字典树 ZOJ1109 HDU1251 PKU1204 HDU1075
又称单词查找树,Trie树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
假设有abc,abcd,abd, b, bcd,efg,hii这7个单词,可构建字典树如下:
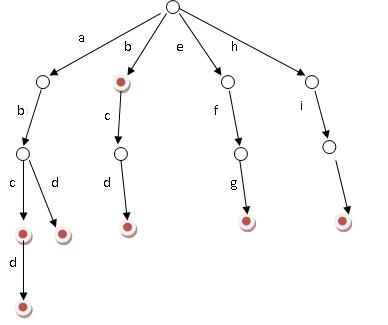
查找一个字符串时,我们只需从根结点按字符串中字符出现顺序依次往下走。如果到最后字符串结束时,对应的结点标记为红色,则该字符串存在;否则不存在。
插入时也只需从根结点往下遍历,碰到已存在的字符结点就往下遍历,否则,建立新结点;最后标记最后一个字符的结点为红色即可。
性质
它有3个基本性质:
根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
基本操作
其基本操作有:查找 插入和删除,当然删除操作比较少见.我在这里只是实现了对整个树的删除操作,至于单个word的删除操作也很简单.
搜索字典项目的方法为:
(1) 从根结点开始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找关键词的第一个字母,并根据该字母选择对应的子树并转到该子树继续进行检索;
(3) 在相应的子树上,取得要查找关键词的第二个字母,并进一步选择对应的子树进行检索。
(4) 迭代过程……
(5) 在某个结点处,关键词的所有字母已被取出,则读取附在该结点上的信息,即完成查找。
其他操作类似处理
以上内容来自百度百科:。对应练习:ZOJ1109 HDU1251
ZOJ1109 Language of FatMouse
map方法 1320MS 9556K
 代码
代码
#include
<
iostream
>
#include
<
string
>
#include
<
map
>
#pragma
warning (disable:4786)
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
map
<
string
,
string
>
m;
int
len,i;
char
str[
40
],a[
20
],b[
20
];
while
(
1
)
{
gets(str);
len
=
strlen(str);
if
(len
==
0
)
break
;
for
(i
=
0
;str[i]
!=
'
'
;i
++
);
strncpy(a,str,i);
a[i]
=
0
;
strncpy(b,str
+
i
+
1
,len
-
i
-
1
);
b[len
-
i
-
1
]
=
0
;
m[b]
=
a;
}
map
<
string
,
string
>
::iterator it;
while
(scanf(
"
%s
"
,str)
!=
EOF)
{
it
=
m.find(str);
if
(it
!=
m.end())
cout
<<
(
*
it).second
<<
endl;
else
puts(
"
eh
"
);
}
return
0
;
}
字典树:140MS 14960K
 代码
代码
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
#include
<
string
.h
>
#define
N 100006
typedef
struct
node{
char
s[
12
];
int
h;
struct
node
*
next[
26
];
}
*
Tree,T;
void
init(Tree
&
root)
{
root
=
(Tree)malloc(
sizeof
(T));
root
->
h
=
0
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;i
<
26
;i
++
)
root
->
next[i]
=
NULL;
}
void
insert(
char
path[],
char
s[],Tree root)
{
int
len,i,j;
len
=
strlen(path);
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
len;i
++
)
{
if
(root
->
next[path[i]
-
'
a
'
]
==
NULL)
{
Tree t
=
(Tree)malloc(
sizeof
(T));
for
(j
=
0
;j
<
26
;j
++
)
{
t
->
next[j]
=
NULL;
t
->
h
=
0
;
}
root
->
next[path[i]
-
'
a
'
]
=
t;
}
root
=
root
->
next[path[i]
-
'
a
'
];
}
root
->
h
=
1
;
strcpy(root
->
s,s);
}
void
find(
char
s[],Tree root)
{
int
len,i;
len
=
strlen(s);
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
len;i
++
)
{
if
(root
->
next[s[i]
-
'
a
'
]
!=
NULL)
root
=
root
->
next[s[i]
-
'
a
'
];
else
break
;
}
if
(i
==
len
&&
root
->
h
==
1
)
puts(root
->
s);
else
puts(
"
eh
"
);
}
int
main()
{
Tree root;
int
len,i;
char
str[
25
],a[
12
],b[
12
];
init(root);
while
(
1
)
{
gets(str);
len
=
strlen(str);
