Letcode-Top 100链表专题
《链表专题》
1.简单 合并两个有序链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// 首先新建一个链表
ListNode newList = new ListNode(0);
ListNode pre = newList;
if(list1==null){
newList.next = list2;
}
if(list2==null){
newList.next = list1;
}
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<list2.val){
newList.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
newList.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
newList = newList.next;
}
if(list1!=null){
newList.next = list1;
}
if(list2!=null){
newList.next = list2;
}
return pre.next;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}else if(list2==null){
return list1;
}else if(list1.val>list2.val){
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}else{
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
}
}
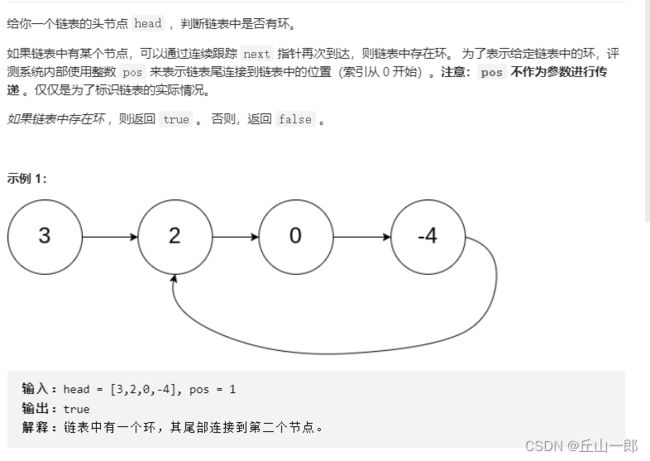
2. 简单 环形链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
int count = 0;
while(count<100000&&head!=null){
head = head.next;
count++;
}
return count<100000?false:true;
}
}
2.快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
3.HashSet特性
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while(head!=null){
if(!set.add(head)){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
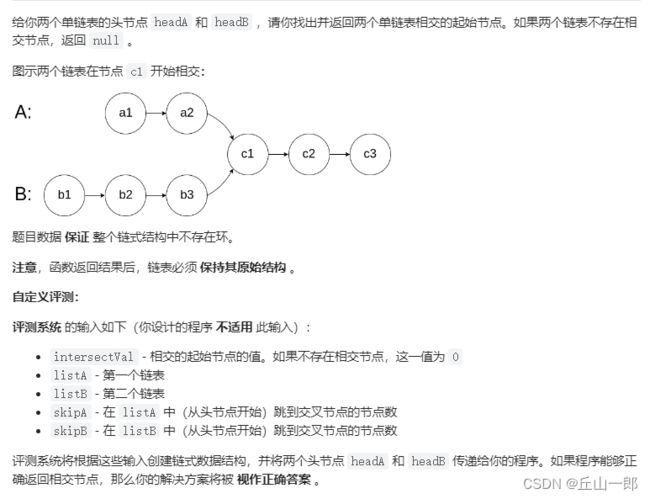
3. 简单 相交链表
1.经典写法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while(a!=null){
countA++;
a = a.next;
}
while(b!=null){
countB++;
b = b.next;
}
int result = Math.abs(countA-countB);
if(countA>countB){
for(int i=0;i<result;i++){
headA = headA.next;
}
}
if(countA<countB){
for(int i=0;i<result;i++){
headB = headB.next;
}
}
while(headA!=null&&headB!=null){
if(headB==headA){
return headA;
}
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
2.使用Set集合
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while(headA!=null){
set.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while(headB!=null){
if(set.contains(headB)){
return headB;
}
headB= headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
while(pA!=pB){
pA = (pA == null?headB:pA.next);
pB = (pB == null?headA:pB.next);
}
return pA;
}
}
4. 简单 反转链表
1.头插法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curNode = head;
while(curNode!=null){
ListNode temp = curNode.next;
curNode.next = newhead.next;
newhead.next = curNode;
curNode = temp;
}
return newhead.next;
}
}
2.迭代插入法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre =cur ;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
5. 简单 回文链表
