多路选择器设计实现
文章目录
- 一、多路选择器
- 二、二选一多路选择器
- 三、四选一多路选择器设计
一、多路选择器
多路选择器是数据选择器的别称。在多路数据传送过程中,能够根据需要将其中任意一路选出来的电路,叫做数据选择器,也称多路选择器或多路开关。
二、二选一多路选择器
二选一多路选择器有两个输入数据,分别为in_a和in_b。为了确定选择那一路数据通过,还有一个选择段sel。
预想设计如下:
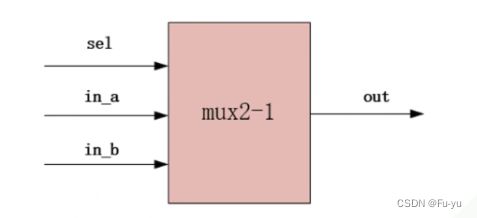
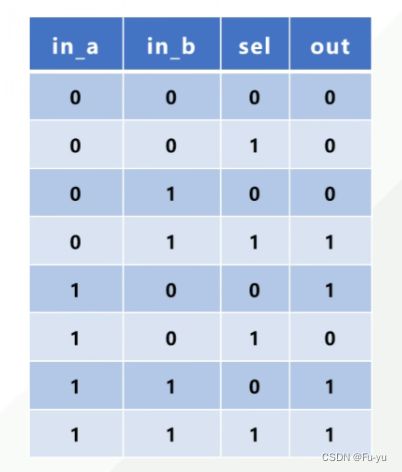
二选一多路选择器设计,sel为0时out输出in_a的值,sel为1时out输出in_b的值。
使用verilog代码设计如下:
第一种设计方案,使用assing赋值,三目元算符的方法:
/*
2023.7.20
二选一多路选择器设计,sel为0时out输出in_a的值,sel为1时out输出in_b的值
*/
module MUX_2_1 (
input wire in_a ,
input wire in_b ,
input wire sel ,
output wire out
);
//使用assign方法直接赋值,三目运算符
assign out = sel ? in_b : in_a;
endmodule //MUX_2_1
使用此方法所设计的电路图如下:
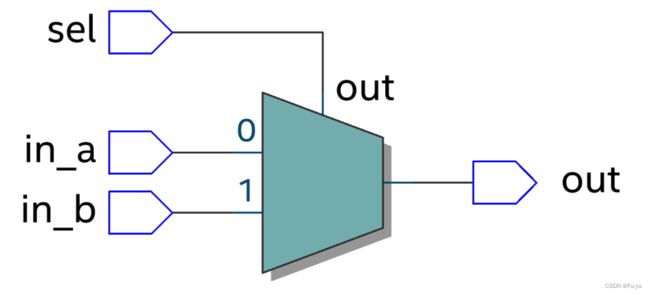
第二种方案使用always语句块,if-else的方法设计:
/*
2023.7.20
二选一多路选择器设计,sel为0时out输出in_a的值,sel为1时out输出in_b的值
*/
module MUX_2_1 (
input wire in_a ,
input wire in_b ,
input wire sel ,
output wire out
);
reg out_r;
// //使用always模块进行赋值
//if-else
always @(*) begin
if(sel) begin
out_r = in_b;
end
else begin
out_r = in_a;
end
end
assign out = out_r;
endmodule //MUX_2_1
使用此方法所设计的电路图如下:
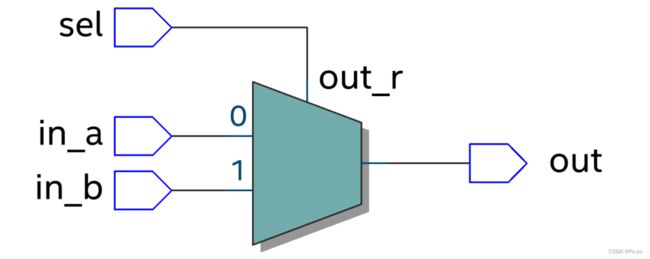
第三种设计方案,使用always语句块,case的方法设计:
/*
2023.7.20
二选一多路选择器设计,sel为0时out输出in_a的值,sel为1时out输出in_b的值
*/
module MUX_2_1 (
input wire in_a ,
input wire in_b ,
input wire sel ,
output wire out
);
reg out_r;
//case语句
always @( *) begin
case(sel)
0 : begin
out_r = in_a;
end
1 : begin
out_r = in_b;
end
default :;
endcase
end
assign out = out_r;
endmodule //MUX_2_1
使用此方法所设计的电路图如下:
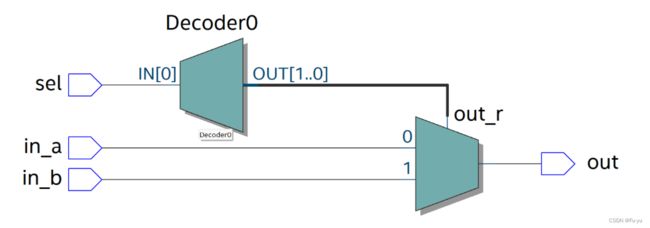
测试验证
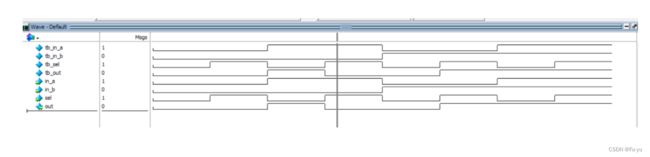
为验证所设计二选一多路选择器设计是否正确,我们通过编写测试仿真代码来验证:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module MUX_2_1_tb();
//激励信号定义
reg tb_in_a;
reg tb_in_b;
reg tb_sel;
//输出信号定义
wire tb_out;
//模拟输入
initial begin
tb_in_a = 0;
tb_in_b = 0;
tb_sel = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 0;
tb_in_b = 0;
tb_sel = 1;
#1;
tb_in_a = 1;
tb_in_b = 0;
tb_sel = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 1;
tb_in_b = 0;
tb_sel = 1;
#1;
tb_in_a = 0;
