html原生table实现合并单元格以及合并表头
前言
因为公司业务越来越复杂,有些页面PC和app其实是一样的,我们肯定不想写两套代码,所以我们看看能不能写一个同时支持PC和app的table组件
思路
首先肯定想到的是原生table进行封装,因为我早就想这么干了,想通过原生的一些基础组件去封装成咱们可用的组件库。说搞就搞,先实现table的一些简单功能,因为公司用的js框架是vue,所以基于vue3去封装。
实现的功能
- 表头分组
- 合并单元格
- 滚动条
- 单元格放组件
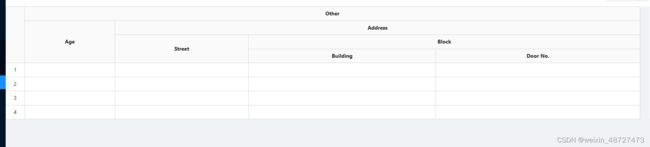
表头分组
表头分组这个概念也是ant-design-vue中看来的,反正我的理解就是合并单元格,但是它叫表头分组,可能专业些,好吧,已经复制了它的叫法。
通过配置去生成分组的表头,首先要对原生table的一些配置要比较熟练,介绍两个最重要的配置
- rowspan 表格横跨的行数
- colspan 表格横跨的列数
配置
copy了一份ant的较为复杂的结构,然后稍微改一了一下标识字段,方便我们自己组件使用
const columns: columnsType[] = [
{ prop: 'index', label: '', width: 3 },
{
label: 'Other',
children: [
{
prop: 'age', label: 'Age',
},
{
label: 'Address',
children: [
{
label: 'Street',
prop: 'street'
},
{
label: 'Block',
children: [
{
label: 'Building',
prop: 'building',
},
{
label: 'Door No.',
prop: 'number',
},
],
},
]
}
]
},
]
主体代码
// 头部
// 使用组件的原因是方便扩展其他业务需求
横跨的行数
首先肉眼看到的肯定是表头横跨了4行。但是我们也不能写死成4行,我们需要通过计算得到这个表头最终横跨的几行。表头行数跨不跨行的判断依据是有无children。所以我这里是通过递归去扁平化这个数组,最终得到表格横跨了几行。
/**
* @description 递归扁平化配置数组,得到渲染表头的数组以及横跨的的行数
* @param columns children
*/
function handleRenderHeaderList(columns:columnsType[]) {
// 用于记录深度
headerIndex.value += 1
if (renderHeaderList.value.length <= headerIndex.value) {
renderHeaderList.value.push(columns)
} else {
renderHeaderList.value[headerIndex.value] = [...renderHeaderList.value[headerIndex.value],...columns]
}
// 用于记录是否重置深度
let isClearIndex = true
columns.forEach((item: columnsType) => {
// 判断是否还有子集
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0 ) {
isClearIndex = false
handleRenderHeaderList(item.children)
}
});
if(isClearIndex){
headerIndex.value = 0
}
}
/**
* @description 单独rowspan的计算
* @param columnsItem 单元格的配置
* @return 单元格的列数
*/
function computedHeaderRowSpan(columnsItem:columnsType){
if(!columnsItem.children){
return renderHeaderList.value.length
}
return 1
}
横跨的列数
这个列数也是不固定的,也需要去通过收集对应的children里面的项数来统计,因为我们是无法确认这个children的深度的,所以我这边用深度遍历来处理子集的收集问题。因为用递归此时vue会报警告,实际上我们也需要知道递归多了,内存就消耗的多,所以我们能不用递归就尽量不用递归。
/**
* @description 单独colSpan的计算
* @param columnsItem 单元格的配置
* @return 单元格的列数
*/
function computedHeaderColSpan(columnsItem:columnsType){
if(!columnsItem.children){
return 1
}
return flatColumnsItemChildren(columnsItem.children).length
}
/**
* @description 深度遍历扁平化数组获取单元格所占的列数
* @param columnsItem 单元格的配置
* @return 返回扁平化后的数组
*/
function flatColumnsItemChildren(columnsItem:columnsType[]){
// 深度遍历,扁平化数组
let node, list = [...columnsItem], nodes = []
while (node = list.shift()) {
// 要过滤一下没有prop的,没有prop的列不参与最终的宽度计算
if(node.prop){
nodes.push(node)
}
node.children && list.unshift(...node.children)
}
return nodes
// 递归会报警告,占内存
// if(columnsItem.length === 0){
// return
// }
// columnsItem.forEach((item:columnsType)=>{
// if(item.children){
// flatColumnsItemChildren(item.children)
// }else{