if
(len
==
0
)
break
;
for
(i
=
0
;str[i]
!=
'
'
;i
++
);
strncpy(a,str,i);
a[i]
=
0
;
strncpy(b,str
+
i
+
1
,len
-
i
-
1
);
b[len
-
i
-
1
]
=
0
;
insert(b,a,root);
}
while
(scanf(
"
%s
"
,str)
!=
EOF)
find(str,root);
return
0
;
}
HDU1251 统计难题 140MS 43736K
 代码
代码
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
#include
<
string
.h
>
typedef
struct
node{
int
cnt;
struct
node
*
next[
26
];
}
*
Tree,T;
Tree root;
void
insert(
char
*
str)
//
建字典树
{
int
i;
Tree p,newnode;
p
=
root;
for
(;
*
str;str
++
)
{
if
(p
->
next[
*
str
-
'
a
'
]
!=
NULL)
{
p
=
p
->
next[
*
str
-
'
a
'
];
p
->
cnt
++
;
}
else
{
newnode
=
(Tree)malloc(
sizeof
(T));
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
26
;i
++
)
newnode
->
next[i]
=
NULL;
p
->
next[
*
str
-
'
a
'
]
=
newnode;
p
=
p
->
next[
*
str
-
'
a
'
];
p
->
cnt
=
1
;
}
}
}
int
find(
char
*
str)
//
查找
{
Tree p;
p
=
root;
for
(;
*
str;str
++
)
{
if
(p
->
next[
*
str
-
'
a
'
]
!=
NULL)
p
=
p
->
next[
*
str
-
'
a
'
];
else
return
0
;
}
return
p
->
cnt;
}
int
main()
{
int
i;
char
str[
20
];
root
=
(Tree)malloc(
sizeof
(T));
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
26
;i
++
)
root
->
next[i]
=
NULL;
root
->
cnt
=
0
;
while
(gets(str))
{
if
(strcmp(str,
""
)
==
0
)
break
;
insert(str);
}
while
(gets(str))
printf(
"
%d\n
"
,find(str));
return
0
;
}
PKU1204 Word Puzzles
字典树:1485MS 14320K(对给定的单词建树,对表进行暴力search)
 代码
代码
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
string
.h
>
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
#define
N 1002
typedef
struct
tree{
int
count;
struct
tree
*
next[
26
];
}
*
Tree,T;
Tree root;
int
l,c,w;
char
map[N][N];
int
result[N][
3
];
int
dir[
8
][
2
]
=
{{
-
1
,
0
},{
-
1
,
1
},{
0
,
1
},{
1
,
1
},{
1
,
0
},{
1
,
-
1
},{
0
,
-
1
},{
-
1
,
-
1
}};
void
insert(
char
*
s,
int
con)
{
Tree p
=
root,q;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;s[i];i
++
)
{
if
(p
->
next[s[i]
-
'
A
'
]
==
NULL)
{
q
=
(Tree)malloc(
sizeof
(T));
memset(q
->
next,
0
,
sizeof
(q
->
next));
q
->
count
=-
1
;
p
->
next[s[i]
-
'
A
'
]
=
q;
}
p
=
p
->
next[s[i]
-
'
A
'
];
}
p
->
count
=
con;
}
void
search(
int
x,
int
y,
int
k)
{
int
x1
=
x,y1
=
y;
Tree p
=
root;
while
(x1
>=
0
&&
x1
<
l
&&
y1
>=
0
&&
y1
<
c)
{
int
id
=
map[x1][y1]
-
'
A
'
;
if
(p
->
next[id]
==
NULL)
break
;
else
p
=
p
->
next[id];
if
(p
->
count
!=-
1
)
{
result[p
->
count][
0
]
=
x;
result[p
->
count][
1
]
=
y;
result[p
->
count][
2
]
=
k
+
'
A
'
;
}
x1
+=
dir[k][
0
]; y1
+=
dir[k][
1
];
}
}
void
slove()
{
int
i,j,k;
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
l;i
