存在!【常用】
- @Resource默认通过byname的方式实现,如果找不到名字,则通过byType实现!如果两个都找不到的情况下就报错!【常用】
- 执行顺序不同。@Autowired通过byType的方式实现,@Resource通过byName的方式实现!
1.使用注解开发
1.bean
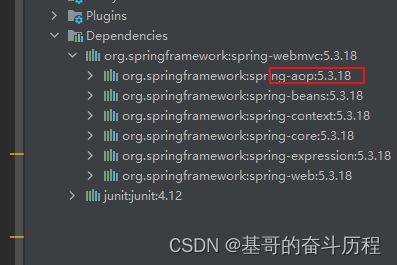
检查AOP的包是否存在
使用注解需要导入context约束,增加注解的支持!
package com.kuang.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//等价于 package mytest;
import com.kuang.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user.name);
}
}
2.属性如何注入
package com.kuang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Component 组件等价于 3.衍生的注解
@Component 有几个衍生注解,我们在web开发中,会按照三层架构分层!
- dao【@Repository】
- service【@Service】
- controller【@Controller】
这四个注解功能都是一样的,都是代表蒋某个类注册刀片Spring中,装配哦Bean。
4.自动装配置
- @Autowired:自动装配类型:1.类型 2.名字
如果@Autowired不能唯一自动装配上属性,则需要@Qualifier(value="xxx");
- @Nullable 字段标记了这个注解,说明这个字段可以为null;
- @Resource : 自动装配通过名字、类型当一个类Class A中需要一个B类型的变量时 在声明变量时加上这个注解 spring会在容器中寻找有没有是标注在一个类上的,作用是将被标注的类注册在spring容器中,将类的实例化交给spring管理完成的是bean的注册
5.作用域
package com.kuang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Component 组件等价于 6.小结
xml与注解:
- xml更加方便,适用于任何场合!维护简单方便
- 注解 不是自己类使用不了,维护相对复杂!
xml 与注解最佳实践:
- xml用来管理bean;
- 注解只负责完成属性的注入
- 我们在使用的过程中,只需要注意一个问题:必须让注解生效,就需要开启注解的支持!
使用Java的方式配置Spring
3. @Bean 可以用于通过方法获取数据库连接池Connection这种对象
注意:1. 如果开启包扫描,加载配置类以后就可以通过反射拿到配置类中的对象了,
2. @Bean只写在方法上,返回的是一个对象,但一般不获取已经在容器中的对象
我们现在要完全不使用Spring的xml配置了,全权交给Java来做!
JavaConfig是Spring的一个子项目。在Spring4之后,它成为了一个核心功能。
配置类
package com.kuang.config;
import com.kuang.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration//这个也会被Spring容器托管,注册到容器中,因为它本来就是一个Component
//@Configuration代表这是一个配置类,就和我们之前看的beans.xml文件一样
@ComponentScan("com.kuang")//扫描,使注解生效
public class KuangConfig {
//注册一个bean,就相当于我们之前小写的一个bean标签,
//这个方法的名字,就相当于bean标签中的id属性
//这个方法的返回值,就相当于bean标签中的class属性
@Bean
public User user(){
return new User();//就是返回要注入到bean的对象
}
}
实体类
package com.kuang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//这里这个注解的意思,就是说明这个类被Spring接管了,注册到了容器中
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Value("JIJIboy")//属性注入值
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
测试类
import com.kuang.config.KuangConfig;
import com.kuang.pojo.User;
import com.sun.xml.internal.bind.v2.schemagen.xmlschema.Annotated;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果完全使用了配置类方式去做,我们就只能通过AnnotationConfig上下文来获取容器,通过配置类的class对象加载!
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(KuangConfig.class);
User user = (User) context.getBean("user");
String name = user.getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
这种纯java的配置方法,在SpringBoot中随处可见!
这个方法得需要多去理解!