Flutter状态管理:RxDart
一、前言
- BLoC《Flutter状态管理:BLoC(Business Logic Component)》
- 编程概念《编程方式:命令式 vs 函数式》
二、StreamController增加版:Subject
其实无论从订阅或者变换都可以看出, Dart 中的 Stream 已经自带了类似 rx 的效果,但是为了让 rx 的用户们更方便的使用,ReactiveX 就封装了 rxdart 来满足用户的熟悉感,如下图所示为它们的对应关系:
| Dart | RxDart |
|---|---|
| StreamController | Subject |
| Stream | Observable |
在 rxdart 中, Observable 是一个 Stream,而 Subject 继承了 Observable 也是一个 Stream,并且 Subject 实现了 StreamController 的接口,所以它也具有 Controller 的作用。
如下代码所示是 rxdart 的简单使用,可以看出它屏蔽了外界需要对 StreamSubscription 和 StreamSink 等的认知,更符合 rx 历史用户的理解
final subject = PublishSubject();
subject.stream.listen(observerA);
subject.add("AAAA1");
subject.add("AAAA2"));
subject.stream.listen(observeB);
subject.add("BBBB1");
subject.close();
以上方代码为例:
- PublishSubject 内部实际创建是创建了一个广播 StreamController
.broadcast ; - 当我们调用 add 或者 addStream 时,最终会调用到的还是我们创建的 StreamController.add;
- 当我们调用 onListen 时,也是将回调设置到 StreamController 中。
- rxdart 在做变换时,我们获取到的 Observable 就是 this,也就是 PublishSubject 自身这个 Stream ,而 Observable 一系列的变换,也是基于创建时传入的 stream 对象,比如:
@override
Observable asyncMap(FutureOr convert(T value)) =>Observable(_stream.asyncMap(convert));
所以我们可以看出来,rxdart 只是对 Stream 进行了概念变换,变成了我们熟悉的对象和操作符,而这也是为什么 rxdart 可以在 StreamBuilder 中直接使用的原因。
RxDart提供了三种StreamController的变体来应用到不同的场景:
- PublishSubject
- BehaviorSubject
- ReplaySubject
以下来分别讲序这三种场景的使用情况。
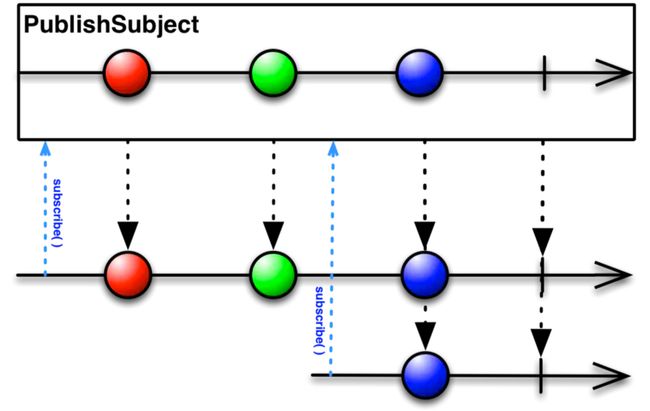
2.1、PublishSubject
PublishSubject最常见,从图中可看到,listener只能监听到订阅之后的事件:
final subject = PublishSubject();
subject.stream.listen((event) => print("observer1 => $event"));
subject.add(1);
subject.add(2);
subject.stream.listen((event) => print("observer2 => $event"));
subject.add(3);
subject.close();
// 打印输出:
// flutter: observer1 => 1
// flutter: observer2 => 3
// flutter: observer1 => 2
// flutter: observer1 => 3
2.2、BehaviorSubject
BehaviorSubject也是广播,与PublishSubject的区别是:它会返回订阅前的最后一次事件:
final subject = BehaviorSubject();
subject.stream.listen((event) => print("observer1 => $event"));
subject.add(1);
subject.add(2);
subject.stream.listen((event) => print("observer2 => $event"));
subject.add(3);
subject.close();
// 打印输出:
// flutter: observer1 => 1
// flutter: observer2 => 2
// flutter: observer2 => 3
// flutter: observer1 => 2
// flutter: observer1 => 3
2.3、ReplaySubject
顾名思义:回放!会将订阅前的事件都发送给新的订阅者:
final subject = ReplaySubject();
subject.stream.listen((event) => print("observer1 => $event"));
subject.add(1);
subject.add(2);
subject.stream.listen((event) => print("observer2 => $event"));
subject.add(3);
subject.close();
// 打印输出:
// flutter: observer1 => 1
// flutter: observer2 => 1
// flutter: observer2 => 2
// flutter: observer2 => 3
// flutter: observer1 => 2
// flutter: observer1 => 3
三、实战演练
3.1、新建Model(CountModel.dart)
import 'package:rxdart/rxdart.dart';
class CountModel {
BehaviorSubject _subject = BehaviorSubject.seeded(0);
get stream => _subject.stream;
get value => _subject.value;
increment() {
_subject.add(value + 1);
}
decrement() {
_subject.add(value - 1);
}
}
3.2、新建页面(RxdartPage.dart)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/model/CountModel.dart';
class RxdartPage extends StatelessWidget {
final CountModel _model = CountModel();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("RxdartPage"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
StreamBuilder(
stream: _model.stream,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
return Text("${snapshot.data}");
},
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _model.increment,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
3.3、修改main文件
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/RxdartPage.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter状态管理',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: RxdartPage(),
);
}
}
以上就是简单的局部状态管理的例子,至于全局共享,与BLoC类似,建个BLoC和Provider,再包裹MyApp就行。
Flutter状态管理:BLoC(Business Logic Component)
一、前言
占位
二、什么是BLoC?
