基于 OpenVINO 的目标识别
YOLOV5原理
YOLOv5是一种快速高效的目标检测算法,具有优秀的实时性能和较高的准确度。该算法利用深度学习技术实现了端到端的目标检测,在计算资源有限的情况下也能够获得出色的表现
YOLOv5采用了一种基于Anchor的检测方式,在输入图像中通过预先定义的Anchor尺寸进行目标检测。相比于传统的滑动窗口方法,该方法能够在不同尺度的特征图上同时进行目标检测,大大提升了检测效率和准确度
在算法实现方面,YOLOv5采用了轻量级网络结构和多尺度训练策略。具体来说,该算法使用了CSPDarknet53作为主干网络,采用了Bottleneck残差块和SPP模块等技术,进一步加强了网络的表示能力和感受野。此外,该算法还引入了多尺度训练策略,通过在不同尺度的图像上训练模型,使模型能够更好地适应不同场景下的目标检测任务
除了算法本身的优化,YOLOv5还采用了一系列技术手段来提高算法的性能和鲁棒性。例如,使用Mish激活函数代替传统的ReLU激活函数,可以有效避免梯度消失问题;使用DropBlock正则化方法可以提高模型的泛化能力和抗过拟合能力;使用AutoAugment数据增强技术可以增加数据的多样性,进一步提高模型的准确度和鲁棒性
总之,YOLOv5是一种快速高效、准确度较高的目标检测算法,通过采用端到端的检测方式、基于Anchor的检测方式、轻量级网络结构和多尺度训练策略等优化措施,成功地实现了在计算资源有限的情况下高效地完成目标检测任务
环境安装
pip install labelimg
pip install openvino-dev[onnx,tensorflow]==2022.2.0
pip install paddle2onnx==1.0.5 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
pip install tensorflow-gpu==2.7.0
pip install paddlepaddle数据处理
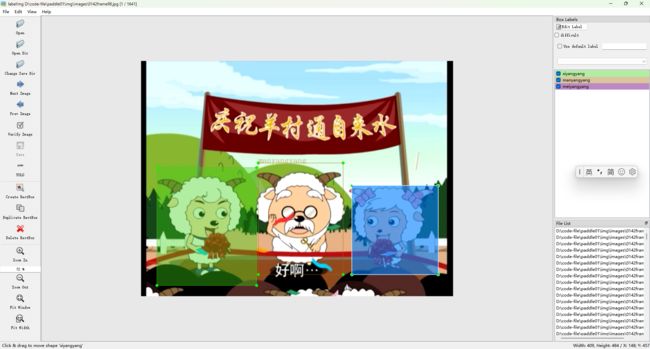
这里我们选择的分类数据是《喜羊羊与灰太狼》其中的七个角色,标签名称设置如下:
meiyangyang
xiyangyang
feiyangyang
lanyangyang
huitailang
manyangyang
hongtailang这里我们采用了1432张图片进行训练,使用 LabelImg 开始打标签:
当我们把所有的标签全部处理完成之后,我们就可以进行数据格式处理:
首先我们进入到 yolo 文件夹下:
mask 中存储刚我们处理过的图片和信息:
当我们完成这一步之后就可以开始数据处理了,首先我们在当前目录下打开 CMD,直接运行 gen.py
然后进入如下路径运行以下命令:
python yolov5_2_coco.py --dir_path dataset/YOLOV5环境搭建
我们在 paddle 新建一个环境,将生成的数据打包上传到 paddle 云端即可,并同时在 github 中下载 PaddleYOLO 一同进行上传
我们需要将数据放到 dataset 路径下:
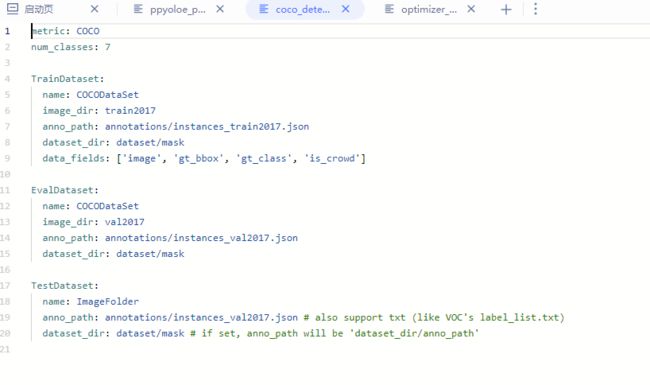
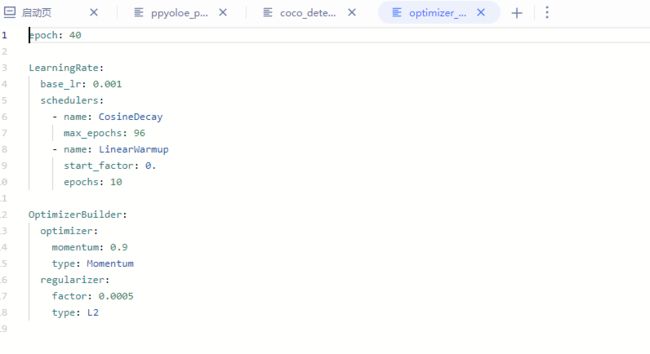
然后我们需要修改我们的配置文件:
数据训练
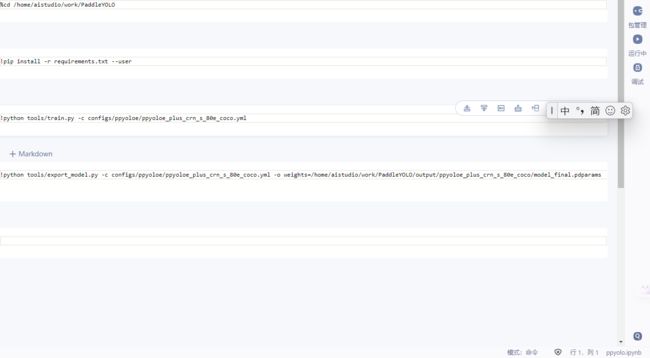
这里我们修改了训练的轮数和数据分类数,然后在最开始的路径下新建一个 notebook 文件运行如下代码:
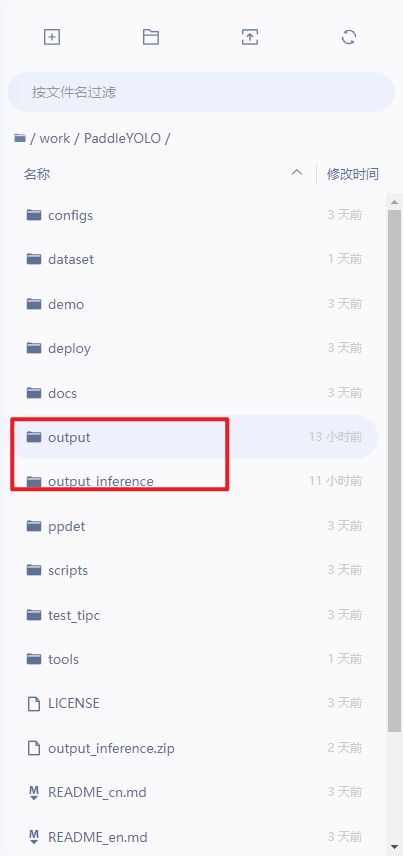
当我们全部运行结束后,会生成这两个文件夹:
这里我们子需要下载以下文件夹即可:
这里我们下载好解压出来即可
模型处理
这里我们需要将我们下载的文件放到如下目录中:
由于我们训练出来的模型并不能直接使用,所以我们按照顺序执行如下代码即可:
python prune_paddle_model.py --model_dir ppyoloe_crn_s_80 --model_filename model.pdmodel --params_filename model.pdiparams --output_names tmp_16 concat_14.tmp_0 --save_dir export_model
