初阶数据结构——栈和队列习题
目录
-
- 括号匹配问题
-
- 思路
- 代码
- 用队列实现栈
-
- 思路
- 注意点
- 代码
- 用栈实现队列
-
- 思路
- 代码
- 设计循环队列
-
- 思路
- 数组实现代码
- 链表实现代码
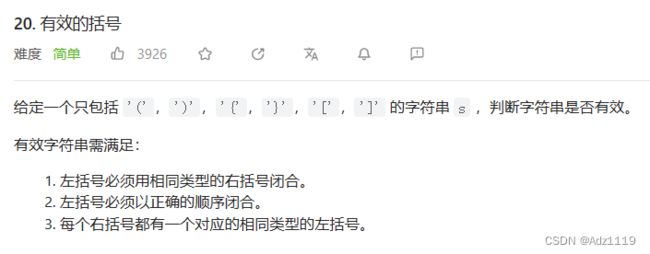
括号匹配问题
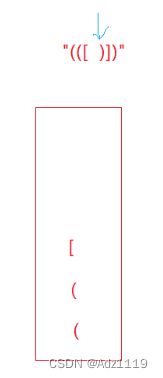
思路
代码
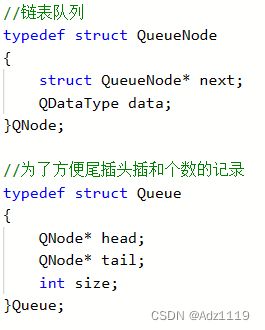
#include用队列实现栈
思路
push数据的时候push到非空的那个队列
pop数据的时候把非空队列的数据转移到空的队列,直到只剩最后一个,然后pop

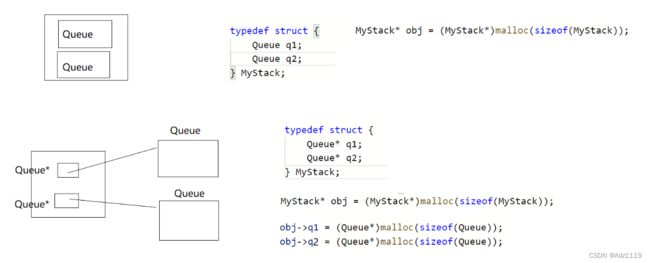
注意点

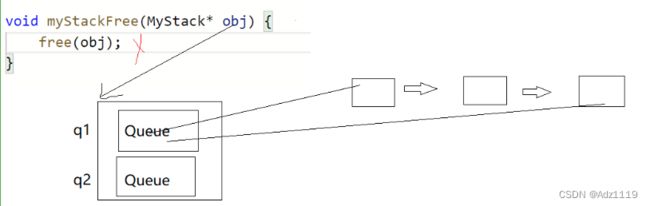
局部结构体变量出了作用域销毁,还去返回它的地址,就是野指针了,所以这样写是不对的
应该malloc一个节点后再返回
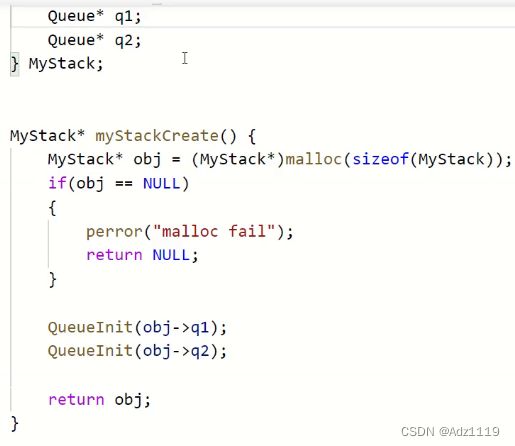
不要为了不想把&obj->q1传递给Init而在MyStack中写成队列的指针,这时候这两个指针没有初始化,到Init函数中就有野指针问题。如果实在想在MyStack中写成队列的指针,可以q1和q2再去malloc
代码
#include用栈实现队列
思路
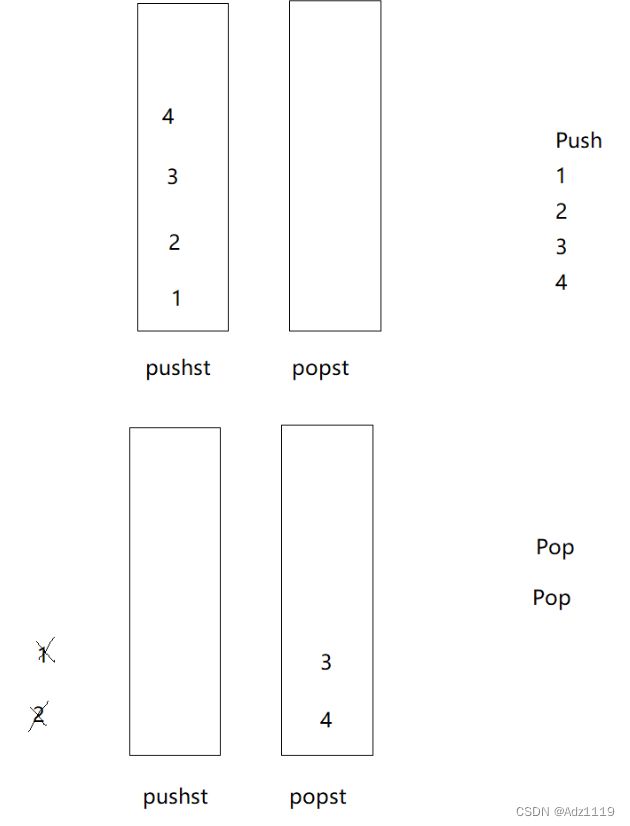
一个栈负责push
一个栈负责pop
push时放进pushst
pop时如果popst为空,则将pushst中数据都放入popst,然后对popst中数据进行pop
如果popst不为空,则直接对popst中数据进行pop
代码
#include设计循环队列
思路
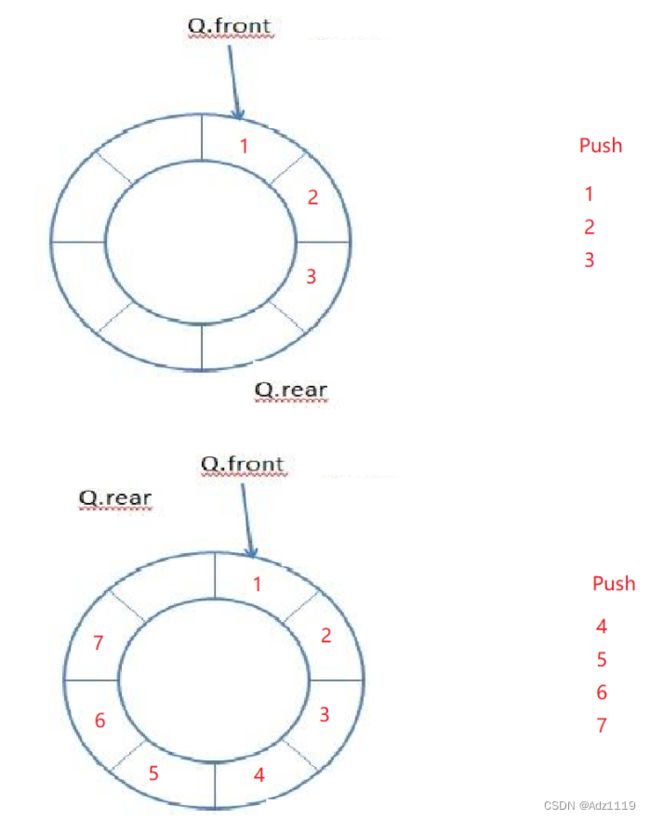
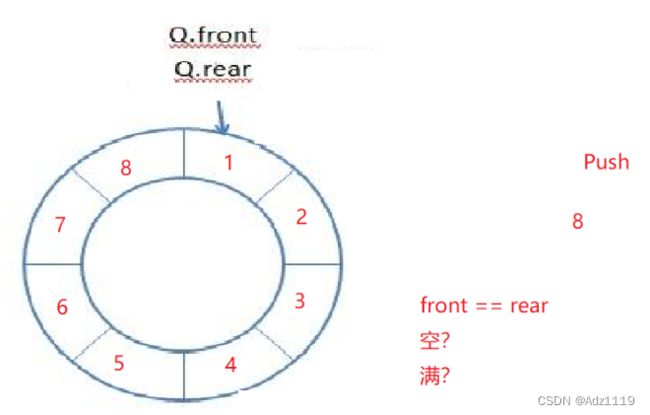
1.多开一个空间。满:real+1 == front
2.增加一个size变量记录数据个数
空:size==0
满:size==8
这里展示多开一个空间的方案
循环队列可以用链表实现也可以用数组实现
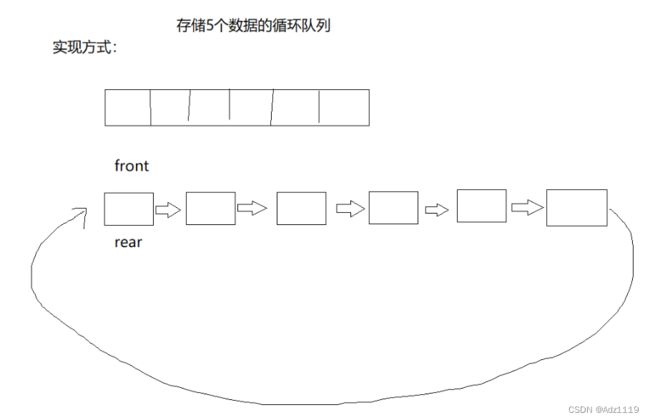
链表实现思路:
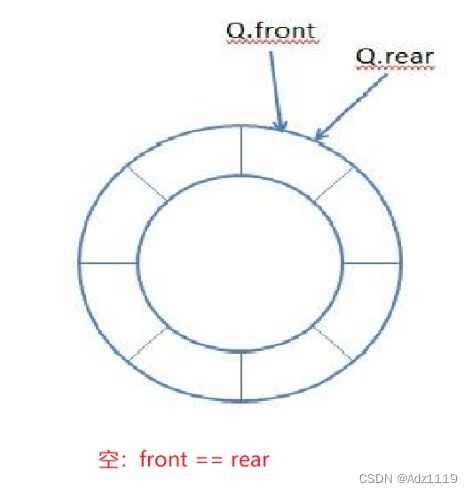
空:front == rear
满:rear->next == front
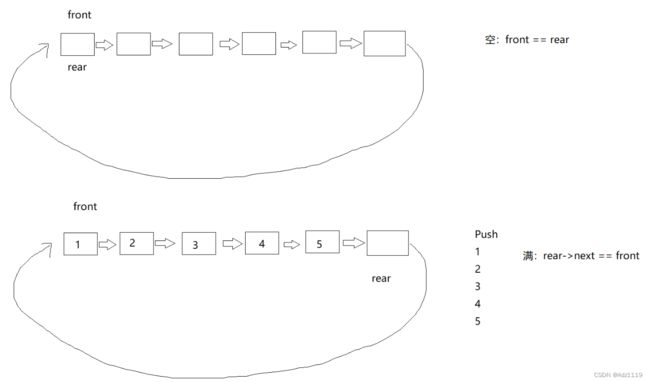