BLoC只是一个概念(Reactive Programming,响应式编程),它是基于“dart:async”中的Stream、StreamController来实现的。
- 用StreamBuilder包裹有状态的部件,StreamBuilder将会监听一个流;
- 这个流来自于BLoC;
- 有状态小部件中的数据来自于监听的流;
- 用户交互手势被检测到,产生了事件。例如按了一下按钮;
- 调用bloc的功能来处理这个事件;
- 在bloc中处理完毕后将会吧最新的数据add进流的sink中;
- StreamBuilder监听到新的数据,产生一个新的snapshot,并重新调用build方法;
- Widget被重新构建;
BLoC能够允许我们完美的分离业务逻辑!再也不用考虑什么时候需要刷新屏幕了,一切交给StreamBuilder和BLoC! BLoC由来自Google的两位工程师 Paolo Soares和Cong Hui设计,并在2018年DartConf期间(2018年1月23日至24日)首次展示!
三、BLoC创建方式
创建方式有三种:
- 局部模式(类似 setState);
- 全局单例模式(单例模式);
- Scoped模式;
3.1、全局单例模式
全局单例模式并不推荐,原因在于:持久占用Stream而不会释放(dispose)
3.1.1、新建Model
// CountBloc.dart
import 'dart:async';
class CountBloc {
int _count = 0;
StreamController _controller;
Stream get count => _controller.stream;
CountBloc() {
_count = 0;
_controller = StreamController.broadcast();
}
void increment() {
_controller.sink.add(++_count);
}
void dispose() {
_controller.close();
}
}
CountBloc bloc = CountBloc();
3.1.2、新建两个页面(BlocPage和BlocPageTwo)
// BlocPage.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/bloc/models/CountBloc.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/BlocPageTwo.dart';
class BlocPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("BlocPage"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
StreamBuilder(
stream: bloc.count,
initialData: 0,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
return Text("${snapshot.data}");
}),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).push(MaterialPageRoute(builder: (BuildContext context) {
return BlocPageTwo();
}));
},
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
// BlocPageTwo.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/bloc/models/CountBloc.dart';
class BlocPageTwo extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("BlocPageTwo"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
StreamBuilder(
stream: bloc.count,
initialData: 0,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
return Text("${snapshot.data}");
}),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
bloc.increment();
},
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
3.1.3、修改main文件
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/BlocPage.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter状态管理',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: BlocPage(),
);
}
}
3.2、Scoped模式
推荐这种模式!该方式类似Provider。
3.2.1、新建Model
import 'dart:async';
class CountBloc {
int _count = 0;
StreamController _controller;
Stream get count => _controller.stream;
CountBloc() {
_count = 0;
_controller = StreamController.broadcast();
}
void increment() {
_controller.sink.add(++_count);
}
void dispose() {
_controller.close();
}
}
3.2.2、新建两个页面(BlocPage和BlocPageTwo)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/bloc/providers/CountProvider.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/BlocPageTwo.dart';
class BlocPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
final _bloc = CountProvider.of(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("BlocPage"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
StreamBuilder(
stream: _bloc.count,
initialData: 0,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
return Text("${snapshot.data}");
}),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).push(MaterialPageRoute(builder: (BuildContext context) {
return BlocPageTwo();
}));
},
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/bloc/providers/CountProvider.dart';
class BlocPageTwo extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
final _bloc = CountProvider.of(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("BlocPageTwo"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
StreamBuilder(
stream: _bloc.count,
initialData: 0,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
return Text("${snapshot.data}");
}),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
_bloc.increment();
},
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
3.2.3、修改main文件
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/bloc/providers/CountProvider.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/BlocPage.dart';
void main() {
runApp(CountProvider(child: MyApp()));
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter状态管理',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: BlocPage(),
);
}
}
四、总结
我们发现,BLoC 和 ScopedModel / Provider 在跨页面间共享数组,
- 相同点:
- 都需要在顶层包一层(即包裹 MaterialApp);
- 包裹的这一层实际是继承于 InheritedWidget ;
- 不同点在于Model:
- ScopedModel / Provider 的 Model 是继承于 Listenable,且需要主动调用 notifyListeners;
- BLoC 的 Model 是通过 StreamController / Stream / Sink / StreamBuilder 的方式来异步刷新;
- 三者 Model 都可以类似 extends / mixins 方式,将多个 Model / Provider 全并起来做全局共享,
然而,因为 BLoC 是基于 Stream方式,当观察的 Model 数量太多时,性能可能会急剧下降;
下篇会讲到 Redux ,它是一个很优秀的全局共享解决方案,可以考虑 全局redux + 局部bloc(rxdart) 管理方案!
