Android开发之Fragment动态添加与管理
文章目录
- 主界面布局资源
- 两个工具Fragment
- 主程序
主界面布局资源
在activity_main.xml中,声明两个按钮备用,再加入一个帧布局,待会儿用来展示Fragment。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:text="@string/push"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:text="@string/replace"/>
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/framelayout"
android:background="@color/purple_200"/>
LinearLayout>
两个工具Fragment
用来展示的Fragment,随便找两个AS预设的即可,这里使用的是一个BlankFragment和一个ItemFragment。
BlankFragment:
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".BlankFragment1">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/hello_blank_fragment" />
FrameLayout>
package com.example.dynamicfragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* A simple {@link Fragment} subclass.
* Use the {@link BlankFragment1#newInstance} factory method to
* create an instance of this fragment.
*/
public class BlankFragment1 extends Fragment {
// TODO: Rename parameter arguments, choose names that match
// the fragment initialization parameters, e.g. ARG_ITEM_NUMBER
private static final String ARG_PARAM1 = "param1";
private static final String ARG_PARAM2 = "param2";
// TODO: Rename and change types of parameters
private String mParam1;
private String mParam2;
public BlankFragment1() {
// Required empty public constructor
}
/**
* Use this factory method to create a new instance of
* this fragment using the provided parameters.
*
* @param param1 Parameter 1.
* @param param2 Parameter 2.
* @return A new instance of fragment BlankFragment1.
*/
// TODO: Rename and change types and number of parameters
public static BlankFragment1 newInstance(String param1, String param2) {
BlankFragment1 fragment = new BlankFragment1();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString(ARG_PARAM1, param1);
args.putString(ARG_PARAM2, param2);
fragment.setArguments(args);
return fragment;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
if (getArguments() != null) {
mParam1 = getArguments().getString(ARG_PARAM1);
mParam2 = getArguments().getString(ARG_PARAM2);
}
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_blank1, container, false);
}
}
ItemFragment:
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/list"
android:name="com.example.dynamicfragment.ItemFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
app:layoutManager="LinearLayoutManager"
tools:context=".ItemFragment"
tools:listitem="@layout/fragment_item" />
package com.example.dynamicfragment;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.GridLayoutManager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import com.example.dynamicfragment.placeholder.PlaceholderContent;
/**
* A fragment representing a list of Items.
