【算法与数据结构】222、LeetCode完全二叉树的节点个数
文章目录
- 一、题目
- 二、一般遍历解法
- 三、利用完全二叉树性质
- 四、完整代码
所有的LeetCode题解索引,可以看这篇文章——【算法和数据结构】LeetCode题解。
一、题目
二、一般遍历解法
思路分析:利用层序遍历,然后用num++记录节点数量。其他的例如递归法和迭代法也是如此。
层序遍历程序如下:
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int num = 0; // 节点数量
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // size必须固定, que.size()是不断变化的
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
num++;
if (node->left) que.push(node->left); // 空节点不入队
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return num;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
递归程序如下(这应该是最精简的版本了):
class Solution2 {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
return root == NULL ? 0 : countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};
三、利用完全二叉树性质
思路分析:完全二叉树具有一个特性,假设它的深度为K,它的节点个数在 [ 2 K − 1 − 1 , 2 K − 1 ] [2^{K-1}-1, 2^K-1] [2K−1−1,2K−1]之间,意味着它只有两种情况,一种是满二叉树,一种是最后一层叶子节点没有满。对于情况一可以用 2 K − 1 2^K-1 2K−1来计算,对于情况二分别递归其左子树和右子树,递归到一定深度一定有左子树或者右子树为满二叉树,然后按照情况一来计算。那么满二叉树的最左边节点和最右边节点的深度一定是相等的,依据这个特性判断子树是否为满二叉树。
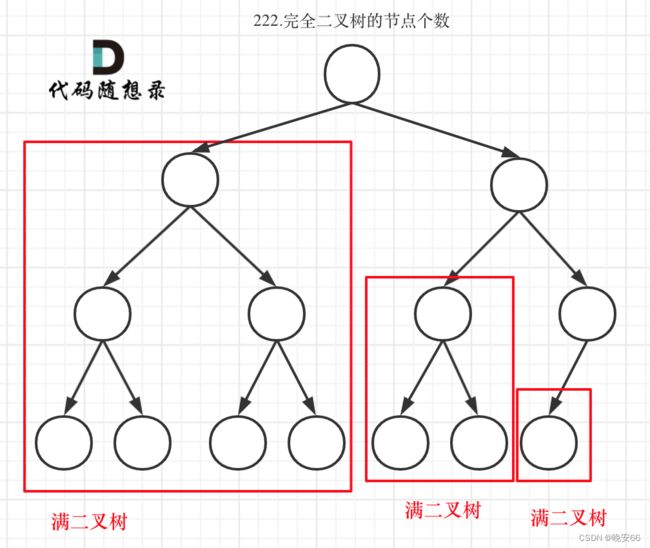
递归程序当中,我们要确定三个步骤,1、输入参数,返回值 2、递归终止条件 3、单层递归逻辑。输入参数为中间节点,返回值为左子树的节点数量+右子树节点数量+1(+1是加上中间节点)。当节点为空时,递归终止,返回0。每次递归我们都要计算最左/右边节点深度,然后判断二者是否相等,如果相等则是满二叉树,返回 2 K − 1 2^K-1 2K−1,K为深度。程序当中使用了左移运算符,因为运算符的优先级问题,记得加括号。左移运算符是二进制运算,计算机计算的更快。
程序如下:
class Solution3 {
public:
// 利用完全二叉树的性质,递归法
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int Ldepth = 0, Rdepth = 0;
while (left) { // 递归左子树
left = left->left;
Ldepth++;
}
while (right) { // 递归右子树
right = right->right;
Rdepth++;
}
if (Ldepth == Rdepth) {
return (2 << Ldepth) - 1; // <<为左移运算符(位运算符),相当于2*leftDepth,但二进制运算计算机算的更快
}
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
四、完整代码
# include end