Flutter状态管理:Redux
二、Redux介绍
有做过H5前端开发的朋友应该很早就接触过这个,Redux在React/VUE中,与在Flutter/Dart中概念一样,没有任何区别;唯一的区别只是使用上的不同。
一句话来介绍Redux:Redux是前端流行的,一种单向(unidirectional)数据流架构!
它主要由三部分组成:
- Store: 它是整个数据的仓库,存储State对象,管理着整个应用的状态;
- Reducer:处理与分发事件的方法,通过返回新的State来更新Store;
- Action: 行为(也可以理解为事件),action将会分发至对应的reducer中;
下图是一个完整的数据触发及更新流程:
- View产生Action(传递事件类型及数据);
- Redux将Action 派发(dispatch)至对应的 Reducer;
- Reducer根据Action的类型,处理完后返回一个全新的 State 至 Store;
- Store收到新的State后将来通知相应的监听者(View)更新;
我们看到上面整个数据流,都是单向的,由View发起,最后到View的更新;
为啥这样设计?
- 单一数据源:整个应用的状态都在一个Store中;
- 状态只读: 无法直接修改Store中的数据,只能通过action -> reducer来完成;
- 纯函数改变:reducer就是一个纯函数,只处理逻辑并返回全新的State;
三、Redux之Middleware
小节二介绍了Redux最基本的原理,但是,如何用Redux来做一些异步操作,比如:加载数据、请求API等?这里就引出来了Redux的中间件(Middleware),中间件能够让我们使得action在到达reducer之前,做些其它“动作”!有了中间件,我们不但可以请求API,还可以改变action,使得分发到其它reducer中去;
上图是有Middleware的流程图。
四、引入Redux相关的第三方库
// pubspec.yaml
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
redux: ^4.0.0+3
flutter_redux: ^0.6.0
- redux:基础库,包含了Store、Reducer和Middleware;
- flutter_redux:用于Flutter的封装好的库(类似React中的react-redux):
- StoreProvider:用于整个APP顶层,提供给所有的Widgets所需的Store;
- StoreBuilder: 接收Store的变化通知;
- StoreConnector:可替代StoreBuilder,能够将Store转成ViewModel;
五、Redux使用方式
Redux在Flutter中的使用与在JavaScript中的使用方式稍微有点不同,为啥?
因为JavaScript是弱类型语言,而Dart是强类型语言,这就使得在JS中每个reducer可以独立管理,而在Flutter中需要由一个大对象来管理!