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public static boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
int totalCount = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
totalCount++;
cur = cur.next;
}
if(totalCount<2){
return true;
}
// 判断奇偶
if(totalCount%2==0){
int i = 0;
while(head!=null){
if(i<(totalCount/2)){
stack.push(head);
}else{
ListNode temp = stack.pop();
if(head.val!=temp.val){
return false;
}
}
head = head.next;
i++;
}
}else if(totalCount%2==1){
int i = 0;
while(head!=null){
if(i<(totalCount/2)){
stack.push(head);
}else if(i==totalCount/2){
// 不用处理
}else{
ListNode temp = stack.pop();
if(head.val!=temp.val){
return false;
}
}
head = head.next;
i++;
}
}
return true;
}
}
2.精简版本的栈
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public static boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while(head!=null){
if(head.val!=stack.pop().val){
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
}
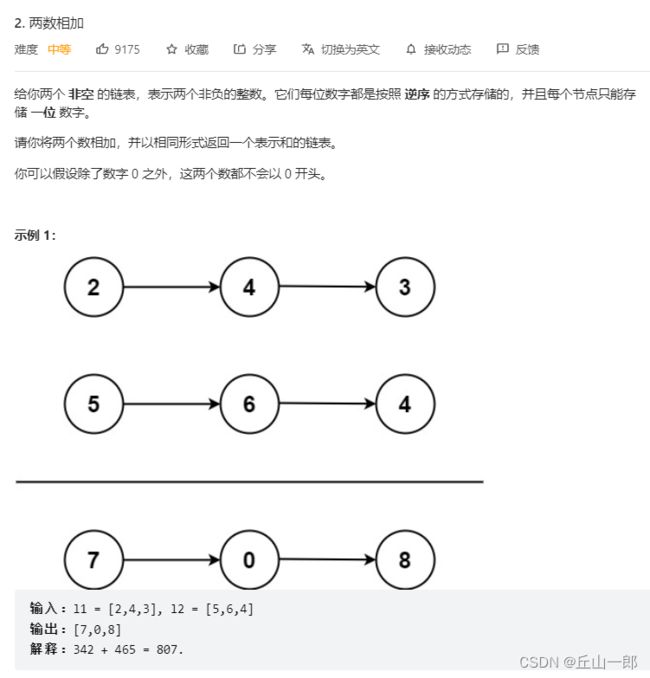
6. 中等 链表相加
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// 循环获取数据
ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
ListNode resultNode = node;
ListNode ll1 = l1;
ListNode ll2 = l2;
int high = 0;
int low = 0;
int sum = 0;
while(ll1!=null||ll2!=null){
if(ll1!=null&&ll2!=null){
sum = ll1.val + ll2.val + high;
}
if(ll1==null&&ll2!=null){
sum = ll2.val + high;
}
if(ll1!=null&&ll2==null){
sum = ll1.val + high;
}
if(ll1==null&&ll2==null){
sum = 0 + high;
}
if(ll1!=null){
ll1=ll1.next;
}
if(ll2!=null){
ll2=ll2.next;
}
high = sum/10;
low = sum%10;
ListNode tempNode = new ListNode(low);
resultNode.next = tempNode;
resultNode = resultNode.next;
}
if(high>0){
ListNode tempNode = new ListNode(high);
resultNode.next = tempNode;
resultNode = resultNode.next;
}
return node.next;
}
}
7 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
// 先统计链表的数量
ListNode node = head;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);
newHead.next = head;
ListNode newNode = newHead;
int total = 0;
while(node!=null){
total++;
node = node.next;
}
if(total==0){
return head;
}
for(int i=0;i<total-n;i++){
newHead = newHead.next;
}
newHead.next = newHead.next.next;
return newNode.next;
}
}
2.快慢指针,快指针先走k步
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 快慢指针
// 快指针先走k步,慢指针再开始一块走
ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
node.next = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = node;
int i=0;
while(i<n){
fast = fast.next;
i++;
}
// 快慢指针一块走
while(fast!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return node.next;
}
}