paddle2onnx --model_dir export_model --model_filename model.pdmodel --params_filename model.pdiparams --input_shape_dict "{'image':[1,3,640,640]}" --opset_version 11 --save_file ppyoloe_crn_s_80.onnx
mo --input_model ppyoloe_crn_s_80.onnx这样我们就得到了我们需要的模型:
我们将这两个模型文件与我们的代码文件放到我们的 jupyter notebook 路径下引入即可:
然后我们直接运行代码即可,代码如下:
from openvino.runtime import Core
import openvino.runtime as ov
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import paddle.fluid as fluid
# OpenVINO 模型推理器
class Predictor:
"""
OpenVINO 模型推理器
"""
def __init__(self, model_path):
ie_core = Core()
model = ie_core.read_model(model=model_path)
self.compiled_model = ie_core.compile_model(model=model, device_name="CPU")
def get_inputs_name(self, num):
return self.compiled_model.input(num)
def get_outputs_name(self, num):
return self.compiled_model.output(num)
def predict(self, input_data):
return self.compiled_model([input_data])
def get_request(self):
return self.compiled_model.create_infer_request()
# 图像预处理
def process_image(input_image, size):
"""输入图片与处理方法,按照PP-Yoloe模型要求预处理图片数据
Args:
input_image (uint8): 输入图片矩阵
size (int): 模型输入大小
Returns:
float32: 返回处理后的图片矩阵数据
"""
max_len = max(input_image.shape)
img = np.zeros([max_len,max_len,3],np.uint8)
img[0:input_image.shape[0],0:input_image.shape[1]] = input_image # 将图片放到正方形背景中
img = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR转RGB
img = cv.resize(img, (size, size), cv.INTER_NEAREST) # 缩放图片
img = np.transpose(img,[2, 0, 1]) # 转换格式
img = img / 255.0 # 归一化
img = np.expand_dims(img,0) # 增加维度
return img.astype(np.float32)
# 图像后处理
def process_result(box_results, conf_results):
"""按照PP-Yolove模型输出要求,处理数据,非极大值抑制,提取预测结果
Args:
box_results (float32): 预测框预测结果
conf_results (float32): 置信度预测结果
Returns:
float: 预测框
float: 分数
int: 类别
"""
conf_results = np.transpose(conf_results,[0, 2, 1]) # 转置
# 设置输出形状
box_results =box_results.reshape(8400,4)
conf_results = conf_results.reshape(8400,2)
scores = []