++
)
for
(j
=
0
;j
<
c;j
++
)
for
(k
=
0
;k
<
8
;k
++
)
search(i,j,k);
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
w;i
++
)
printf(
"
%d %d %c\n
"
,result[i][
0
],result[i][
1
],result[i][
2
]);
}
int
main()
{
int
i;
char
word[N];
scanf(
"
%d%d%d
"
,
&
l,
&
c,
&
w);
getchar();
root
=
(Tree)malloc(
sizeof
(T));
memset(root
->
next,
0
,
sizeof
(root
->
next));
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
l;i
++
)
gets(map[i]);
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
w;i
++
)
{
gets(word);
insert(word,i);
}
slove();
return
0
;
}
据说这题还可以用AC自动机实现,不了解AC自动机,有待提高……
HDU1075 同ZOJ1109同一道理,字典树基本应用。
map方法 3375MS 42368K 752B
 代码
代码
#include
<
iostream
>
#include
<
string
>
#include
<
map
>
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
map
<
string
,
string
>
M;
string
a,b;
cin
>>
a;
while
(cin
>>
a,a
!=
"
END
"
)
{
cin
>>
b;
M[b]
=
a;
}
cin
>>
a;
getchar();
char
tmp[
3005
];
while
(gets(tmp),strcmp(tmp,
"
END
"
))
{
int
len
=
strlen(tmp);
tmp[len
++
]
=
'
'
;
tmp[len]
=
0
;
b
=
""
;
for
(
int
i
=
0
;i
<
len;i
++
)
{
if
(
!
islower(tmp[i]))
{
if
(M[b]
!=
""
)
cout
<<
M[b];
else
cout
<<
b;
b
=
""
;
if
(i
!=
len
-
1
)
cout
<<
tmp[i];
}
else
b
+=
tmp[i];
}
cout
<<
endl;
}
return
0
;
}
字典树:437MS 59796K 1274B(可以用做模板了吧)
 代码
代码
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
string
.h
>
#include
<
ctype.h
>
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
typedef
struct
node{
node
*
next[
26
];
int
h;
char
word[
12
];
node()
{
h
=
0
;
memset(next,
0
,
sizeof
(next));
}
}
*
Tree,T;
Tree root
=
new
node();
void
insert(
char
*
eng,
char
*
mar)
{
Tree p
=
root;
while
(
*
mar)
{
int
id
=*
mar
-
'
a
'
;
if
(p
->
next[id]
==
NULL)
p
->
next[id]
=
new
node();
p
=
p
->
next[id];
mar
++
;
}
p
->
h
=
1
;
strcpy(p
->
word,eng);
}
char
*
find(
char
*
str)
{
Tree p
=
root;
while
(
*
str)
{
int
id
=*
str
-
'
a
'
;
if
(p
->
next[id]
==
NULL)
break
;
p
=
p
->
next[id];
str
++
;
}
if
(
*
str
==
NULL
&&
p
->
h
==
1
)
return
p
->
word;
else
return
NULL;
}
int
main()
{
int
i,k,len;
char
a[
12
],b[
12
],tmp[
3005
],tp[
3005
];
char
*
p;
scanf(
"
%s
"
,a);
while
(scanf(
"
%s
"
,a)
&&
strcmp(a,
"
END
"
)
!=
0
)
{
scanf(
"
%s
"
,b);
insert(a,b);
}
scanf(
"
%s
"
,a);
getchar();
k
=
0
;
while
(gets(tmp),strcmp(tmp,
"
END
"
))
{
len
=
strlen(tmp);
tmp[len
++
]
=
'
'
;
tmp[len]
=
0
;
for
(i
=
0
;i
<
len;i
++
)
{
if
(
!
islower(tmp[i]))
{
tp[k]
=
0
;
k
=
0
;
p
=
find(tp);
if
(p)
printf(
"
%s
"
,p);
else
printf(
"
%s
"
,tp);
if
(i
!=
len
-
1
)
putchar(tmp[i]);
}
else
tp[k
++
]
=
tmp[i];
}
puts(
""
);
}
return
0
;
}