tb_in_b = 1;
tb_sel = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 0;
tb_in_b = 1;
tb_sel = 1;
#1;
tb_in_a = 1;
tb_in_b = 1;
tb_sel = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 1;
tb_in_b = 1;
tb_sel = 1;
#1;
end
//模块例化
MUX_2_1 u_MUX_2_1(
.in_a (tb_in_a) ,
.in_b (tb_in_b) ,
.sel (tb_sel) ,
.out (tb_out)
);
endmodule
通过观察仿真时序图可以发现,当sel信号为0时,out的输出值与in_a的值相同,当sel信号为1时,out的输出值与in_b的值相同,和我们预期所相符合。
三、四选一多路选择器设计
在刚才所做的二选一的多路选择器的基础上,设计一个新的四选一的多路选择器。
代码设计如下:
/*
2023.7.10
四选一多路选择器设计
*/
module MUX_4_1 (
input wire [3:0] in_a,//4位的输入
input wire [1:0] sel,//sel选择in_a哪一位的输出
output reg out
);
always @( *) begin
case (sel)
0 : begin
out = in_a[0];
end
1 : begin
out = in_a[1];
end
2 : begin
out = in_a[2];
end
3 : begin
out = in_a[3];
end
default :;
endcase
end
endmodule //MUX_4_1
测试文件:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module MUX_4_1_tb();
//输入信号
reg [3:0] tb_in_a;
reg [1:0] tb_seg;
//输出信号
wire tb_out;
//模块实例化
MUX_4_1 u_MUX_4_1(
. in_a (tb_in_a) ,
. sel (tb_seg) ,
. out (tb_out)
);
initial begin
tb_in_a = 4'b0001;//输出1
tb_seg = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b1000;//输出0
tb_seg = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b0100;//输出0
tb_seg = 0;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b1001;//输出0
tb_seg = 1;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b1110;//输出1
tb_seg = 1;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b0010;//输出1
tb_seg = 1;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b0011;//输出0
tb_seg = 2;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b0100;//输出1
tb_seg = 2;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b1011;//输出1
tb_seg = 3;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b0111;//输出0
tb_seg = 3;
#1;
tb_in_a = 4'b1100;//输出1
tb_seg = 3;
#1;
end
endmodule
通过仿真,观察波形图:
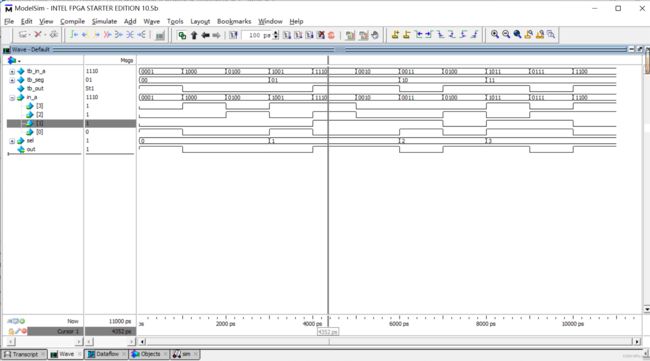
从图中可以观察到,当sel信号为0时,out的输出值与in_a[0]的值相同;当sel信号为1时,out的输出值与in_a[1]的值相同;当sel信号为2时,out的输出值与in_a[2]的值相同;当sel信号为3时,out的输出值与in_a[3]的值相同。