// flatChildrenList.value.push(item)
// }
// })
}
实现效果图
合并单元格以及单元格放组件
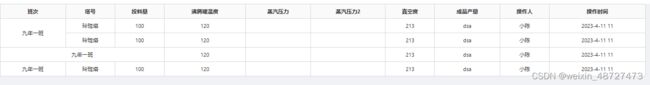
合并单元格稍微简单些,只需要把每个单元格的colspan和rowspan写成一个函数并且暴露出来就能处理
配置
const columns: columnsType[] = [
{
prop: 'monitor',
label: '班次',
customCell: (_?: rowType, index?: number, columns?: columnsType) => {
if (index === 2 && columns?.prop === 'monitor') {
return { colspan:3 };
}
if (index === 0 && columns?.prop === 'monitor') {
return { rowspan:2 };
}
if (index === 1 && columns?.prop === 'monitor') {
return { rowspan:0 };
}
return {colspan:1,rowspan:1};
},
},
{
prop: 'taHao',
label: '塔号',
customCell: (_?: rowType, index?: number, columns?: columnsType) => {
if (index === 2 && columns?.prop === 'taHao') {
return {colspan : 0};
}
return {colspan:1};
},
},
{
prop: 'materialNum',
label: '投料量',
customCell: (_?: rowType, index?: number, columns?: columnsType) => {
if (index === 2 && columns?.prop === 'materialNum') {
return {colspan : 0};
}
return {colspan:1};
},
},
{ prop: 'temperature', label: '沸腾罐温度', rowSpan: 2 },
{
prop: 'steamPressure',
label: '蒸汽压力'
},
{
prop: 'steamPressure1',
label: '蒸汽压力2'
},
{ prop: 'oxygen', label: '真空度' },
{ prop: 'productNum', label: '成品产量' },
{
prop: 'operatorName',
label: '操作人'
},
{
prop: 'operatorTime',
label: '操作时间'
},
];
主体代码以及单元格放组件
// 动态组件提前写好组件去渲染对应的组件,此时的table单元格扩展性就变得非常强,不 仅可以做展示用,也可以放输入框,下拉选择器之类的组件。
横跨的行数
每个单元格渲染的时候,暴露一个函数出去,此函数的返回值有rowspan以及colspan,这样能准确的知道渲染每个单元格时此单元格占位多少。
/**
* @description 计算单元格rowspan的占位
* @param item 单元格一行的值
* @param index 索引
* @param columns 当前的单元格配置
* @return colspan
*/
function computedTdRowspan(item: rowType, index: number, columns: columnsType): number|undefined {
if (columns.customCell) {
let rowspan: number| undefined = 1
if(columns.customCell(item, index, columns).rowspan ===0){
rowspan = 0
}
if(columns.customCell(item, index, columns).rowspan){
rowspan = columns.customCell(item, index, columns).rowspan
}
return rowspan
}
return 1;
}
横跨的列数
每个单元格渲染的时候,暴露一个函数出去,此函数的返回值有rowspan以及colspan,这样能准确的知道渲染每个单元格时此单元格占位多少。
/**
* @description 计算单元格colspan的占位
* @param item 单元格一行的值
* @param index 索引
* @param columns 当前的单元格配置
* @return colspan
*/
function computedTdColspan(item: rowType, index: number, columns: columnsType): number|undefined {
if (columns.customCell) {
let colspan: number| undefined = 1
if(columns.customCell(item, index, columns).colspan ===0){
colspan = 0
}
if(columns.customCell(item, index, columns).colspan){
colspan = columns.customCell(item, index, columns).colspan
}
return colspan
}
return 1;
}
实现效果图
滚动条
table自身是响应式的,按照一定规则自动去分配宽度和高度的,如果不在table外面包裹一层元素的话,table会一直自适应,没法带有滚动条,我们需要给外层元素设置一个宽度或者高度,然后table也设置一个固定的宽度或者是高度,这样内部的table就会在限定的宽度或者高度下具有滚动条。
总结
为了更好的在特定场景去控制table的高宽以及单元格的高宽,我们可以将他们的样式设定为动态的,我们可以通过配置去动态的改变他们的样式。然后就是处理一些无法确认层级的树形结构数据,我们也可以不通过递归去实现,节省内存。