由于需要获取队尾元素,
解决思路有:1.双向链表 2.增加一个prev指针 3.遍历获得队尾数据
数组实现思路:
空:front == real
满:(rear+1)%(k+1) == front
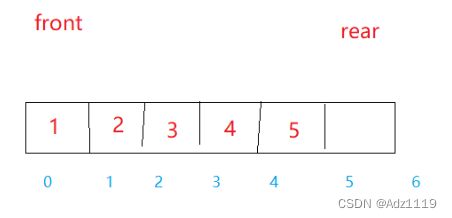
相比来说数组实现会简单一些,因为链表实现起来结构更复杂
数组实现代码
typedef struct {
int* a;
int front;
int real;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue*obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));//多开一个空间方便判满
obj->front=0;
obj->real=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
return false;
obj->a[obj->real++]=value;
obj->real%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return false;
obj->front++;
obj->front%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
if(obj->real==0)
return obj->a[obj->k];
else
return obj->a[obj->real-1];
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->real;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return (obj->real+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
obj->real=obj->front=obj->k=0;
free(obj);
}
链表实现代码
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode*next;
int data;
}QNode;
typedef struct {
QNode*front;
QNode*real;
QNode*prev;
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);
QNode* QueueInit(int k)
{
QNode*phead=(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
QNode*cur=phead;
while(k--)
{
QNode*next=(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
cur->next=next;
cur->data=0;
next->next=phead;
cur=next;
}
return phead;
}
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue*obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return NULL;
}
QNode*phead=QueueInit(k);
obj->front=phead;
obj->real=phead;
obj->prev=NULL;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
return false;
obj->real->data=value;
obj->prev=obj->real;//记录前一个
obj->real=obj->real->next;
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return false;
obj->front=obj->front->next;
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
return obj->front->data;
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
return obj->prev->data;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->real;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->real->next==obj->front;
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
QNode*cur=obj->front;
QNode*next=cur->next;
while(next!=obj->front)
{
free(cur);
cur=next;
next=cur->next;
}
free(cur);
obj->front=NULL;
obj->real=NULL;
obj->prev=NULL;
free(obj);
}