FFMPEG硬件编解码器使用
在前文《视频编解码硬件方案漫谈》中我们介绍硬件视频编解码的一般方案,本文我们进一步介绍音视频编解码如何在ffmpeg使用显卡硬件进行加速。
一、基本概况
ffmpeg对显卡厂家SDK进行封装和集成,实现部分的硬件编解码
| NVIDIA |
AMD |
INTEL |
|
| 编码器 |
xxx_nvenc |
xxx_amf |
xxxx_qsv |
| 解码器 |
xxx_ cuvid |
暂未实现 |
xxxx_qsv |
ffmpeg硬解编解码应用
其中xxx标识编码类型,如h264,h265,mpeg2,vp8,vp9等。其次在ffmpeg中软件编解码器可以实现相关硬解加速。如在h264解码器中可以使用cuda 加速,qsv加速,dxva2 加速,d3d11va加速,opencl加速等。
| cuda |
qsv |
dxva2/d3d11va |
opencl |
|
| 应用场景 |
适应NVIDIA显卡平台,但跨OS |
适应Intel显卡平台,但跨OS |
适用Windows OS,但跨硬件平台 |
仅仅支持opencl的硬件平台 |
二、命令行的使用
在ffmpeg中,如果使用-vcodec xxx 指定硬件编解码器,否则使用软件编解码。
如:
ffplay -x 800 -y 600 -vcodec h264_qsv h264.mp4
ffplay -x 800 -y 600 -vcodec hevc_qsv 4k_hevc.mp4
ffmpeg.exe -i test.ts -vcodec hevc_amf -s 1280x720 output.ts
二、代码中使用
1)使用特定的编解码器
任何一个编解码器包都是由AVCodec来描述的。其中ID代表一类编码器或解码。如:
AV_CODEC_ID_H264;代表是h264编解码器。而name代表某一个编码器或解码器。通常我们使用avcodec_find_decoder(ID)和avcodec_find_encoder(ID)来解码器和编码器。默认采用的软件编解码。如果我们需要使用硬件编解码,采用avcodec_find_encoder_by_name(name)和avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(name)来指定编码器。其他代码流程与软件编解码一致。
如:
//codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
codec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h264_cuvid");
if (!codec) {
fprintf(stderr, "Codec not found\n");
exit(1);
}
2)使用硬件加速
使用特定的编解码器好处就是跨操作系统,不论是Windows还是Linux都是一套代码,但缺点就是不跨硬件,不同显卡厂家采用不同编解码器。而基于软件编码器的硬件加速是跨硬件显卡的,如Windows d3d11va硬件加速,无论底层是AMD显卡还是Intel显卡还是nvidia显卡都适用,相当于windows 系统屏蔽了硬件细节,我们只需要调用windows的API实现即可。下面一个基于硬件加速的demo
static AVBufferRef* hw_device_ctx = NULL;
static enum AVPixelFormat hw_pix_fmt;
static FILE* output_file = NULL;
//硬件加速初始化
static int hw_decoder_init(AVCodecContext* ctx, const enum AVHWDeviceType type)
{
int err = 0;
//创建一个硬件设备上下文
if ((err = av_hwdevice_ctx_create(&hw_device_ctx, type,
NULL, NULL, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create specified HW device.\n");
return err;
}
ctx->hw_device_ctx = av_buffer_ref(hw_device_ctx);
return err;
}
//获取GPU硬件解码帧的格式
static enum AVPixelFormat get_hw_format(AVCodecContext* ctx,
const enum AVPixelFormat* pix_fmts)
{
const enum AVPixelFormat* p;
for (p = pix_fmts; *p != -1; p++) {
if (*p == hw_pix_fmt)
return *p;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to get HW surface format.\n");
return AV_PIX_FMT_NONE;
}
//解码后数据格式转换,GPU到CPU拷贝,YUV数据dump到文件
static int decode_write(AVCodecContext* avctx, AVPacket* packet)
{
AVFrame* frame = NULL, * sw_frame = NULL;
AVFrame* tmp_frame = NULL;
uint8_t* buffer = NULL;
int size;
int ret = 0;
ret = avcodec_send_packet(avctx, packet);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error during decoding\n");
return ret;
}
while (1) {
if (!(frame = av_frame_alloc()) || !(sw_frame = av_frame_alloc())) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can not alloc frame\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(avctx, frame);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) {
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_frame_free(&sw_frame);
return 0;
}
else if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error while decoding\n");
goto fail;
}
if (frame->format == hw_pix_fmt) {
/* 将解码后的数据从GPU内存存格式转为CPU内存格式,并完成GPU到CPU内存的拷贝*/
if ((ret = av_hwframe_transfer_data(sw_frame, frame, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error transferring the data to system memory\n");
goto fail;
}
tmp_frame = sw_frame;
}
else
tmp_frame = frame;
//计算一张YUV图需要的内存 大小
size = av_image_get_buffer_size((AVPixelFormat)tmp_frame->format, tmp_frame->width,
tmp_frame->height, 1);
//分配内存
buffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(size);
if (!buffer) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can not alloc buffer\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
//将图片数据拷贝的buffer中(按行拷贝)
ret = av_image_copy_to_buffer(buffer, size,
(const uint8_t* const*)tmp_frame->data,
(const int*)tmp_frame->linesize, (AVPixelFormat)tmp_frame->format,
tmp_frame->width, tmp_frame->height, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can not copy image to buffer\n");
goto fail;
}
//buffer数据dump到文件
if ((ret = fwrite(buffer, 1, size, output_file)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to dump raw data.\n");
goto fail;
}
fail:
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_frame_free(&sw_frame);
av_freep(&buffer);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
}
int main(int argc,char * argv[])
{
AVFormatContext* input_ctx = NULL;
int video_stream, ret;
AVStream* video = NULL;
AVCodecContext* decoder_ctx = NULL;
AVCodec* decoder = NULL;
AVPacket packet;
enum AVHWDeviceType type;
int i;
if (argc < 4) {
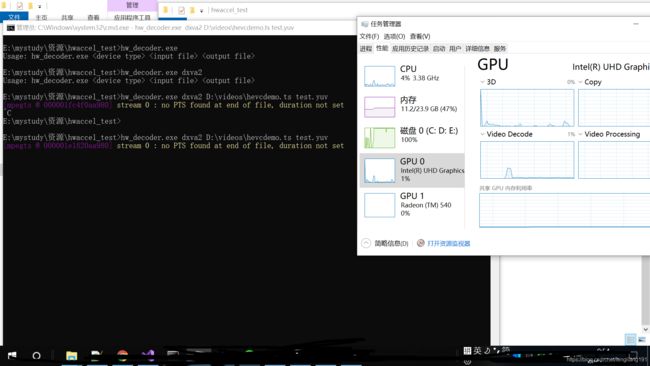
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s 编译后生成hw_decoder.exe,解码生成YUV文件如下:
hw_decoder.exe dxva2 D:\videos\hevcdemo.ts test.yuv
由此可见,GPU解码器有利用率,CPU占用率极低,硬件加速成功。
更多更详细的信息请关注微信公众号:AV_Chat