classes = []
boxes = []
for i in range(8400):
conf = conf_results[i,:] # 预测分数
score = np.max(conf) # 获取类别
# 筛选较小的预测类别
if score > 0.5:
classes.append(np.argmax(conf))
scores.append(score)
boxes.append(box_results[i,:])
scores = np.array(scores)
boxes = np.array(boxes)
result_box = []
result_score = []
result_class = []
# 非极大值抑制筛选重复的预测结果
if len(boxes) != 0:
# 非极大值抑制结果
indexs = tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes,scores,len(scores),0.25,0.35)
for i, index in enumerate(indexs):
result_score.append(scores[index])
result_box.append(boxes[index,:])
result_class.append(classes[index])
# 返回结果
return np.array(result_box),np.array(result_score),np.array(result_class)
# 画出预测框
def draw_box(image, boxes, scores, classes, labels):
"""将预测结果绘制到图像上
Args:
image (uint8): 原图片
boxes (float32): 预测框
scores (float32): 分数
classes (int): 类别
lables (str): 标签
Returns:
uint8: 标注好的图片
"""
colors = [(0, 0, 255), (0, 255, 0)]
scale = max(image.shape) / 640.0 # 缩放比例
if len(classes) != 0:
for i in range(len(classes)):
box = boxes[i,:]
x1 = int(box[0] * scale)
y1 = int(box[1] * scale)
x2 = int(box[2] * scale)
y2 = int(box[3] * scale)
label = labels[classes[i]]
score = scores[i]
cv.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), colors[classes[i]], 2, cv.LINE_8)
cv.putText(image,label+":"+str(score),(x1,y1-10),cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.55, colors[classes[i]], 2)
return image
# 读取标签
def read_label(label_path):
with open(label_path, 'r') as f:
labels = f.read().split()
return labels
# 同步推理
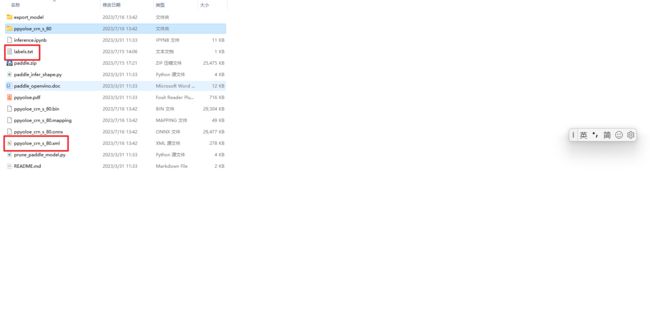
label_path = "labels.txt"
yoloe_model_path = "ppyoloe_crn_s_80.xml"
predictor = Predictor(model_path = yoloe_model_path)
boxes_name = predictor.get_outputs_name(0)
conf_name = predictor.get_outputs_name(1)
labels = read_label(label_path=label_path)
cap = cv.VideoCapture(0)
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
frame = cv.flip(frame, 180)