5.1、目录结构
无论在JS中还是在Flutter中,通常都将action、reducer、store各自建一目录,放在redux目录下,目录结构如下:
.src
|-- pages/
|-- redux/
|-- actions/
|-- XxxAction.dart
|-- YyyAction.dart
|-- reducers/
|-- XxxReducer.dart
|-- YyyReducer.dart
|-- index.dart // App整个的reducers
|-- states/ //(Flutter中需要,JS不需要)
|-- XxxState.dart
|-- YyyState.dart
|-- index.dart // App整个的状态对象
|-- store/
|-- index.dart // App整个的store
|-- main.dart
5.2、创建Action
// CountAction.dart
class SetCountAction {
final int value;
SetCountAction(this.value);
}
class IncrementCountAction {}
class DecrementCountAction {}
// FirstAction.dart
class SetFirstAction {
final String value;
SetFirstAction(this.value);
}
5.3、创建State
// CountState.dart
class CountState {
final int count;
CountState(this.count);
}
// FirstState.dart
class FirstState {
String title;
FirstState(this.title);
}
// index.dart (App整个的State大对象)
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/CountState.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/FirstState.dart';
class AppState {
final FirstState firstState;
final CountState countState;
AppState(this.firstState, this.countState);
}
5.4、创建Reducer
// CountReducer.dart
import 'package:redux/redux.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/actions/CountAction.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/CountState.dart';
// 以下用两种方式创建 reducer
// 1. 基本的 switch-case
// 2. 使用 combineReducers + TypedReducer
//CountState countReducer(state, action) {
// switch (action.runtimeType) {
// case IncrementCountAction:
// return CountState(state.count + 1);
//
// case DecrementCountAction:
// return CountState(state.count - 1);
//
// case SetCountAction:
// return CountState((action as SetCountAction).value);
//
// default:
// return state;
// }
//}
// 使用 combineReducers 避免写 switch-case
// TypedReducer 的作用就是将 Function 与 Action 关联
final countReducer = combineReducers([
TypedReducer(_increment),
TypedReducer(_decrement),
TypedReducer(_set),
]);
CountState _increment(state, action) => CountState(state.count + 1);
CountState _decrement(state, action) => CountState(state.count - 1);
CountState _set(state, SetCountAction action) => CountState(action.value);
// FirstReducer
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/actions/FirstAction.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/FirstState.dart';
FirstState firstReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.runtimeType) {
case SetFirstAction:
return FirstState((action as SetFirstAction).value);
default:
return state;
}
}
// index.dart
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/reducers/CountReducer.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/reducers/FirstReducer.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/index.dart';
AppState reducers(AppState state, action) {
return AppState(
firstReducer(state.firstState, action),
countReducer(state.countState, action),
);
}
5.5、创建Store
// index.dart
import 'package:redux/redux.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/reducers/index.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/CountState.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/FirstState.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/index.dart';
final store = Store(
reducers,
initialState: AppState(
FirstState(null),
CountState(0),
),
);
5.6、新建两个页面(ReduxPage和ReduxPage2)
ReduxPage在build中,也可以直接用StoreBuilder(参考ReduxPage2中写法),因为StoreBuilder也是InheritedWidget。
// ReduxPage.dart
import 'dart:math';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_redux/flutter_redux.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/ReduxPage2.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/actions/CountAction.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/actions/FirstAction.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/CountState.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/index.dart';
class ReduxPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("ReduxPage")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
StoreConnector(
converter: (store) {
return store.state.countState;
},
builder: (context, state) {
return Text("${state.count}");
},
)
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: StoreBuilder(
builder: (context, store) {
return Row(
children: [
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => store.dispatch(IncrementCountAction()),
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
heroTag: 'Increment',
),
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => store.dispatch(DecrementCountAction()),
tooltip: 'Decrement',
child: Icon(Icons.close),
heroTag: 'Decrement',
),
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => store.dispatch(SetCountAction(100)),
tooltip: 'Set',
child: Icon(Icons.settings),
heroTag: 'Set',
),
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => store.dispatch(SetFirstAction("chris's age = ${Random().nextInt(100)}")),
tooltip: 'First',
child: Icon(Icons.event),
heroTag: 'First',
),
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).push(MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) {
return ReduxPage2();
}));
},
tooltip: 'NextPage',
child: Icon(Icons.message),
heroTag: 'NextPage',
)
],
);
},
),
);
}
}
// ReduxPage2.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_redux/flutter_redux.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/index.dart';
class ReduxPage2 extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return _body(context);
}
Widget _body(BuildContext context) {
return StoreBuilder(
builder: (context, store) => Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("${store.state.firstState.title}"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
Text("${store.state.countState.count}")
],
),
),
),
);
}
}
5.7、修改main文件
// main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_redux/flutter_redux.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/pages/ReduxPage.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/states/index.dart';
import 'package:stateresearch/redux/store/index.dart';
void main() {
runApp(StoreProvider(store: store, child: MyApp()));
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter状态管理',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: ReduxPage(),
);
}
}
六、总结
正因为Redux在Flutter中与在JS中不同,因此,在Flutter中,建议:
- 如果只是局部使用,不涉及到跨 widget / page 共享,那么最好不要使用 Redux;
- 相反,Redux 只放全局共享数据 (毕竟是大对象);