*/
public class ItemFragment extends Fragment {
// TODO: Customize parameter argument names
private static final String ARG_COLUMN_COUNT = "column-count";
// TODO: Customize parameters
private int mColumnCount = 1;
/**
* Mandatory empty constructor for the fragment manager to instantiate the
* fragment (e.g. upon screen orientation changes).
*/
public ItemFragment() {
}
// TODO: Customize parameter initialization
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static ItemFragment newInstance(int columnCount) {
ItemFragment fragment = new ItemFragment();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putInt(ARG_COLUMN_COUNT, columnCount);
fragment.setArguments(args);
return fragment;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
if (getArguments() != null) {
mColumnCount = getArguments().getInt(ARG_COLUMN_COUNT);
}
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_item_list, container, false);
// Set the adapter
if (view instanceof RecyclerView) {
Context context = view.getContext();
RecyclerView recyclerView = (RecyclerView) view;
if (mColumnCount <= 1) {
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(context));
} else {
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new GridLayoutManager(context, mColumnCount));
}
recyclerView.setAdapter(new MyItemRecyclerViewAdapter(PlaceholderContent.ITEMS));
}
return view;
}
}
主程序
在主程序里,我们要实现点击按钮显示不同的Fragment。这里使用一种新的实现按钮方式,在声明MainActivity类的时候引用View.OnClickListener接口,然后在button1.setOnClickListener(this);中传入this,这样按钮被点击时就会自动调用后面写的OnClick函数。
在OnClick函数被调用时,我们判断是哪一个按钮被点击了,然后根据按钮ID将不同的Fragment展现在帧布局上。
package com.example.dynamicfragment;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment;
import androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager;
import androidx.fragment.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button1 = findViewById(R.id.button1);
Button button2 = findViewById(R.id.button2);
button1.setOnClickListener(this);
button2.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()){
case R.id.button1:
replaceFragment(new BlankFragment1());
break;
case R.id.button2:
replaceFragment(new ItemFragment());
break;
}
}
private void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.framelayout, fragment);//创建replace事件
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
transaction.commit();//执行transaction中的事件
}
}
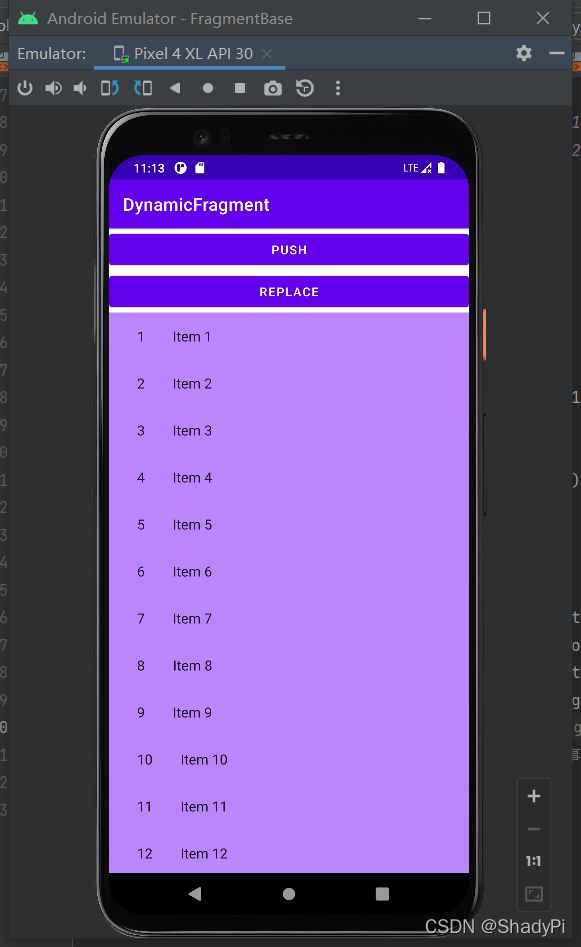
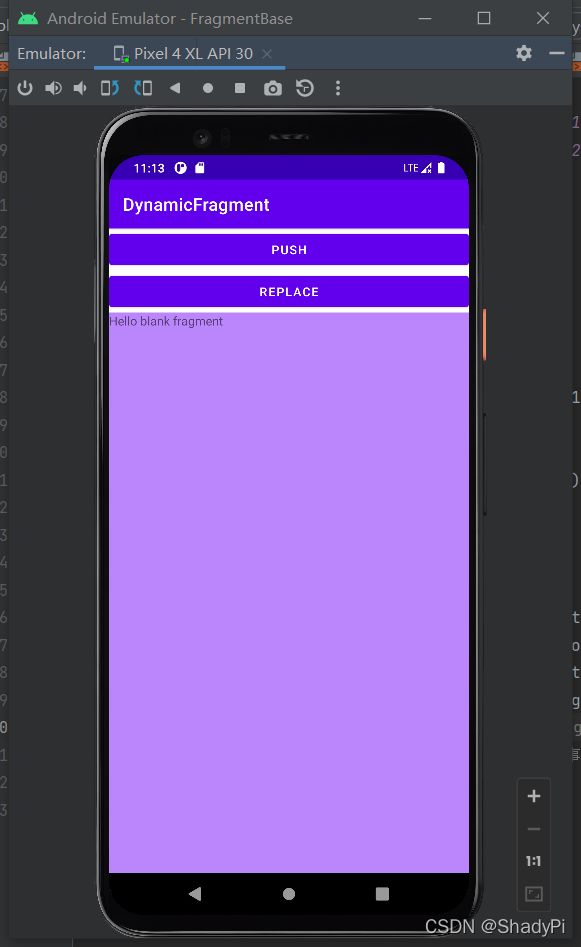
还需要重点讲解一下的是replaceFragment函数中的栈,transaction.addToBackStack(null);中的null指代的是默认栈。加入该语句后,每次更新都会向栈中加入一个Fragment,且屏幕上显示的即是栈顶的Fragment。当我们点击返回按钮时,栈顶的Fragment被弹出,屏幕上显示下一个Fragment。
试验如下,交替点击两个按钮若干次,屏幕上会依次出现两个Fragment交替覆盖,而点击返回按钮后,最顶上Fragment则会被撤除。