cv.namedWindow("MaskDetection", 0) # 0可调大小,注意:窗口名必须imshow里面的一窗口名一直
cv.resizeWindow("MaskDetection", 640, 480) # 设置长和宽
input_frame = process_image(frame, 640)
results = predictor.predict(input_data=input_frame)
boxes, scores, classes = process_result(box_results=results[boxes_name], conf_results=results[conf_name])
result_frame = draw_box(image=frame, boxes=boxes, scores=scores, classes=classes, labels=labels)
cv.imshow('MaskDetection', result_frame)
key = cv.waitKey(1)
if key == 27: #esc退出
break
cap.release()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
# 异步推理
label_path = "labels.txt"
yoloe_model_path = "ppyoloe_crn_s_80.xml"
predictor = Predictor(model_path = yoloe_model_path)
input_layer = predictor.get_inputs_name(0)
labels = read_label(label_path=label_path)
cap = cv.VideoCapture(0)
curr_request = predictor.get_request()
next_request = predictor.get_request()
ret, frame = cap.read()
curr_frame = process_image(frame, 640)
curr_request.set_tensor(input_layer, ov.Tensor(curr_frame))
curr_request.start_async()
while cap.isOpened():
ret, next_frame = cap.read()
next_frame = cv.flip(next_frame, 180)
cv.namedWindow("MaskDetection", 0) # 0可调大小,注意:窗口名必须imshow里面的一窗口名一直
cv.resizeWindow("MaskDetection", 640, 480) # 设置长和宽
in_frame = process_image(next_frame, 640)
next_request.set_tensor(input_layer, ov.Tensor(in_frame))
next_request.start_async()
if curr_request.wait_for(-1) == 1:
boxes_name = curr_request.get_output_tensor(0).data
conf_name = curr_request.get_output_tensor(1).data
boxes, scores, classes = process_result(box_results=boxes_name, conf_results=conf_name)
frame = draw_box(image=frame, boxes=boxes, scores=scores, classes=classes, labels=labels)
cv.imshow('MaskDetection', frame)
frame = next_frame
curr_request, next_request = next_request, curr_request
key = cv.waitKey(1)
if key == 27: #esc退出
break
cap.release()
cv.destroyAllWindows()这里同步推理和异步推理我们只需要使用一个即可
最后我们的运行效果如下: